Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24(3), 1842; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24031842 - 17 Jan 2023
Cited by 15 | Viewed by 3543
Abstract
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is diagnosed many years after its onset, under a significant degradation of the nigrostriatal dopaminergic system, responsible for the regulation of motor function. This explains the low effectiveness of the treatment of patients. Therefore, one of the highest priorities in
[...] Read more.
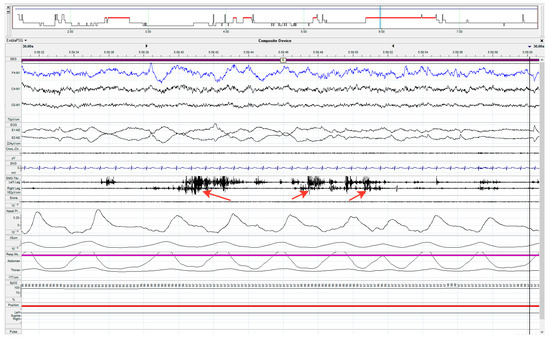
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is diagnosed many years after its onset, under a significant degradation of the nigrostriatal dopaminergic system, responsible for the regulation of motor function. This explains the low effectiveness of the treatment of patients. Therefore, one of the highest priorities in neurology is the development of the early (preclinical) diagnosis of PD. The aim of this study was to search for changes in the blood of patients at risk of developing PD, which are considered potential diagnostic biomarkers. Out of 1835 patients, 26 patients were included in the risk group and 20 patients in the control group. The primary criteria for inclusion in a risk group were the impairment of sleep behavior disorder and sense of smell, and the secondary criteria were neurological and mental disorders. In patients at risk and in controls, the composition of plasma and the expression of genes of interest in lymphocytes were assessed by 27 indicators. The main changes that we found in plasma include a decrease in the concentrations of l-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (L-DOPA) and urates, as well as the expressions of some types of microRNA, and an increase in the total oxidative status. In turn, in the lymphocytes of patients at risk, an increase in the expression of the DA D3 receptor gene and the lymphocyte activation gene 3 (LAG3), as well as a decrease in the expression of the Protein deglycase DJ-1 gene (PARK7), were observed. The blood changes we found in patients at risk are considered candidates for diagnostic biomarkers at the prodromal stage of PD.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Brain as a Manager of the Body—Molecular Aspects of Development and Functioning in Health and Disease)
►
Show Figures