Bioinformatics Approaches to Biomedicine
Share This Topical Collection
Editor
 Dr. Giulia Fiscon
Dr. Giulia Fiscon
 Dr. Giulia Fiscon
Dr. Giulia Fiscon
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Department of Computer, Control, and Management Engineering (DIAG), Sapienza University of Rome, 00179 Rome, Italy
Interests: biomedical engineering; computational biology; bioinformatics; systems biology; computational medicine; network medicine
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Bioinformatics has become an indispensable tool in understanding the biological complexity of diseases and providing unprecedented insights into the biomedical sciences. The growth of omics data allowed studies at different molecular levels of the same sample, aiding to the identification of novel potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets, as well as disease patients’ classification. This Topical Collection aims at presenting computational methods in bioinformatics, along with their application to biomedical sciences.
The contributions may describe novel or and existing approaches to aid: the identification of diagnostic, prognostic, or predictive biomarkers; the discovery of potential therapeutic targets and important disease-related pathways; or provide valuable insights into a precision medicine.
Potential topics include, but are not limited to:
- Biological data mining;
- Omics data analysis (genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics);
- Omics data integration;
- Modelling Analysis in Health Informatics and Biomedicine;
- Network-based methods and machine learning methods for precision medicine;
- Biomarkers discovery and disease classification.
Dr. Giulia Fiscon
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Current Issues in Molecular Biology is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2200 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- computational medicine
- network theory
- biological data mining
- omics data analysis
- potential therapeutic targets
Published Papers (5 papers)
2024
Open AccessArticle
Exome Sequencing for the Diagnostics of Osteogenesis Imperfecta in Six Russian Patients
by
Yulia S. Koshevaya, Mariia E. Turkunova, Anastasia O. Vechkasova, Elena A. Serebryakova, Maxim Yu. Donnikov, Svyatoslav I. Papanov, Alexander N. Chernov, Lev N. Kolbasin, Lyudmila V. Kovalenko, Andrey S. Glotov and Oleg S. Glotov
Viewed by 298
Abstract
Osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) is a group of inherited disorders of connective tissue that cause significant deformities and fragility in bones. Most cases of OI are associated with pathogenic variants in collagen type I genes and are characterized by pronounced polymorphisms in clinical manifestations
[...] Read more.
Osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) is a group of inherited disorders of connective tissue that cause significant deformities and fragility in bones. Most cases of OI are associated with pathogenic variants in collagen type I genes and are characterized by pronounced polymorphisms in clinical manifestations and the absence of clear phenotype–genotype correlation. The objective of this study was to conduct a comprehensive molecular–genetic and clinical analysis to verify the diagnosis of OI in six Russian patients with genetic variants in the
COL1A1 and
COL1A2 genes. Clinical and laboratory data were obtained from six OI patients who were observed at the Medical Genetics Center in Saint Petersburg from 2016 to 2023. Next-generation sequencing on MGISEQ G400 (MGI, China) was used for DNA analysis. The GATK bioinformatic software (version 4.5.0.0) was used for variant calling and hard filtering. Genetic variants were verified by the direct automatic sequencing of PCR products using the ABI 3500X sequencer. We identified six genetic variants, as follows pathogenic c.3505G>A (p. Gly1169Ser), c.769G>A (p.Gly257Arg), VUS c.4123G>A (p.Ala1375Thr), and c.4114A>T (p.Asn1372Tyr) in
COL1A1; and likely pathogenic c.2035G>A (p.Gly679Ser) and c.739-2A>T in
COL1A2. In addition, clinical cases are presented due to the presence of the c.4114A>T variant in the
COL1A2 gene. Molecular genetics is essential for determining different OI types due to the high similarity across various types of the disease and the failure of unambiguous diagnosis based on clinical manifestations alone. Considering the variable approaches to OI classification, an integrated strategy is required for optimal patient management.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Genetic Signatures for Distinguishing Chemo-Sensitive from Chemo-Resistant Responders in Prostate Cancer Patients
by
Lemohang Gumenku, Mamello Sekhoacha, Beynon Abrahams, Samson Mashele, Aubrey Shoko and Ochuko L. Erukainure
Viewed by 1040
Abstract
Prostate cancer remains a significant public health concern in sub-Saharan Africa, particularly impacting South Africa with high mortality rates. Despite many years of extensive research and significant financial expenditure, there has yet to be a definitive solution to prostate cancer. It is not
[...] Read more.
