Roles of Prolyl Isomerases in RNA-Mediated Gene Expression
Abstract
:1. Roles of Peptidyl Prolyl Isomerases (PPIases) in mRNA Remodeling
2. Cyclophilin-Type PPIases that Participate in Pre-mRNA Splicing and Epigenetic Control of Transcription
2.1 PPIL1 (also called CYPL1, hCyPX, CGI-124)

| Name in Review | Other Names | PDB Code/s | Proline Isomerase Activity? | Interacting Proteins in RNA Metabolism | Other Domains Present |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PPIL1 | CYPL1, hCyPX, CGI-124 | 1XWN (NMR) 2K7N (NMR) 2X7K (X-ray) | Yes | Ski-interacting protein (SKIP) | None |
| PPIL2 | CYC4, Cyp60, UBOX7, Cyp58 | 1ZKC (ring-domain) | No | unknown | N-terminal U-box (E3 ligase) |
| PPIL3b | CyPJ | 2OJU (X-ray) 2OK3 (X-ray) 1XYH (X-ray) | Unknown | Unknown protein in the U2snRNP | None |
| PPIE | CYP33, CYP-33 | 3UCH (X-ray PPIase) 2CQB (NMR-RRM) 2KYX (NMR-RRM) 3LPY (X-ray RRM) 3MDF (X-ray RRM) 2R99 (X-ray PPIase) 1ZMF (X-ray PPIase) 2KU7 (MLL1 PHD3-Cyp33 RRM chimeric protein) | Yes | MLL1 histone methyltransferase | N-terminal RRM |
| PPIL4 | CyP57 | None | Yes | RNA Pol II CTD | C-terminal RRM |
| PPWD1 | CyP73 | 2A2N (X-ray PPIase) | Yes | Unknown | WD40 repeats |
| PPIH | Snu-Cyp20, USA-Cyp, CyPH | 1MZW (X-ray PPIase) | Yes | hPrp4; hPrp18 | None |
| PPIG | SR-Cyp, CARS-Cyp, CYPG, Matrin-CyP (rat) | 2GW2 (X-ray PPIase) | Yes | Clk kinase; RNA Pol II CTD | N-terminal RS domains; Nopp140 repeats |

2.2. PPIL2 (Also Called CYC4, Cyp60, UBOX7, Cyp58)
2.3. PPIL3b (Also Called CyPJ)
2.4. PPIE (Also Called CYP33, CYP-33)
2.5. PPIL4 or CyP57
2.6. PPWD1 (Also Called CyP73)
2.7. PPIH (Also Called Snu-Cyp20, USA-Cyp, CyPH)
2.8. PPIG (Also Called SR-Cyp, CARS-Cyp, CYPG, Matrin-CyP (Rat))
3. FK506 Binding Proteins (FKBP) Involved in Epigenetic Silencing and mRNA Stability
3.1. FKBP4 and FKBP5
| Name in Review | Other Names | PDB Code/s (for PPIase Domain Containing Structures) | Proline Isomerase Activity? | Interacting Proteins in RNA Metabolism | Other Domains Present |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FKBP4 | FKBP51 FKBP52 FKBP59 | 1Q1C (X-ray); 4DRJ (X-ray); 1QZ2 (X-ray); 4TW8 (X-ray); 1ROU (NMR); 1ROT (NMR); 1N1A (X-ray); 4LAY (X-ray); 4LAX (X-ray); 4LAW (X-ray); 4LAV (X-ray); 1P5Q (X-ray) | Yes | Hsp90, Ago2 | C-terminal TPR |
| FKBP5 | FKBP51 FKBP54 | 3G6P (X-ray); 3G6Q (X-ray); 3G6R (X-ray); 3G6T (X-ray); 3G6U (X-ray); 1KT0 (X-ray); 1KT1 (X-ray); 4TW6 (X-ray); 4TXO (X-ray); 3O5D (X-ray); 3O5E (X-ray); 3O5G (X-ray); 3O5I (X-ray); 3O5J (X-ray); 3O5K (X-ray); 3O5L (X-ray); 3O5M (X-ray); 3O5O (X-ray); 3O5P (X-ray); 3O5Q (X-ray); 3O5R (X-ray); 4DRK (X-ray); 4DRM (X-ray); 4DRN (X-ray); 4DRO (X-ray); 4DRP (X-ray); 4DRQ (X-ray); 4JFI (X-ray); 4JFJ (X-ray); 4JFK (X-ray); 4JFL (X-ray); 4JFM (X-ray); 4TW7 (X-ray); 4W9O (X-ray); 4W9P (X-ray); 4W9Q (X-ray); 4DRH (X-ray); 4DRI (X-ray); | Yes | Hsp90, Ago2, Akt | C-terminal TPR |
