-
 Optical Genome Mapping: A New Tool for Cytogenomic Analysis
Optical Genome Mapping: A New Tool for Cytogenomic Analysis -
 Genomic Regions Associated with Respiratory Disease in Holstein Calves in the Southern United States
Genomic Regions Associated with Respiratory Disease in Holstein Calves in the Southern United States -
 ABCC6 Involvement in Cerebral Small Vessel Disease: Potential Mechanisms and Associations
ABCC6 Involvement in Cerebral Small Vessel Disease: Potential Mechanisms and Associations -
 Increased Prevalence of Psychiatric Disorders in Children with RASopathies: Comparing NF1, Noonan Syndrome Spectrum Disorder, and the General Population
Increased Prevalence of Psychiatric Disorders in Children with RASopathies: Comparing NF1, Noonan Syndrome Spectrum Disorder, and the General Population -
 Identification of Key Genes Associated with Overall Survival in Glioblastoma Multiforme Using TCGA RNA-Seq Expression Data
Identification of Key Genes Associated with Overall Survival in Glioblastoma Multiforme Using TCGA RNA-Seq Expression Data
Journal Description
Genes
Genes
is a peer-reviewed, open access journal of genetics and genomics published monthly online by MDPI. The Spanish Society for Nitrogen Fixation (SEFIN) is affiliated with Genes and their members receive discounts on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, SCIE (Web of Science), PubMed, MEDLINE, PMC, Embase, PubAg, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Genetics and Heredity) / CiteScore - Q2 (Genetics (clinical))
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 14.6 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.5 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: Reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Impact Factor:
2.8 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
3.2 (2024)
Latest Articles
Integrating WGCNA, TCN, and Alternative Splicing to Map Early Caste Programs in Day-2 Honeybee Larvae
Genes 2025, 16(12), 1409; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121409 - 26 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: The larval stage plays a pivotal role in determining caste and sex in Apis mellifera. This study integrates RNA-seq, WGCNA, and alternative splicing analyses to explore gene expression differences among 2-day-old worker, drone, and queen larvae. Methods: RNA-seq was conducted on
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: The larval stage plays a pivotal role in determining caste and sex in Apis mellifera. This study integrates RNA-seq, WGCNA, and alternative splicing analyses to explore gene expression differences among 2-day-old worker, drone, and queen larvae. Methods: RNA-seq was conducted on 2-day-old larvae from all three castes. Differential expression, WGCNA, and alternative splicing patterns were investigated. A deep learning TCN model was trained using WGCNA-derived modules and demonstrated high classification accuracy. Results: The TCN model highlighted a top-10 gene set, including PDHB, Fibroin3, and LOC724161. Significant caste- and sex-specific splicing events were detected in Tk, Csd, and Fem, with AF events being most prevalent. Splicing differences between sexes exceeded those observed among castes. Conclusions: The 2-day-old larval stage is crucial for both caste and sex differentiation in honeybees. This study identifies key genes and splicing events, offering new insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying caste formation and sex determination.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Epigenomics)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Heat Shock Protein 104 (Hsp104) in the Marine Diatom Ditylum brightwellii: Identification and Transcriptional Responses to Environmental Stress
by
Han-Sol Kim, Jong-Won Lee and Jang-Seu Ki
Genes 2025, 16(12), 1408; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121408 - 26 Nov 2025
Abstract
Backgrounds: The marine diatom Ditylum brightwellii has been widely used as a model species for ecotoxicological assessments in marine environments. Heat shock proteins (Hsps) function as molecular chaperones that protect cells under diverse stress conditions. Of them, Hsp104 participates in the protein restoration
[...] Read more.
Backgrounds: The marine diatom Ditylum brightwellii has been widely used as a model species for ecotoxicological assessments in marine environments. Heat shock proteins (Hsps) function as molecular chaperones that protect cells under diverse stress conditions. Of them, Hsp104 participates in the protein restoration system by reversing protein aggregation. Methods: In the present study, we determined the full-length sequence of DbHsp104 in D. brightwellii using transcriptome sequencing and gene cloning. Results: The open reading frame (ORF) was 2745 bp in length, encoding a protein of 915 amino acids (101.15 kDa). Phylogenetic and domain structural analysis revealed that DbHsp104 possesses conserved features of eukaryotic Hsp104. In addition, transcriptional responses of the gene were evaluated after exposures to thermal stress at 20, 25, and 30 °C, and heavy metals and endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) for 24 h. Relative gene expression analysis showed that DbHsp104 was significantly up-regulated under thermal stress and copper exposures, peaking at 4.87- and 5.55-fold (p < 0.001) increases, respectively. In contrast, no significant changes were observed in response to nickel, bisphenol A (BPA), polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB), and endosulfan (EDS) treatments. Conclusions: These results suggest that DbHsp104 is specifically responsive to acute stress induced by thermal stress and copper, highlighting its potential as a molecular biomarker in marine environments.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Genes & Environments)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Longitudinal Multimodal Assessment of Structure and Function in INPP5E-Related Retinopathy
by
Andrea Cusumano, Marco Lombardo, Benedetto Falsini, Michele D’Ambrosio, Jacopo Sebastiani, Enrica Marchionni, Maria Rosaria D’Apice, Barbara Rizzacasa, Francesco Martelli and Giuseppe Novelli
Genes 2025, 16(12), 1407; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121407 - 26 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background: INPP5E-related retinopathy (INPP5E-RR) is a rare genetic disorder caused by biallelic pathogenic variants in the INPP5E gene, which encodes an enzyme critical for phosphoinositide signaling. While early-onset rod–cone dystrophy is a hallmark feature, detailed longitudinal data on the
[...] Read more.