Prostate cancer remains a significant public health concern in sub-Saharan Africa, particularly impacting South Africa with high mortality rates. Despite many years of extensive research and significant financial expenditure, there has yet to be a definitive solution to prostate cancer. It is not just individuals who vary in their response to treatment, but even different nodules within the same tumor exhibit unique transcriptome patterns. These distinctions extend beyond mere differences in gene expression levels to encompass the control and networking of individual genes. Escalating chemotherapy resistance in prostate cancer patients has prompted increased research into its underlying mechanisms. The heterogeneous nature of transcriptomic organization among men makes the pursuit of universal biomarkers and one-size-fits-all treatments impractical. This study delves into the expression of drug resistance-associated genes, ABCB1 and CYP1B1, in cancer cells. Employing bioinformatics, we explored the molecular pathways and cascades linked to drug resistance following upregulation of these genes. Samples were obtained from archived prostate cancer patient specimens through pre-treatment biopsies of two categories: good vs. poor responders, with cDNAs synthesized from isolated RNAs subjected to qPCR analysis. The results revealed increased ABCB1 and CYP1B1 expression in tumor samples of the poor responders. Gene enrichment and network analysis associated ABCB1 with ABC transporters and LncRNA-mediated therapeutic resistance (WP3672), while CYP1B1 was linked to ovarian steroidogenesis, tryptophan metabolism, steroid hormone biosynthesis, benzo(a)pyrene metabolism, the sulindac metabolic pathway, and the estrogen receptor pathway, which are associated with drug resistance. Both ABCB1 and CYP1B1 correlated with microRNAs in cancer and the Nuclear Receptors Meta-Pathway. STRING analysis predicted protein–protein interactions of ABCB1 and CYP1B1 with Glutathione S-transferase Pi, Catechol O-methyltransferase, UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1-6, Leucine-rich Transmembrane and O-methyltransferase (LRTOMT), and Epoxide hydrolase 1, with scores of 0.973, 0.971, 0.966, 0.966, and 0.966, respectively. Furthermore, molecular docking analysis of the chemotherapy drug, docetaxel, with CYP1B1 and ABCB1 revealed robust molecular interactions, with binding energies of −20.37 and −15.25 Kcal/mol, respectively. These findings underscore the susceptibility of cancer patients to drug resistance due to increased ABCB1 and CYP1B1 expression in tumor samples from patients in the poor-responders category that affects associated molecular pathways. The potent molecular interactions of ABCB1 and CYP1B1 with docetaxel further emphasize the potential basis for chemotherapy resistance.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
In Silico Approach to Molecular Profiling of the Transition from Ovarian Epithelial Cells to Low-Grade Serous Ovarian Tumors for Targeted Therapeutic Insights
by
Asim Leblebici, Ceren Sancar, Bahar Tercan, Zerrin Isik, Mehmet Emin Arayici, Ender Berat Ellidokuz, Yasemin Basbinar and Nuri Yildirim
Viewed by 1062
Abstract
This paper aims to elucidate the differentially coexpressed genes, their potential mechanisms, and possible drug targets in low-grade invasive serous ovarian carcinoma (LGSC) in terms of the biologic continuity of normal, borderline, and malignant LGSC. We performed a bioinformatics analysis, integrating datasets generated
[...] Read more.
This paper aims to elucidate the differentially coexpressed genes, their potential mechanisms, and possible drug targets in low-grade invasive serous ovarian carcinoma (LGSC) in terms of the biologic continuity of normal, borderline, and malignant LGSC. We performed a bioinformatics analysis, integrating datasets generated using the GPL570 platform from different studies from the GEO database to identify changes in this transition, gene expression, drug targets, and their relationships with tumor microenvironmental characteristics. In the transition from ovarian epithelial cells to the serous borderline, the FGFR3 gene in the “Estrogen Response Late” pathway, the ITGB2 gene in the “Cell Adhesion Molecule”, the CD74 gene in the “Regulation of Cell Migration”, and the IGF1 gene in the “Xenobiotic Metabolism” pathway were upregulated in the transition from borderline to LGSC. The ERBB4 gene in “Proteoglycan in Cancer”, the AR gene in “Pathways in Cancer” and “Estrogen Response Early” pathways, were upregulated in the transition from ovarian epithelial cells to LGSC. In addition, SPP1 and ITGB2 genes were correlated with macrophage infiltration in the LGSC group. This research provides a valuable framework for the development of personalized therapeutic approaches in the context of LGSC, with the aim of improving patient outcomes and quality of life. Furthermore, the main goal of the current study is a preliminary study designed to generate in silico inferences, and it is also important to note that subsequent in vitro and in vivo studies will be necessary to confirm the results before considering these results as fully reliable.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessBrief Report
Association between Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Monoamine Oxidase and the Severity of Addiction to Betel Quid
by
Chung-Chieh Hung, Ying-Chin Ko and Chia-Min Chung
Viewed by 714
Abstract
Betel quid (BQ) is the fourth most popular psychoactive substance in the world, and BQ use disorder (BUD) is prevalent in Asian countries. Although the mechanisms underlying BUD remain unclear, studies have reported influences from monoamine oxidase inhibitor. We enrolled 50 patients with
[...] Read more.
