Sensors 2022, 22(17), 6568; https://doi.org/10.3390/s22176568 - 31 Aug 2022
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 2910
Abstract
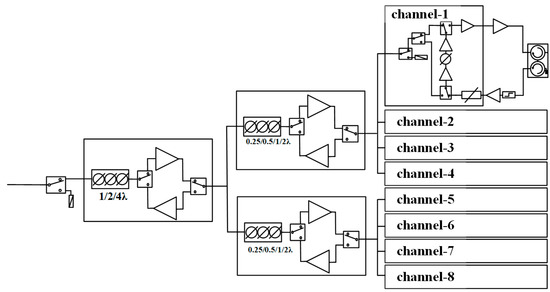
Ku-band drive amplification and a 7-bit true-time-delay (TTD) function were realized as a part of a LTCC-based T/R module to increase integration. The 8-channel T/R module was fabricated and its key characteristics were measured, including a 3-bit (1/2/4 λ) TTD, 4-bit (0.25/0.5/1/2 λ)
[...] Read more.
Ku-band drive amplification and a 7-bit true-time-delay (TTD) function were realized as a part of a LTCC-based T/R module to increase integration. The 8-channel T/R module was fabricated and its key characteristics were measured, including a 3-bit (1/2/4 λ) TTD, 4-bit (0.25/0.5/1/2 λ) TTD, receive gain, noise figure and output power. The 8-channel T/R module can be further adopted to increase bandwidth and scanning angle of phased arrays without beam squint.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Recent Advance in Mobile Edge Computing and Wireless Communication Technology)
►
Show Figures