Background: INPP5E-related retinopathy (INPP5E-RR) is a rare genetic disorder caused by biallelic pathogenic variants in the INPP5E gene, which encodes an enzyme critical for phosphoinositide signaling. While early-onset rod–cone dystrophy is a hallmark feature, detailed longitudinal data on the phenotype are scarce. This study aims to report a 6-year longitudinal assessment of retinal structure and function in a case of non-syndromic INPP5E-RR. Methods: A 42-year-old female proband with compound heterozygous pathogenic missense variants in INPP5E (p.Arg486Cys and p.Arg378Cys) was monitored from 2019 to 2025. She underwent serial comprehensive ophthalmologic evaluations, including optical coherence tomography (OCT), fundus autofluorescence, adaptive optics transscleral flood illumination, full-field 30Hz flicker electroretinography (ERG), and macular frequency-doubling technology perimetry. Results: Over the 6-year follow-up, OCT imaging revealed a progressive decline in the ellipsoid zone (EZ) width, from 1220 µm to 720 µm (~80 µm/year), and in the inner nuclear layer (INL) thickness. The central outer nuclear layer (ONL) thickness was preserved, but intraretinal cysts developed. Functional testing revealed a progressive decline in cone flicker ERG amplitudes, while visual acuity and macular perimetry remained stable. Conclusions: In this genotypically confirmed case, the longitudinal data identify EZ width, INL thickness, and cone flicker ERG as robust biomarkers of disease progression in INPP5E-RR. These parameters are ideal candidates for monitoring therapeutic outcomes in future clinical trials.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Current Advances in Inherited Retinal Disease)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Unexpected Diagnosis of Fahr’s Disease in a Patient with Severe Obesity and a Heterozygotic Variant in the TMEM67 Gene
by
Katarzyna Piekarska, Paulina Oczoś, Julia Grzybowska-Adamowicz, Ewa Zmysłowska-Polakowska, Michał Pietrusiński and Agnieszka Zmysłowska
Genes 2025, 16(12), 1406; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121406 - 26 Nov 2025
Abstract
Objective: The genetic causes of obesity are complex and include diabetes and obesity monogenic syndromes like autosomal recessive Bardet–Biedl syndrome (BBS). Other clinical manifestations of this syndrome include metabolic disorders, polydactyly, retinal dystrophy, and endocrine, urological, and neurological abnormalities. Moreover, isolated clinical
[...] Read more.
Objective: The genetic causes of obesity are complex and include diabetes and obesity monogenic syndromes like autosomal recessive Bardet–Biedl syndrome (BBS). Other clinical manifestations of this syndrome include metabolic disorders, polydactyly, retinal dystrophy, and endocrine, urological, and neurological abnormalities. Moreover, isolated clinical manifestations have been described in carriers of heterozygous mutations in BBS genes. On the other hand, Fahr’s disease is characterized by the accumulation of calcium deposits in various areas within the brain, leading to neurodegeneration, and the course of the disease is variable. Case presentation: We present the case of a 21-year-old female with severe obesity, diagnosed at the age of six years. The patient also experienced hypertension, hyperlipidemia, insulin resistance, and polycystic ovarian syndrome. During an MRI examination, hyperintensity in the region of the dentate nuclei and hyperintensity in the globus pallidus were described. NGS (next-generation sequencing) results showed a heterozygous variant in the TMEM67 gene, which revealed the patient to be a carrier of BBS, and a homozygotic variant in the MYORG gene, leading to a Fahr’s disease diagnosis. However, due to an insufficient number of phenotypic criteria and only one causative variant in the TMEM67 gene, the diagnosis of BBS could not be established. Conclusions: Attempts to identify the cause of obesity can lead to unexpected results, which can be resolved through collaboration between clinicians of different specialties and the use of NGS molecular testing. The status of being a BBS carrier, which coexists with Fahr’s disease, may be a potential contributing factor to severe obesity and metabolic disorders in the patient.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Genetic Diagnosis)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Comprehensive Analysis of Sorghum CNGC Genes Reveals Their Potential Roles in Abiotic Stress Responses
by
Yu Luo, Wenda Jiao, Kun Huang, Xiang Li, Jiaqi Li, Minli Wang, Ruidong Zhang and Xiong Cao
Genes 2025, 16(12), 1405; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121405 - 25 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Cyclic nucleotide-gated channel (CNGC) genes play crucial roles in plant growth, development, and stress responses, yet their functions in sorghum remain poorly understood. Methods: This study systematically analyzed sorghum CNGC genes through genome-wide identification, encompassing chromosomal mapping, phylogenetic relationships, gene
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Cyclic nucleotide-gated channel (CNGC) genes play crucial roles in plant growth, development, and stress responses, yet their functions in sorghum remain poorly understood. Methods: This study systematically analyzed sorghum CNGC genes through genome-wide identification, encompassing chromosomal mapping, phylogenetic relationships, gene structure, cis-acting elements, miRNA regulation, and GO/KEGG annotation. Results: A total of 23 sorghum CNGC genes were identified and classified into five subclasses (I–IV-b), exhibiting high evolutionary conservation with rice and maize. Promoter and miRNA analyses revealed multi-level regulation involving light, hormones (ABA, JA), and stress response elements. Several SbCNGC genes were predicted to be regulated by multiple miRNAs. Expression profiling and qRT-PCR validation indicated that most SbCNGC genes responded to both high-temperature and low-temperature stress. Expression analysis revealed tissue specificity and stress-induced transcriptional responses. Notably, SbCNGC1 remains consistently upregulated under both cold and heat stress, suggesting a potential key role in Ca2+-mediated signaling. Conclusions: This study systematically characterizes SbCNGC genes for the first time, reveals their potential role in abiotic stress tolerance, and provides a valuable resource for sorghum functional genomics and molecular breeding.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Plant Genetics and Genomics)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Comparative Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Regulation of Growth Activity in Poria cocos Under Different Light Duration Stimulations
by
Chengwen Wu, Shanwen Ye, Xuhui Wei and Rong Zheng
Genes 2025, 16(12), 1404; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121404 - 24 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background: Light is an important environmental signal that regulates the growth and metabolism of fungi. This study aims to reveal the molecular regulatory mechanism of different light durations on the growth activity of Poria cocos. Methods: By setting up three
[...] Read more.
