Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23(15), 8184; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158184 - 25 Jul 2022
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 2904
Abstract
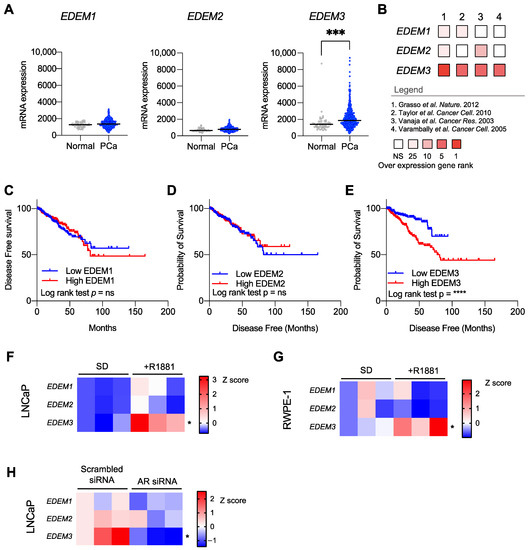
Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men, and it is primarily driven by androgen steroid hormones. The glycosylation enzyme EDEM3 is controlled by androgen signalling and is important for prostate cancer viability. EDEM3 is a mannosidase that trims mannose from mis-folded
[...] Read more.
Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men, and it is primarily driven by androgen steroid hormones. The glycosylation enzyme EDEM3 is controlled by androgen signalling and is important for prostate cancer viability. EDEM3 is a mannosidase that trims mannose from mis-folded glycoproteins, tagging them for degradation through endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation. Here, we find that EDEM3 is upregulated in prostate cancer, and this is linked to poorer disease-free survival. Depletion of EDEM3 from prostate cancer cells induces an ER stress transcriptomic signature, and EDEM3 overexpression is cyto-protective against ER stressors. EDEM3 expression also positively correlates with genes involved in the unfolded protein response in prostate cancer patients, and its expression can be induced through exposure to radiation. Importantly, the overexpression of EDEM3 promotes radio-resistance in prostate cancer cells and radio-resistance can be reduced through depletion of EDEM3. Our data thus implicate increased levels of EDEM3 with a role in prostate cancer pathology and reveal a new therapeutic opportunity to sensitise prostate tumours to radiotherapy.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Prostate Cancer: Signaling Pathways and Molecular Targets)
►
Show Figures