Sensors 2023, 23(2), 748; https://doi.org/10.3390/s23020748 - 9 Jan 2023
Cited by 26 | Viewed by 3162
Abstract
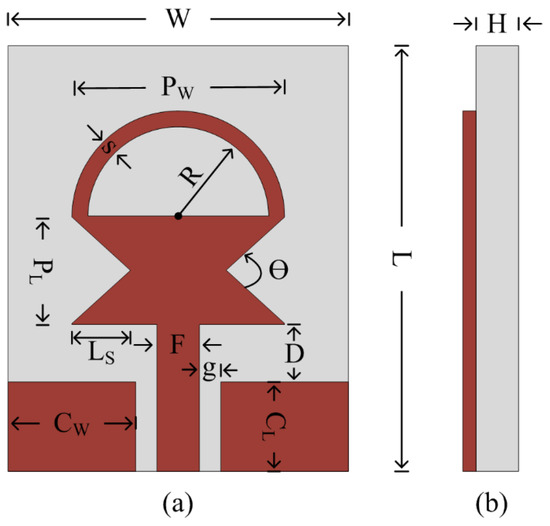
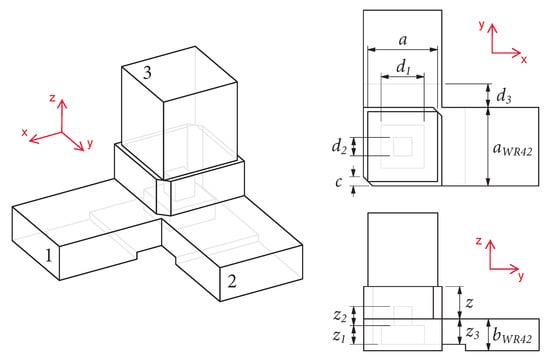
In this manuscript, a compact in size yet geometrically simple Ultra-Wideband (UWB) antenna is demonstrated. The flexible-by-nature substrate ROGERS 5880, having a thickness of 0.254 mm, is utilized to design the proposed work. The antenna configuration is an excerpt of a traditional rectangular
[...] Read more.
In this manuscript, a compact in size yet geometrically simple Ultra-Wideband (UWB) antenna is demonstrated. The flexible-by-nature substrate ROGERS 5880, having a thickness of 0.254 mm, is utilized to design the proposed work. The antenna configuration is an excerpt of a traditional rectangular monopole antenna resonating at 5 GHz. Initially, a pair of triangular slots are employed to extend the impedance bandwidth of the antenna. In addition, a semi-circular-shaped, short-ended stub is connected at the upper edges of the patch to further increase the operational bandwidth. After optimization, the proposed antenna offers UWB ranging from 2.73–9.68 GHz, covering almost the entire spectrum allocated globally for UWB applications. Further, the antenna offers a compact size of 15 × 20 mm2 that can easily be integrated into small, flexible electronics. The flexibility analysis is done by bending the antenna on both the x and y axes. The antenna offers performance stability in terms of return loss, radiation pattern, and gain for both conformal and non-conformal conditions. Furthermore, the strong comparison between simulated and measured results for both rigid and bent cases of the antenna, along with the performance comparison with the state-of-the-art, makes it a potential candidate for present and future compact-sized flexible devices.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Antenna Design and Optimization for 5G, 6G, and IoT)
►
Show Figures