Background: Light is an important environmental signal that regulates the growth and metabolism of fungi. This study aims to reveal the molecular regulatory mechanism of different light durations on the growth activity of Poria cocos. Methods: By setting up three groups of light treatment: 0 days (sample 1), 15 days (sample 2), and 30 days (sample 3), and combining transcriptome sequencing (RNA-seq) with qRT-PCR for verification, the effects of light on the gene expression of Poria cocos (Poria cocos (Schw.) Wolf) were systematically analyzed. Results: A total of 4332 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified in this study. Among them, the blue light-responsive genes, BLI-3 and BLI-4, were significantly upregulated at the DT15 stage, reaching 576.08 times and 31.30 times, respectively, while they were sharply downregulated at the DT30 stage. The KEGG enrichment analysis revealed that the DEGs were mainly involved in secondary metabolite synthesis, carbon metabolism, amino acid synthesis, redox reactions, and the MAPK signaling pathway. At the DT15 stage, genes related to growth metabolism, such as CYP, SNF1, and COX, were highly expressed, indicating active metabolism at this stage. However, in the DT0 and DT30 stages, ROS-related genes such as NADPH-dependent oxidoreductases were upregulated, leading to oxidative stress damage and inhibiting growth. Additionally, the high expression of BLI-3 and BLI-4 significantly activated ergosterol synthesis genes, enhancing cell membrane stability. The WGCNA co-expression network analysis revealed a high degree of correlation between BLI-4 and MAPKKK and CYP genes and proposed a potential “BLI-4-MAPKKK-CYP” regulatory axis, providing insights into the molecular pathway by which light regulates the metabolism and homeostasis of Poria cocos. Conclusions: This study has for the first time systematically revealed the molecular mechanism by which light duration regulates the growth activity of Poria cocos. It has clarified the core role of the BLI gene family in light signal perception and metabolic regulation. It has also elucidated the molecular pathways by which light regulates the synthesis of ergosterol, energy metabolism, and oxidative stress response in Poria cocos. This provides innovative theoretical support for optimizing the light regulation strategies in Poria cocos cultivation and also offers important references for the study of environmental response mechanisms in other medicinal fungi.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Plant Genetics and Genomics)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Addressing Ancestral Underrepresentation in Oncobiology: The Need for Sub-Saharan African-Specific In Vitro Models
by
Carla S. dos Santos, Ana C. Magalhães, Ricardo J. Pinto, Carla Carrilho, Cláudia Pereira, Fernando Miguel, Pamela Borges, Lúcio Lara Santos and Luisa Pereira
Genes 2025, 16(12), 1403; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121403 - 24 Nov 2025
Abstract
Cancer is an increasing public health burden, including in Sub-Saharan African (SSA) populations, where cancer incidence is predicted to increase by around 140% between 2022 and 2050. These rates require a better understanding of the epidemiological, clinical, and genetic/molecular characteristics of cancer in
[...] Read more.
Cancer is an increasing public health burden, including in Sub-Saharan African (SSA) populations, where cancer incidence is predicted to increase by around 140% between 2022 and 2050. These rates require a better understanding of the epidemiological, clinical, and genetic/molecular characteristics of cancer in SSA populations. There is an urgent need to improve the genomic characterization of SSA tumour samples and also to establish suitable in vitro models for hypothesis testing. In fact, even though thousands of cancer cell lines (CCLs) have been established employing different methods of cell immortalization and have been included in deep molecular characterization panels, SSA ancestry is limited to only ~6% (mostly African Americans, who represent limited diversity in the context of the African continent) of publicly available CCLs. This disparity needs to be addressed by using next-generation immortalization methods such as conditional reprogramming to establish CCLs derived from SSA cancer patients that also represent the diversity within the African continent. Research in SSA oncobiology has the potential to add essential information to better understand the diverse molecular pathways leading to cancer and to find promising therapeutic avenues. We also discuss the challenges to conducting oncobiology studies with cell modelling derived from SSA patients in low-to-middle-income African countries, such as Portuguese-speaking African countries.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Human Genomics and Genetic Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Telomere Length and Mitochondrial Copy Number as Potential Biomarkers for Male Infertility in Iraqi Men
by
Mustafa Faeq Kadhim, Farah Thamer Samawi and Ali Gargouri
Genes 2025, 16(12), 1402; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121402 - 24 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Male infertility is one of the major problems in Iraqi health and society; it is caused by several factors, such as acquired, environmental, and genetic factors. Awareness of the crucial role of telomeres and mitochondria in sperm production and fertility has
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Male infertility is one of the major problems in Iraqi health and society; it is caused by several factors, such as acquired, environmental, and genetic factors. Awareness of the crucial role of telomeres and mitochondria in sperm production and fertility has increased in recent years. This study aimed to evaluate the association between mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) copy number and telomere length in sperm and the degree of infertility in Iraqi males. Methods: Of the 200 study participants, 50 were healthy controls and 150 were infertile. Sperm count, motility, and morphology were assessed by collecting and analyzing semen samples. After DNA extraction, the mitochondrial ND1 gene and the reference nuclear gene GAPDH were analyzed by quantitative PCR (qPCR) to determine the mtDNA copy number. To determine telomere length, another qPCR analysis was used. Results: The mtDNA copy number of infertile men was significantly higher than that of healthy controls with a p-value (0.001). In addition, the sperm of the patient group showed a significant reduction in telomere length (p = 0.001). According to the results of the study, male infertility in Iraqi men is associated with a higher number of mtDNA copies and shorter telomere length. DNA damage or a disruption in the mitochondrial energy production pathway could be the cause of this association. Conclusions: This study reveals that a higher number of mtDNA copies and shorter telomere lengths are associated with male infertility in Iraqi men. These results highlight the importance of continuing research and exploring new avenues in the field of male infertility.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Human Genomics and Genetic Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures
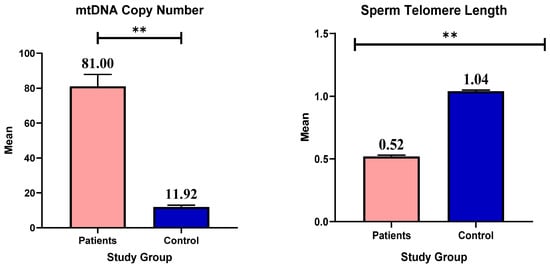
Figure 1
Open AccessBrief Report
Optimizing an Ex Vitro RUBY-Equipped Method for Hairy Root Transformation of Peanuts: An Efficient Approach for the Functional Study of Genes in Peanut Roots
by
Xinyue Li, Jun Zhou, Fei Kong, Xiaoyun Li, Dong Xiao, Aiqin Wang, Longfei He and Jie Zhan
Genes 2025, 16(12), 1401; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121401 - 24 Nov 2025
Abstract
Agrobacterium rhizogenes (A. rhizogenes)-mediated transformation of hairy roots is a favored and flexible method for root gene functional analysis. However, the selection of transformants can be complex and time-consuming. Here, we describe our simplified method for the A. rhizogenes-mediated
[...] Read more.
Agrobacterium rhizogenes (A. rhizogenes)-mediated transformation of hairy roots is a favored and flexible method for root gene functional analysis. However, the selection of transformants can be complex and time-consuming. Here, we describe our simplified method for the A. rhizogenes-mediated hairy root induction in young peanut shoots using an expression vector with RUBY for direct visual selection of transformants. Analyses verified that this method provides a high-efficiency gene transformation technique for peanut, with transformant frequencies between 46.2 and 73.7%. To test the utility of this method in gene functional analyses, it was used to overexpress AhLRX6 in hairy roots and we present our preliminary results indicating the production of thicker cells walls in root tips relative to the WT.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Molecular Genetics of Stress Response in Crops)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Sperm-Derived Extracellular Vesicles (Sperm-EVs), Emerging Biomarkers and Functional Modulators in Male Infertility and Assisted Reproduction
by
Charalampos Voros, Fotios Chatzinikolaou, Georgios Papadimas, Spyridon Polykalas, Despoina Mavrogianni, Aristotelis-Marios Koulakmanidis, Diamantis Athanasiou, Vasiliki Kanaka, Maria Kanaka, Kyriakos Bananis, Antonia Athanasiou, Aikaterini Athanasiou, Ioannis Papapanagiotou, Dimitrios Vaitsis, Charalampos Tsimpoukelis, Maria Anastasia Daskalaki, Marianna Theodora, Nikolaos Thomakos, Panagiotis Antsaklis, Dimitrios Loutradis and Georgios Daskalakisadd
Show full author list
remove
Hide full author list
Genes 2025, 16(12), 1400; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121400 - 22 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Approximately 50% of infertility cases are attributable to male factors; yet conventional semen examination can not identify the molecular abnormalities that hinder sperm functionality. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) derived from sperm, such as testicular EVs, prostasomes, and epididymosomes, have become important modulators of
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Approximately 50% of infertility cases are attributable to male factors; yet conventional semen examination can not identify the molecular abnormalities that hinder sperm functionality. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) derived from sperm, such as testicular EVs, prostasomes, and epididymosomes, have become important modulators of oocyte activation, sperm maturation, capacitation, acrosome stability, motility, and early embryonic development. This study aimed to evaluate the potential diagnostic and translational uses of sperm-associated extracellular vesicles (EVs) in male infertility and assisted reproduction, while also consolidating recent insights on their origins, composition, and functional significance. Methods: A focused narrative search of PubMed (2000–2025) was conducted using backward and forward citation tracking. Studies that qualified included human clinical cohorts, functional sperm extracellular vesicle tests, and omics analyses using MISEV-aligned extracellular vesicle isolation and characterisation methodologies. When human mechanistic understanding was constrained, knowledge from animal research was selectively integrated. Results: The cargo signatures specific to the source identified in sperm-derived and seminal EVs encompass proteins, small RNAs, lipids, and enzymatic modules that govern sperm maturation, capacitation, acrosome reaction, redox balance, calcium signalling, zona binding, and DNA integrity. Density-resolved seminal extracellular vesicle subfractions (EV-H/EV-M/EV-L) have unique functional and proteomic characteristics linked to progesterone-induced hyperactivation, oxidative stress, and motility. Asthenozoospermia and oligoasthenoteratozoospermia are associated with changes in extracellular vesicle composition, reduced embryonic developmental potential, compromised oocyte activation (related to PLCζ), and increased sperm DNA fragmentation. Numerous EV-related miRNA and protein signatures may predict TESE results, identify functional sperm anomalies not recognised by conventional semen analysis, and differentiate between obstructive and non-obstructive azoospermia. Conclusions: The available findings indicate that sperm-derived extracellular vesicles are significant functional regulators of sperm physiology and may serve as valuable non-invasive indicators for male infertility. The standardisation of EV isolation, characterisation, and clinical validation is essential prior to widespread use; nonetheless, their integration into liquid biopsy methods and assisted reproductive technology processes represents a significant improvement.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Human Genomics and Genetic Diseases)
Open AccessCase Report
A Complex Case of Retinoblastoma Solved by the Combined Approach of Humor/Plasma cfDNA-NGS and LR-WGS
by
Simona Innamorato, Simona L. Basso, Omaima Belakhdar, Mirella Bruttini, Chiara Fallerini, Heyran Huseynli, Giulia Caccialupi, Elena Pasquinelli, Mariarosaria Adduci, Giorgio Signori, Felice Arcuri, Valeria Malagnino, Maria Chiara Siciliano, Stefano Lazzi, Simone Pesaresi, Daniela Galimberti, Paolo Galluzzi, Sonia De Francesco, Theodora Hadijstillanou, Anna Maria Pinto, Alessandra Renieri and Francesca Arianiadd
Show full author list
remove
Hide full author list
Genes 2025, 16(12), 1399; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121399 - 22 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background: Complex cases of retinoblastoma (RB) often require integrative molecular approaches to define tumor etiology and guide clinical management. Purpose: Our aim was to evaluate the usefulness of combining aqueous humor (AH)/plasma cell-free DNA next-generation sequencing (cfDNA-NGS) and long-read–whole-genome sequencing (LR-WGS) to resolve
[...] Read more.
Background: Complex cases of retinoblastoma (RB) often require integrative molecular approaches to define tumor etiology and guide clinical management. Purpose: Our aim was to evaluate the usefulness of combining aqueous humor (AH)/plasma cell-free DNA next-generation sequencing (cfDNA-NGS) and long-read–whole-genome sequencing (LR-WGS) to resolve diagnostically challenging RB cases. Case Description: We report the case of a 3-year-old Caucasian girl, conceived by heterologous assisted reproductive technology (ART), presenting with unilateral, widely infiltrative RB in the right eye. She exhibited limited verbal communication, a glabellar angioma extending to the nasal bridge and philtrum, and mild hypertelorism. Standard blood testing revealed no pathogenic SNVs, CNVs, or methylation abnormalities in the RB1 gene. Targeted cfDNA analysis using the Illumina TruSight Oncology 500 (TSO500) panel on AH and plasma identified a somatic RB1 splice-site variant (c.1498+2T>C) with a variant allele frequency (VAF) of 98.5%, consistent with biallelic inactivation. Additional gains (fold change > 1.5) were found in AH and confirmed in plasma, suggesting a germline 13q duplication. Third-generation LR-WGS, performed with Oxford Nanopore Technology (ONT), on blood confirmed a 24.6 Mb duplication on chromosome 13, compatible with the rare 13q duplication syndrome characterized by psychomotor delay, craniofacial dysmorphism, and hemangiomas. AH-cfDNA revealed additional somatic copy-number alterations, including amplifications (i.e., MDM4 and ALK) and deletions (i.e., BRCA2), indicating progressive clonal tumor evolution. Conclusions: This experience tells us that a combined approach with TSO500 Illumina NGS on cfDNA, along with LR-WGS, is able to help solve complex cases and define the appropriate treatment and surveillance strategy.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Next-Generation Sequencing in Rare Genetic Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Dysfunction and Pathological Origins of Lymphatic Endothelial Cells in Atherosclerosis Revealed by Single-Cell Transcriptomics
by
Qinhang Shen, Guangchao Gu, Dan Yang and Yuehong Zheng
Genes 2025, 16(12), 1398; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121398 - 21 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background: Atherosclerosis, a leading cause of cardiovascular disease, involves complex interactions between vascular and immune cells. The role of lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs) in this process remains incompletely characterized, limiting our understanding of disease mechanisms. This study aimed to delineate the phenotypic and
[...] Read more.
Background: Atherosclerosis, a leading cause of cardiovascular disease, involves complex interactions between vascular and immune cells. The role of lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs) in this process remains incompletely characterized, limiting our understanding of disease mechanisms. This study aimed to delineate the phenotypic and functional dynamics of LECs during atherosclerosis progression. Methods: We performed single-cell RNA sequencing on aortic cells from ApoE-/- mice on a high-fat diet at baseline, 8 weeks (early disease), and 16 weeks (late disease). Bioinformatic analyses, including clustering, differential expression, trajectory inference, and cell-cell communication analysis, were applied to characterize LEC subpopulations and their transcriptional reprogramming. Results: Our analysis identified two LEC subpopulations that exhibited a biphasic numerical response: expansion at the early stage followed by a decline by the late stage. Early-disease LECs displayed altered immunomodulatory capacity, with features of reduced T cell tolerance and enhanced activation via IL-7/IL-7R signaling, coupled with a downregulation of key lipid-handling genes (Ldlr, Abca1). Trajectory analysis suggested multiple cellular origins, including a conventional but delayed differentiation path from vascular endothelial cells and an atherosclerosis-specific transdifferentiation path from fibroblasts observed only in early disease. Conclusions: Our findings indicate that LECs undergo substantial phenotypic and functional alterations during atherosclerosis. The maladaptive differentiation and acquired dysfunction in lipid transport and immune regulation may contribute to disease progression. This study provides a foundational transcriptional atlas for understanding lymphatic involvement in vascular disease and highlights potential contexts for therapeutic modulation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Human Genomics and Genetic Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures
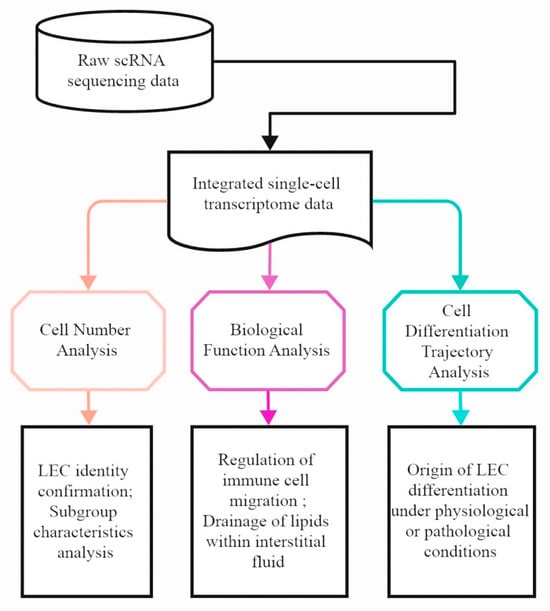
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Comprehensive Transcriptomic and Epitranscriptomic Profiling of Hepatitis B Virus Transcripts in Two Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Lines
by
Qinan Zhang, Bohan Zhang, Lei Wang, Yongjian Liu, Jingwan Han, Lei Jia, Hanping Li, Xiaolin Wang, Jingyun Li, Changyuan Yu and Lin Li
Genes 2025, 16(12), 1397; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121397 - 21 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Despite extensive research on hepatitis B virus (HBV), its post-transcriptional regulatory mechanisms remain incompletely characterized, particularly regarding epitranscriptomic modifications. This study aims to systematically profile the transcriptomic complexity and RNA modification landscape of HBV in hepatocellular carcinoma models. Methods: We
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Despite extensive research on hepatitis B virus (HBV), its post-transcriptional regulatory mechanisms remain incompletely characterized, particularly regarding epitranscriptomic modifications. This study aims to systematically profile the transcriptomic complexity and RNA modification landscape of HBV in hepatocellular carcinoma models. Methods: We transfected PLC/PRF/5 and Huh7 cells with the HBV 1.3-mer WT replicon plasmid, followed by qPCR measurement of viral load. Total nucleic acids extracted from transfected cells underwent nanopore direct RNA sequencing. The complete HBV transcriptome was then analyzed in two established hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines (PLC/PRF/5 and Huh7), with alternative splicing, polyadenylation, and RNA modifications identified through comprehensive bioinformatics analysis. Results: Our analysis revealed substantial transcriptomic diversity, identifying 34 distinct splice variants—including 14 previously unreported isoforms—with cell-type-specific expression patterns. Additionally, we detected 30 high-confidence RNA modification sites across HBV transcripts, with 93% (28 sites) conserved between both cellular environments. Notably, we observed significant intercellular heterogeneity in poly(A) tail length distributions. Conclusions: A comparison of the post-transcriptional processing modifications of HBV in PLC/PRF/5 and Huh7 cells reveals that the former may be better able to mimic the immune evasion mechanisms of chronic HBV infection. In contrast, the longer poly(A) tails present in Huh7 cells facilitate efficient replication, rendering these cells more amenable to the study of HBV transcription and replication mechanisms. These findings comprehensively elucidate the post-transcriptional regulatory mechanisms of hepatitis B virus in different hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines, establishing a critical benchmark for selecting appropriate experimental models in virology research. The identified transcriptomic features may provide new insights for developing antiviral strategies targeting the viral epigenome.