Betel quid (BQ) is the fourth most popular psychoactive substance in the world, and BQ use disorder (BUD) is prevalent in Asian countries. Although the mechanisms underlying BUD remain unclear, studies have reported influences from monoamine oxidase inhibitor. We enrolled 50 patients with BUD and assessed their BQ consumption habits, emotional conditions, and the clinical severity of addiction—assessed using the
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders [Fifth Edition] (
DSM-5) criteria, Substance Use Severity Rating Scale, and Yale–Brown Obsessive Compulsive Disorder Rating Scale for BQ. Patients were categorized into the severe group when showing six or more symptoms defined by
DSM-5. A genome-wide association study was conducted for single nucleotide polymorphisms in
BRCA1,
COL9A1,
NOTCH1,
HSPA13,
FAT1, and
MAOA by using patients’ blood samples. More severe BUD symptoms were associated with younger age of using BQ and poor oral hygiene and with severe craving for and more anxiety toward BQ use. The
MAOA rs5953210 polymorphism was significantly associated with severe BUD (odds ratio, 6.43; 95% confidence interval, 5.12–7.74;
p < 0.01) and might contribute to BQ-associated cancer risk. Further studies are required to investigate the addictive properties of BQ and the development of novel diagnostic tools and pharmacotherapeutic alternatives to BUD treatment.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
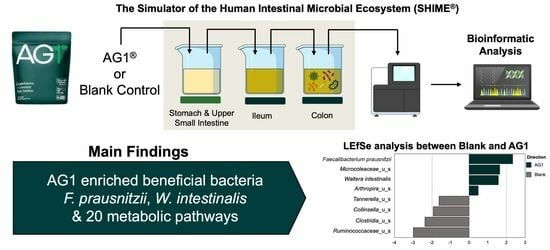
AG1® Induces a Favorable Impact on Gut Microbial Structure and Functionality in the Simulator of Human Intestinal Microbial Ecosystem® Model
by
Trevor O. Kirby, Philip A. Sapp, Jeremy R. Townsend, Marlies Govaert, Cindy Duysburgh, Massimo Marzorati, Tess M. Marshall and Ralph Esposito
Viewed by 1865
Abstract
Modulation of the human gut microbiome has become an area of interest in the nutraceutical space. We explored the effect of the novel foundational nutrition supplement AG1
® on the composition of human microbiota in an in vitro experimental design. Employing the Simulator
[...] Read more.
Modulation of the human gut microbiome has become an area of interest in the nutraceutical space. We explored the effect of the novel foundational nutrition supplement AG1
® on the composition of human microbiota in an in vitro experimental design. Employing the Simulator of Human Intestinal Microbial Ecosystem (SHIME
®) model, AG1
® underwent digestion, absorption, and subsequent colonic microenvironment simulation under physiologically relevant conditions in healthy human fecal inocula. Following 48 h of colonic simulation, the gut microbiota were described using shallow shotgun, whole genome sequencing. Metagenomic data were used to describe changes in community structure (alpha diversity, beta diversity, and changes in specific taxa) and community function (functional heterogeneity and changes in specific bacterial metabolic pathways). Results showed no significant change in alpha diversity, but a significant effect of treatment and donor and an interaction between the treatment and donor effect on structural heterogeneity likely stemming from the differential enrichment of eight bacterial taxa. Similar findings were observed for community functional heterogeneity likely stemming from the enrichment of 20 metabolic pathways characterized in the gene ontology term database. It is logical to conclude that an acute dose of AG1 has significant effects on gut microbial composition that may translate into favorable effects in humans.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures