Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19(10), 6345; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19106345 - 23 May 2022
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 4449
Abstract
The coparenting relationship begins with a process of planning and negotiation about having children. Available psychological instruments have not been adapted to sexual minority people, which compromises their ecological validity. This mixed method study aimed to adapt and validate a prospective version of
[...] Read more.
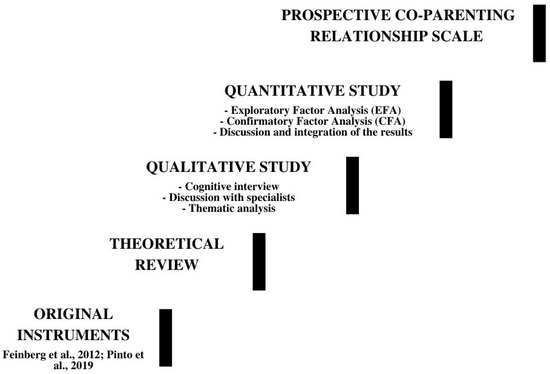
The coparenting relationship begins with a process of planning and negotiation about having children. Available psychological instruments have not been adapted to sexual minority people, which compromises their ecological validity. This mixed method study aimed to adapt and validate a prospective version of the Co-Parenting Relationship Scale in a Portuguese sample of sexual minority and heterosexual adults who did not have children and who were in a dyadic relationship. In study 1, cognitive interviews were used to gather participants’ reflections about the original items and the role played by the family of origin and anticipated stigma in coparenting (n = 6). In study 2, using a sample of individuals from 18 to 45 years old, two Exploratory Factor Analyses (EFA) were conducted separately for sexual minority (n = 167) and heterosexual persons (n = 198), and a Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA) was conducted for heterosexual persons (n = 176). Results showed underscored the importance of families of origin independent of sexual orientation. Different factorial structures for sexual minority and heterosexual persons were observed. Among sexual minority persons, the role of stigma was also highlighted. Implications for practice and research are discussed.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Health and Well-Being Related to New Family Forms: Perspectives of Adult Individuals, Couples, Extended Family Members, Children, and Professionals)
►
Show Figures