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Bioinformatics)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase Complex Subunit 1 (VKORC1) Gene Polymorphisms Predict Arterial Stiffness and Serum MGP Levels in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients
by
David H. Chen, Cees Vermeer, John R. Cockcroft, David C. Wheeler, Kevin M. O’Shaughnessy and Yasmin
Genes 2025, 16(12), 1396; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121396 - 21 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Arterial stiffness increases with progressive worsening of renal function and predicts cardiovascular mortality in patients with chronic kidney disease. The effects of vitamin K-dependent proteins in vascular health and the implications of vitamin K epoxide reductase gene (VKORC1) polymorphisms in calcification
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Arterial stiffness increases with progressive worsening of renal function and predicts cardiovascular mortality in patients with chronic kidney disease. The effects of vitamin K-dependent proteins in vascular health and the implications of vitamin K epoxide reductase gene (VKORC1) polymorphisms in calcification and warfarin sensitivity are well known, but their roles in arterial stiffness are not known. We investigated the influence of common polymorphisms in this gene (−1639G>A, +1173C>T, +1542G>C, +2255C>T, and +3730G>A) on stiffness and calcification markers in 302 CKD patients. Methods: Blood pressure, aortic pulse wave velocity (aPWV), coronary artery calcification (CAC), and aortic calcification (AC) were assessed together with the total uncarboxylated matrix Gla protein (t-uncMGP). Results: Genotyping subjects for +1542G>C and +3730G>A showed higher genotype-specific aPWV and lower t-uncMGP (p < 0.05). The combined recessive allele model showed a significant stepwise reduction in aPWV (p < 0.005); subjects homozygous for both risk alleles had the highest aPWV compared to those carrying one or none. In a multiple regression model adjusting for age, gender, mean pressure, BMI, and racial group, each +1542G allele and +3730A allele were independently associated with a 0.8 m/s (95% CI 0.09 to 1.57) and 1.0 m/s (95% CI 0.14 to 1.98) elevation of aPWV, respectively. Although serum t-uncMGP levels correlated inversely with CAC score (p < 0.001), VKORC1 genotypes did not. Conclusions: We demonstrated for the first time that VKORC1 polymorphisms (+1542G>C and +3730G>A) influence arterial stiffness and serum t-uncMGP levels in CKD patients. These findings suggest that vitamin K-dependent processes may be important in arterial stiffness, possibly by modulating calcification of the vessel wall.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Human Genomics and Genetic Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Transcriptome Analysis Suggests Dietary Tributyrin Enhances Feeding Intensity via Modulating Steroid Biosynthesis in Mandarin Fish (Siniperca chuatsi)
by
Er-Xue Xu, Hao-Yu Li, Zhi-Guang Hou, Yi-Huan Xu, Jun Wu, Teng-Fei Bao, Cheng-Bin Wu, Xiao-Wei Gao and Yan-Miao Tan
Genes 2025, 16(12), 1395; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121395 - 21 Nov 2025
Abstract
Blackground/Objectives: Tributyrin (TB), a stable derivative of butyric acid, has been widely used in animal feeds for its health-promoting effects. This study evaluated the efficacy of dietary TB serving as a functional feed additive in enhancing intestinal health of mandarin fish (Siniperca
[...] Read more.
Blackground/Objectives: Tributyrin (TB), a stable derivative of butyric acid, has been widely used in animal feeds for its health-promoting effects. This study evaluated the efficacy of dietary TB serving as a functional feed additive in enhancing intestinal health of mandarin fish (Siniperca chuatsi), with a focus on elucidating the associated molecular mechanisms. Methods: A total of 300 juvenile mandarin fish (200.0 ± 5.2 g) were randomly assigned to one of three dietary groups: a control group (0 mg/kg TB), a low-dose TB group (TB1, 500 mg/kg), or a high-dose TB group (TB2, 1000 mg/kg). The one-month feeding trial was conducted under strictly controlled conditions, with water quality maintained within optimal range. Fish were fed their respective diets twice daily to apparent satiety. Results: Results showed that TB supplementation significantly increased villus height in the mid- and hindgut, with the TB2 group showing the most pronounced improvement. Furthermore, transcriptome analysis revealed that TB altered the expression of genes involved in energy metabolism, fatty acid oxidation, and steroid biosynthesis pathways. Notably, TB supplementation up-regulated key genes such as gls2b (energy metabolism) and cpt1b (fatty acid oxidation), and modulated especially modulated steroid biosynthesis through genes sqlea and dhcr24h. Co-expression network analysis further identified hub genes associated with energy metabolism (etfb), immune regulation (il20ra, foxp1b), and cell cycle regulation (cdc20, ccnb1). Conclusions: These findings elucidate the mechanism of action of TB as a functional feed additive, providing a theoretical foundation for its application in aquaculture to enhance intestinal health.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Animal Genetics and Genomics)
►▼
Show Figures
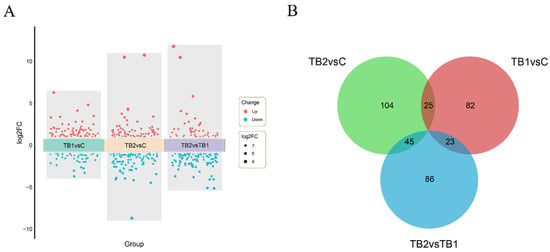
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
A Single-Cell Omics Technical Guide for Advancing Neuropsychiatric Research
by
Kayleigh Casmey, Maria Zimmermann, Yuxin Xie, Sierra A. Codeluppi-Arrowsmith and Gustavo Turecki
Genes 2025, 16(12), 1394; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121394 - 21 Nov 2025
Abstract
Single-cell omics technology has advanced rapidly since its inception, offering increasing precision, resolution, and technical diversity to explore cell-specific molecular features in the human brain and neuropsychiatric disorders. While traditional bulk genomic analyses have provided valuable insights into the molecular processes of these
[...] Read more.
Single-cell omics technology has advanced rapidly since its inception, offering increasing precision, resolution, and technical diversity to explore cell-specific molecular features in the human brain and neuropsychiatric disorders. While traditional bulk genomic analyses have provided valuable insights into the molecular processes of these disorders, single-cell omics allows for the investigation of cellular heterogeneity in the brain, which is crucial for dissecting underlying pathology. Neuropsychiatric disorders—such as dementia and depression—are complex and heterogenous brain disorders driven by intricate interactions of genetic and environmental factors. Methodological developments in single-cell omic technologies have enabled their application directly to human brain tissue for the study of neuropsychiatric disorders, yielding cell-specific insights in transcriptomics and epigenomics, with emerging findings in proteomics, metabolomics, multi-omics, and beyond. This review discusses different single-cell omic technologies, focusing on their application to postmortem human brain tissue, highlighting key findings from the use of these methods in neuropsychiatric disorders, and providing considerations for future implementation to elucidate the molecular landscape of brain changes associated with these conditions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Neuropsychiatric Disorders: Genetics and Targeted Therapy)
►▼
Show Figures
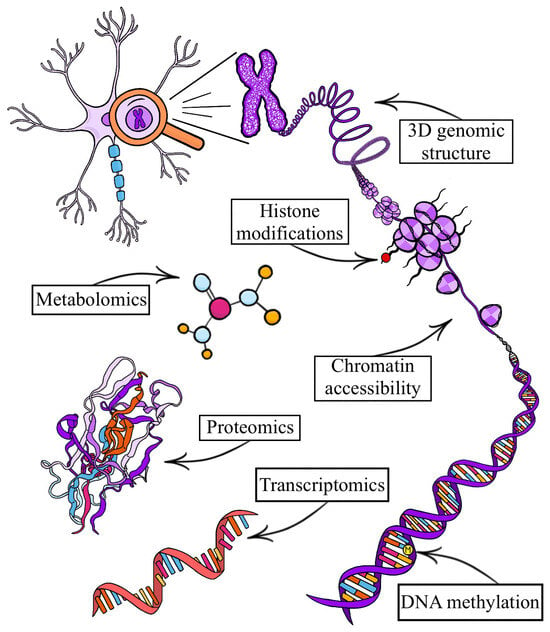
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Mountains, Lakes, and Ancient Drainage Networks Sculpt the Phylogeographic Architecture of the Stream Headwater Fish Acrossocheilus kreyenbergii in China
by
Yun Chen, Guangmin Deng, Ziyu Le and Cuizhang Fu
Genes 2025, 16(12), 1393; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16121393 - 21 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background: Phylogeographic surveys of obligate freshwater fishes could serve as a pivotal lens through which the biological footprints of historic drainage rearrangements can be deciphered. Methods: Focusing on the headwater-restricted cyprinid Acrossocheilus kreyenbergii in the Pearl, Yangtze, and Huai river basins, we examined
[...] Read more.
Background: Phylogeographic surveys of obligate freshwater fishes could serve as a pivotal lens through which the biological footprints of historic drainage rearrangements can be deciphered. Methods: Focusing on the headwater-restricted cyprinid Acrossocheilus kreyenbergii in the Pearl, Yangtze, and Huai river basins, we examined variations in mitochondrial cytochrome b gene (Cyt b) to elucidate the phylogeographic architecture and evolutionary history of this stream fish in South–Central China through integrative analyses of phylogeny, ancestral area reconstruction, genetic structure, and population demography. Results: A time-calibrated phylogeny recovered two primary lineages, K-I and K-II, which diverged ca. 2.15 Ma: K-I split into K-Ia (Huai River) and K-Ib (Yangtze–Poyang Lake catchment) at 1.53 Ma, whereas K-II gave rise to K-IIa, K-IIb, and K-IIc through sequential divergences at 1.29 Ma and 0.83 Ma, with K-IIa restricted to the Poyang Lake catchment. K-IIb was shared between the Poyang Lake catchment and the Qiupu River (Yangtze basin), and K-IIc was distributed in the Xijiang River (Pearl basin) as well as the Yangtze–Dongting Lake catchment. Conclusions: Our findings reveal that the phylogeographic architecture of A. kreyenbergii was sculpted by a succession of geologic and anthropocentric events: the Late-Cenozoic collapse of the Zhe–Min Uplift first fractured its range; the intervening Mufu–Lianyun–Luoxiao Mountains then acted as a persistent barrier; the large waters of Poyang and Dongting Lakes served as biological filters; and the 2200-year-old Lingqu Canal—constructed during the Qin dynasty—briefly re-established a corridor for gene flow. Together, these forces disrupted and reorganized the species’ genetic connections, leaving a visible imprint today.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Animal Genetics and Genomics)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Reprogramming Fibrosis: How Protein PTMs Reshape the IPF Proteome
by
Yunze Li, Wei Kong, Hanqi Zhang, Xinfeng Wei, Junxuan Yi, Mingwei Wang, Shunzi Jin and Duo Yu
Genes 2025, 16(11), 1392; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16111392 - 20 Nov 2025
Abstract
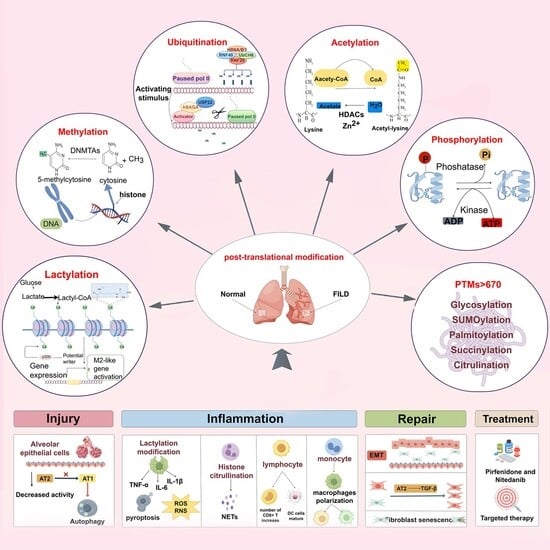
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a fatal and progressive lung disorder. Its pathological process involves persistent epithelial damage, ongoing inflammation, and dysregulated tissue repair. Currently, there are no effective treatment methods to improve patient survival. However, post-translational modifications (PTMs) have gradually garnered widespread
[...] Read more.
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a fatal and progressive lung disorder. Its pathological process involves persistent epithelial damage, ongoing inflammation, and dysregulated tissue repair. Currently, there are no effective treatment methods to improve patient survival. However, post-translational modifications (PTMs) have gradually garnered widespread attention. They are the processes by which various chemical groups are added to or removed from proteins’ amino acid side chains or the N- or C-terminal ends of the polypeptide chain following synthesis. Additionally, they can regulate the energy supply of cells, regulate the cell cycle, and affect important signaling pathways such as TGF-β. This review systematically summarizes different categories of PTMs, organizes the PTMs involved in various injury stages of IPF, outlines the roles of different cells throughout the process, and analyzes future clinical diagnosis and treatment strategies as well as intervention targets for IPF, providing guiding significance for the systematic intervention of IPF in the future.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Genetics and Genomics of Lung Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessCorrection
Correction: Marszałek-Kruk et al. Treacher Collins Syndrome: Genetics, Clinical Features and Management. Genes 2021, 12, 1392
by
Bożena Anna Marszałek-Kruk, Piotr Wójcicki, Krzysztof Dowgierd and Robert Śmigiel
Genes 2025, 16(11), 1391; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16111391 - 20 Nov 2025
Abstract
Error in Figure [...]
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Genetic Diagnosis)
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 2
Open AccessArticle
High Allelic Heterogeneity in Kazakhstani Patients with Neurofibromatosis Type 1: Results from the First Molecular Study
by
Zhannat Idrissova, Farida Rakhimbekova, Madina Orazgaliyeva, Madina Zhaksybek, Kristina Kovaleva, Saltanat Abdikerim, Aizhan Ormankyzy and Petr Vasiluev
Genes 2025, 16(11), 1390; https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16111390 - 19 Nov 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: This study presents the first molecular characterization of NF1 gene variants in Kazakhstani patients, expanding regional understanding of neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1). The NF1 gene encodes neurofibromin, a tumor suppressor protein that regulates the MAPK signaling pathway; its inactivation results in
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: This study presents the first molecular characterization of NF1 gene variants in Kazakhstani patients, expanding regional understanding of neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1). The NF1 gene encodes neurofibromin, a tumor suppressor protein that regulates the MAPK signaling pathway; its inactivation results in NF1, a multisystem disorder with pigmentary and tumor manifestations. Methods: A total of 60 pediatric and young adult patients of University Clinic Aksai were selected based on Legius criteria and studied clinically; genetic variants of NF1 gene were determined with AmpliSeq for Illumina Myeloid Panel (next generation sequencing). Results: Pathogenic or likely pathogenic (with some variants of unknown significance) were detected in 58 of 60 (96.7%) patients. Among them, 27 (46.6%) carried point variants, 21 (36.2%) had genomic deletions, 3 (5.2%) had duplications, 3 (5.2%) insertions, and 4 (6.9%) had exon–intron splicing site variants. Notably, all patients with duplication insertions and splicing variants presented with plexiform neurofibromas. Conclusions: The study defines the first variant spectrum in a Kazakhstani population, confirming genotype–phenotype correlations consistent with European cohorts (l.). These data highlight the predominance of structural and splicing alterations in patients with plexiform neurofibromas and support the integration of molecular testing into clinical management of NF1 in Kazakhstan.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Human Genomics and Genetic Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures
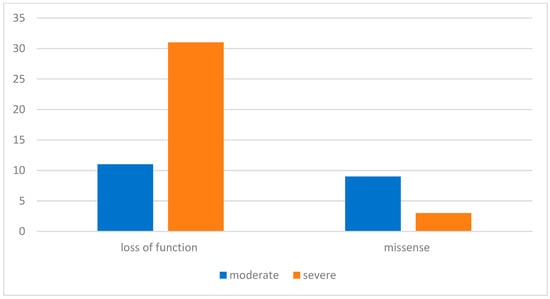
Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Genes Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Animals, CIMB, Genes, IJMS, DNA
Advances in Molecular Genetics and Breeding of Cattle, Sheep, and Goats
Topic Editors: Xiukai Cao, Hui Li, Huitong ZhouDeadline: 30 November 2025
Topic in
BioTech, DNA, Genes, IJMS, CIMB
Single-Cell Technologies: From Research to Application
Topic Editors: Ken-Hong Lim, Chung-Der Hsiao, Pei-Ming YangDeadline: 31 December 2025
Topic in
Animals, Dairy, Genes, Agriculture, Poultry, Ruminants, Veterinary Sciences
Application of Reproductive and Genomic Biotechnologies for Livestock Breeding and Selection: 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Manuel García-Herreros, Pedro Manuel AponteDeadline: 30 April 2026
Topic in
Biomedicines, Future Pharmacology, Pharmacy, IJMS, Biomolecules, Genes
Prospects of Multi-Target Agonists in Metabolic and Epigenetic Medicine
Topic Editors: Riham Abouleisa, Yanming LiDeadline: 30 November 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Genes
The CranioFacial Biology Group at the University of Adelaide Collection: Genetic, Epigenetic and Environmental Factors in Complex Adaptive Systems, Multilayer Complex Interactive Networks, and Multiple Models During Oral Development
Guest Editors: Alan H. Brook, Matthew Brook O'DonnellDeadline: 5 December 2025
Special Issue in
Genes
Genetics of Neuromuscular and Metabolic Diseases
Guest Editors: Micheal Palladino, Claudia RicciDeadline: 5 December 2025
Special Issue in
Genes
Genetics and Genomics of Lung Diseases
Guest Editor: Jun YangDeadline: 10 December 2025
Special Issue in
Genes
The Genetics of Male Infertility and Clinical Implications
Guest Editor: Gianmaria SalvioDeadline: 10 December 2025
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Genes
Tools for Population and Evolutionary Genetics
Collection Editors: David Alvarez-Ponce, Julie M. Allen, Won C. Yim, Marco Fondi
Topical Collection in
Genes
Eukaryotic Non-coding RNAs: Diversity, Structure/Function, Implication in Cardiovascular Disease
Collection Editors: Morten Andre Høydal, Christiane Branlant
Topical Collection in
Genes
Genetics and Genomics of Hereditary Disorders of Connective Tissue
Collection Editors: Nazli B. Mcdonnell, Bert Callewaert, Clair A. Francomano, Philippe Khau-Van-Kien, Yves Dulac