| FKBP6 | FKBP36 | 3B7X | No | Hsp90, Hsp27 | C-terminal TPR |
| FKBP25 | FKBP3 | 3KZ7 (X-ray); 1PBK (X-ray); 4JYS (X-ray); 2KFV (NMR) | Yes | HDAC1, HDAC2, YY1, CK2, Nucleolin, HMG II | Extended N-terminus |
3.2. FKBP6
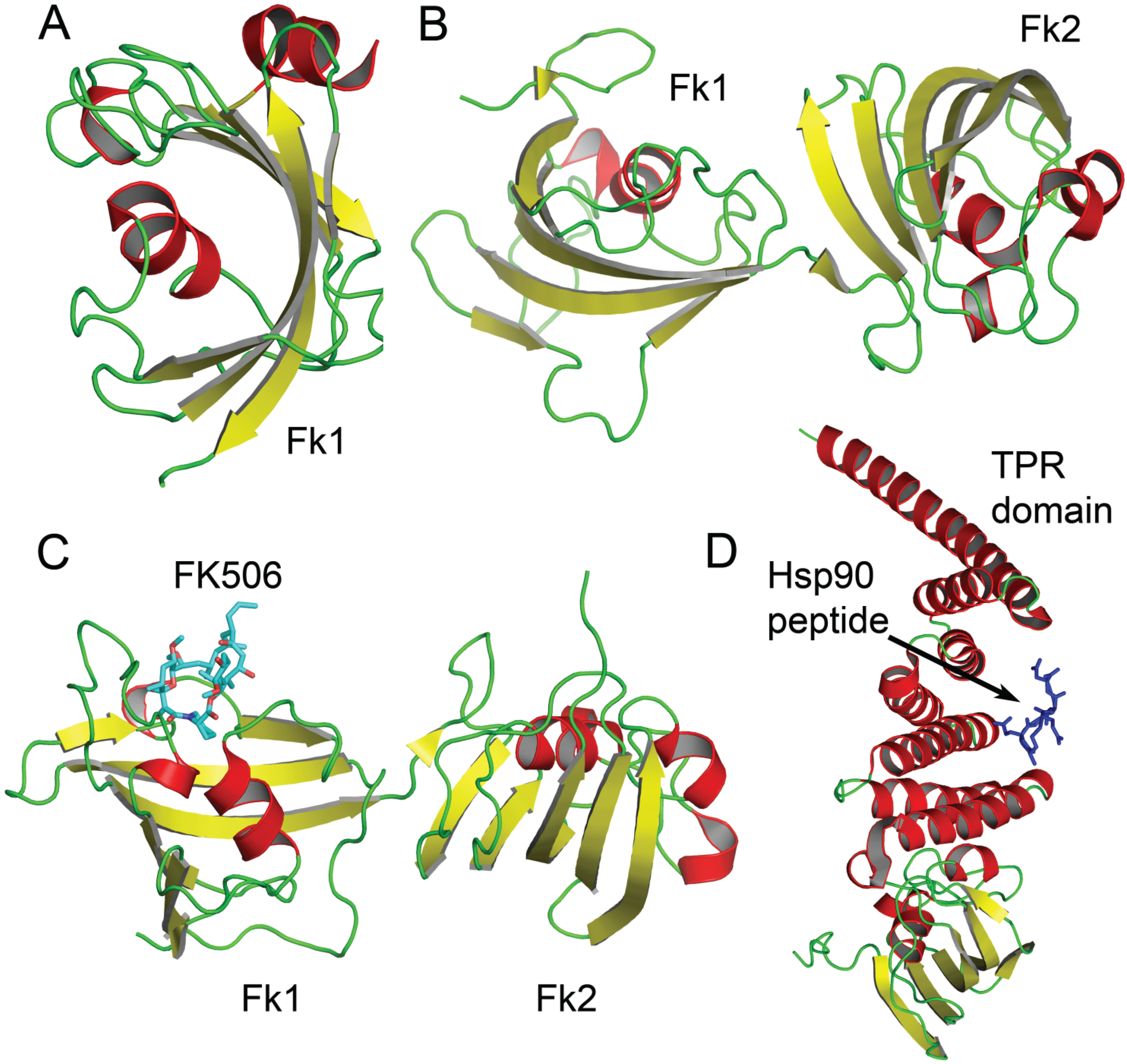
3.3. FKBP25
4. Parvulins Involved in Regulating Transcription and mRNA Turnover
4.1. Pin1
| Name in Review | Other Names | PDB Code/s (for PPIase Domain Containing Structures) | Proline Isomerase Activity? | Interacting Proteins in RNA Metabolism | Other Domains Present |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pin1 | DOD, UBL5 Ess1 (yeast) | 1PIN (X-ray), 1NMV (NMR) 1NMW (NMR), 1F8A (X-ray) 2ITK (X-ray), 4TYO (X-ray) 2F21 (X-ray), 3TDB (X-ray) 3TCZ (X-ray), 3WH0 (X-ray) 3KAG (X-ray), 3KAI (X-ray) 3KCE (X-ray), 3KAH (X-ray) 3KAC (X-ray), 3KAB (X-ray) 3KAD (X-ray), 3KAF (X-ray) 1ZCN (X-ray), 2RUC (NMR) 2RUD (NMR), 2Q5A (X-ray) 3I6C (X-ray), 3ITK (X-ray) 3JYJ (X-ray), 3ODK (X-ray) 3IK8 (X-ray), 3IKD (X-ray) 3IKG (X-ray), 2ZQS (X-ray) 2ZQT (X-ray), 2ZQU (X-ray) 4U96 (X-ray), 4QIB (X-ray) 4TNS (X-ray), 4U84 (X-ray) 4U85 (X-ray), 2ZR4 (X-ray) 2ZR5 (X-ray), 2ZR6 (X-ray) 1YW5 (Ess1) | Yes | AUF1 KSRP HuR SLBP RNA Pol II CTD | WW |
| Par14 | PIN4 | 1EQ3 (NMR) 1FJD (NMR) 3UI4 (X-ray 0.8 Å) 3UI5 (X-ray 1.4 Å) 3UI6 (X-ray 0.89 Å w/oxidized DTT) | Yes | Unknown | N-terminal basic domain |
| Par17 | PIN4 | Same as above. Par17 is related to Par14 | Yes | Unknown | N-terminal basic domain + helical extension |
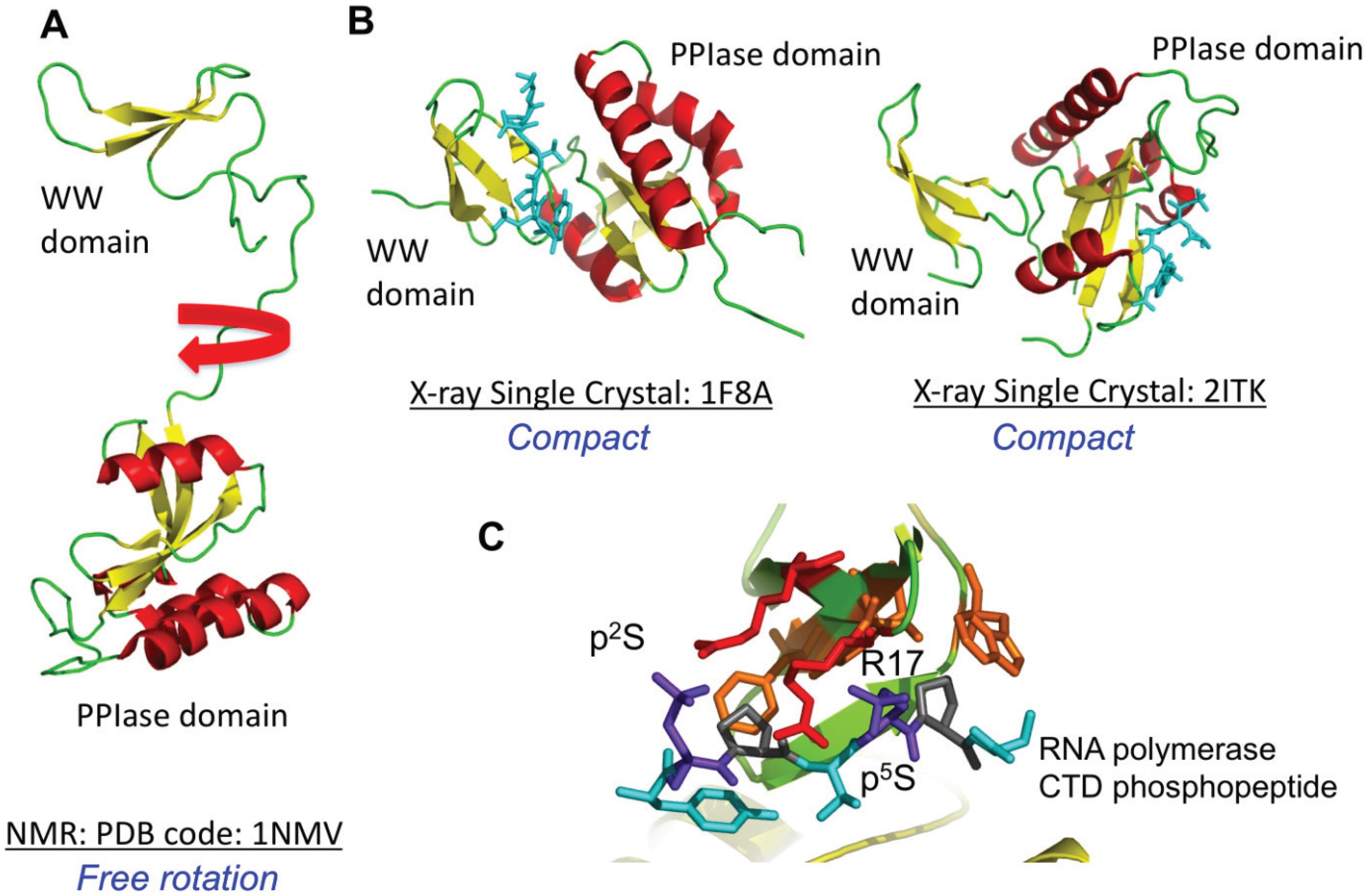
4.2. Par14 and Par17
5. Conclusions and Implications for Development of Therapeutics
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, C.Y.; Shyu, A.B. Emerging mechanisms of mRNP remodeling regulation. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2014, 5, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moore, M.J. From birth to death: The complex lives of eukaryotic mRNAs. Science 2005, 309, 1514–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothbart, S.B.; Strahl, B.D. Interpreting the language of histone and DNA modifications. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1839, 627–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margueron, R.; Reinberg, D. Chromatin structure and the inheritance of epigenetic information. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handschumacher, R.E.; Harding, M.W.; Rice, J.; Drugge, R.J.; Speicher, D.W. Cyclophilin: A specific cytosolic binding protein for cyclosporin A. Science 1984, 226, 544–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harding, M.W.; Handschumacher, R.E. Cyclophilin, a primary molecular target for cyclosporine. Structural and functional implications. Transplantation 1988, 46, 29S–35S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandts, J.F.; Halvorson, H.R.; Brennan, M. Consideration of the possibility that the slow step in protein denaturation reactions is due to cis-trans isomerism of proline residues. Biochemistry 1975, 14, 4953–4963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanghanel, J.; Fischer, G. Insights into the catalytic mechanism of peptidyl prolyl cis/trans isomerases. Front. Biosci. 2004, 9, 3453–3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiene-Fischer, C. Multidomain peptidyl prolyl cis/trans isomerases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahl, M.C.; Will, C.L.; Luhrmann, R. The spliceosome: Design principles of a dynamic RNP machine. Cell 2009, 136, 701–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessonov, S.; Anokhina, M.; Will, C.L.; Urlaub, H.; Luhrmann, R. Isolation of an active step I spliceosome and composition of its RNP core. Nature 2008, 452, 846–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Zhang, J.; Huang, X.; Sun, J.; Xu, Y.; Tang, Y.; Wu, J.; Shi, Y.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Solution structure of human peptidyl prolyl isomerase-like protein 1 and insights into its interaction with skip. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 15900–15908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.; Huang, X.; Xu, C.; Wang, W.; Liu, Z.; Wu, J.; Shi, Y. A large intrinsically disordered region in skip and its disorder-order transition induced by PPIL1 binding revealed by NMR. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 4951–4963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stegmann, C.M.; Luhrmann, R.; Wahl, M.C. The crystal structure of PPIL1 bound to cyclosporine a suggests a binding mode for a linear epitope of the skip protein. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrosio, D.L.; Badjatia, N.; Gunzl, A. The spliceosomal PRP19 complex of trypanosomes. Mol. Microbiol. 2014, 95, 885–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushkarsky, T.; Yurchenko, V.; Vanpouille, C.; Brichacek, B.; Vaisman, I.; Hatakeyama, S.; Nakayama, K.I.; Sherry, B.; Bukrinsky, M.I. Cell surface expression of CD147/EMMPRIN is regulated by cyclophilin 60. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 27866–27871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatakeyama, S.; Yada, M.; Matsumoto, M.; Ishida, N.; Nakayama, K.I. U box proteins as a new family of ubiquitin-protein ligases. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 33111–33120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espeseth, A.S.; Huang, Q.; Gates, A.; Xu, M.; Yu, Y.; Simon, A.J.; Shi, X.P.; Zhang, X.; Hodor, P.; Stone, D.J.; et al. A genome wide analysis of ubiquitin ligases in app processing identifies a novel regulator of bace1 mRNA levels. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2006, 33, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Licklider, L.J.; Gygi, S.P.; Reed, R. Comprehensive proteomic analysis of the human spliceosome. Nature 2002, 419, 182–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Ying, K.; Dai, J.; Tang, R.; Wang, W.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Xie, Y.; Mao, Y. Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel peptidylprolyl isomerase (cyclophilin)-like gene (PPIL3) from human fetal brain. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 2001, 92, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folk, P.; Puta, F.; Skruzny, M. Transcriptional coregulator snw/skip: The concealed tie of dissimilar pathways. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2004, 61, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.L.; Zhao, X.M.; Huang, C.Q.; Yu, L.; Xia, Z.X. Structure of recombinant human cyclophilin J, a novel member of the cyclophilin family. Acta Crystallogr. D 2005, 61, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Han, R.; Zhang, W.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Long, Y.; Mi, H. Human CyP33 binds specifically to mRNA and binding stimulates PPIase activity of hCyP33. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 835–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, H.; Kops, O.; Zimmermann, E.; Jaschke, A.; Tropschug, M. A nuclear RNA-binding cyclophilin in human T cells. FEBS Lett. 1996, 398, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Yun, C.H.; Gu, S.Y.; Chang, W.R.; Liang, D.C. 1.88 A crystal structure of the C domain of hCyP33: A novel domain of peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 333, 845–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Song, J.; Milne, T.A.; Wang, G.G.; Li, H.; Allis, C.D.; Patel, D.J. Pro isomerization in MLL1 PHD3-bromo cassette connects H3K4me readout to CyP33 and HDAC-mediated repression. Cell 2010, 141, 1183–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grow, E.J.; Wysocka, J. Flipping MLL1’s switch one proline at a time. Cell 2010, 141, 1108–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Osmers, U.; Raman, G.; Schwantes, R.H.; Diaz, M.O.; Bushweller, J.H. The PHD3 domain of MLL acts as a CyP33-regulated switch between MLL-mediated activation and repression. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 6576–6586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hom, R.A.; Chang, P.Y.; Roy, S.; Musselman, C.A.; Glass, K.C.; Selezneva, A.I.; Gozani, O.; Ismagilov, R.F.; Cleary, M.L.; Kutateladze, T.G.; et al. Molecular mechanism of MLL PHD3 and RNA recognition by the CyP33 RRM domain. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 400, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegele, A.; Kamburov, A.; Grossmann, A.; Sourlis, C.; Wowro, S.; Weimann, M.; Will, C.L.; Pena, V.; Luhrmann, R.; Stelzl, U.; et al. Dynamic protein-protein interaction wiring of the human spliceosome. Mol. Cell 2012, 45, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bannikova, O.; Zywicki, M.; Marquez, Y.; Skrahina, T.; Kalyna, M.; Barta, A. Identification of RNA targets for the nuclear multidomain cyclophilin AtCyp59 and their effect on PPIase activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 1783–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gullerova, M.; Barta, A.; Lorkovic, Z.J. AtCyp59 is a multidomain cyclophilin from arabidopsis thaliana that interacts with sr proteins and the C-terminal domain of the RNA polymerase II. RNA 2006, 12, 631–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, T.L.; Walker, J.R.; Ouyang, H.; MacKenzie, F.; Butler-Cole, C.; Newman, E.M.; Eisenmesser, E.Z.; Dhe-Paganon, S. The crystal structure of human WD40 repeat-containing peptidylprolyl isomerase (PPWD1). FEBS J. 2008, 275, 2283–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teigelkamp, S.; Achsel, T.; Mundt, C.; Gothel, S.F.; Cronshagen, U.; Lane, W.S.; Marahiel, M.; Luhrmann, R. The 20 KD protein of human [U4/U6.U5] tri-snRNPs is a novel cyclophilin that forms a complex with the U4/U6-specific 60 KD and 90 KD proteins. RNA 1998, 4, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ingelfinger, D.; Gothel, S.F.; Marahiel, M.A.; Reidt, U.; Ficner, R.; Luhrmann, R.; Achsel, T. Two protein-protein interaction sites on the spliceosome-associated human cyclophilin CypH. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 4791–4796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horowitz, D.S.; Lee, E.J.; Mabon, S.A.; Misteli, T. A cyclophilin functions in pre-mRNA splicing. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reidt, U.; Wahl, M.C.; Fasshauer, D.; Horowitz, D.S.; Luhrmann, R.; Ficner, R. Crystal structure of a complex between human spliceosomal cyclophilin H and a U4/U6 snRNP-60 K peptide. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 331, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reidt, U.; Reuter, K.; Achsel, T.; Ingelfinger, D.; Luhrmann, R.; Ficner, R. Crystal structure of the human U4/U6 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle-specific snucyp-20, a nuclear cyclophilin. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 7439–7442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nestel, F.P.; Colwill, K.; Harper, S.; Pawson, T.; Anderson, S.K. RS cyclophilins: Identification of an NK-TR1-related cyclophilin. Gene 1996, 180, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortillaro, M.J.; Berezney, R. Matrin CYP, an SR-rich cyclophilin that associates with the nuclear matrix and splicing factors. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 8183–8192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourquin, J.P.; Stagljar, I.; Meier, P.; Moosmann, P.; Silke, J.; Baechi, T.; Georgiev, O.; Schaffner, W. A serine/arginine-rich nuclear matrix cyclophilin interacts with the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 2055–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bierer, B.E.; Mattila, P.S.; Standaert, R.F.; Herzenberg, L.A.; Burakoff, S.J.; Crabtree, G.; Schreiber, S.L. Two distinct signal transmission pathways in T lymphocytes are inhibited by complexes formed between an immunophilin and either FK506 or rapamycin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 9231–9235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tocci, M.J.; Matkovich, D.A.; Collier, K.A.; Kwok, P.; Dumont, F.; Lin, S.; Degudicibus, S.; Siekierka, J.J.; Chin, J.; Hutchinson, N.I.; et al. The immunosuppressant FK506 selectively inhibits expression of early T cell activation genes. J. Immunol. 1989, 143, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mattila, P.S.; Ullman, K.S.; Fiering, S.; Emmel, E.A.; McCutcheon, M.; Crabtree, G.R.; Herzenberg, L.A. The actions of cyclosporin a and FK506 suggest a novel step in the activation of T lymphocytes. EMBO J. 1990, 9, 4425–4433. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Flanagan, W.M.; Corthesy, B.; Bram, R.J.; Crabtree, G.R. Nuclear association of a T-cell transcription factor blocked by FK-506 and cyclosporin A. Nature 1991, 352, 803–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Farmer, J.D., Jr.; Lane, W.S.; Friedman, J.; Weissman, I.; Schreiber, S.L. Calcineurin is a common target of cyclophilin-cyclosporin A and FKBP-FK506 complexes. Cell 1991, 66, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hay, N.; Sonenberg, N. Upstream and downstream of mtor. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 1926–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bracher, A.; Kozany, C.; Thost, A.K.; Hausch, F. Structural characterization of the PPIase domain of FKBP51, a cochaperone of human Hsp90. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2011, 67, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Li, P.; Liu, Y.; Lou, Z.; Ding, Y.; Shu, C.; Ye, S.; Bartlam, M.; Shen, B.; Rao, Z.; et al. 3D structure of human fk506-binding protein 52: Implications for the assembly of the glucocorticoid receptor/Hsp90/immunophilin heterocomplex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 8348–8353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, N.J.; Chang, H.M.; Borrajo Jde, R.; Gregory, R.I. The co-chaperones FKBP4/5 control Argonaute2 expression and facilitate risc assembly. RNA 2013, 19, 1583–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pare, J.M.; LaPointe, P.; Hobman, T.C. Hsp90 cochaperones p23 and FKBP4 physically interact with hAgo2 and activate RNA interference-mediated silencing in mammalian cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2013, 24, 2303–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiol, J.; Cora, E.; Koglgruber, R.; Chuma, S.; Subramanian, S.; Hosokawa, M.; Reuter, M.; Yang, Z.; Berninger, P.; Palencia, A.; et al. A role for FKBP6 and the chaperone machinery in pirna amplification and transposon silencing. Mol. Cell 2012, 47, 970–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.M.; Yao, Y.L.; Seto, E. The FK506-binding protein 25 functionally associates with histone deacetylases and with transcription factor YY1. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 4814–4825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Jackson, V.; Lei, M. The FK506-binding protein, FPR4, is an acidic histone chaperone. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 4357–4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, C.J.; Santos-Rosa, H.; Kouzarides, T. Proline isomerization of histone H3 regulates lysine methylation and gene expression. Cell 2006, 126, 905–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galat, A.; Thai, R. Rapamycin-binding FKBP25 associates with diverse proteins that form large intracellular entities. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 450, 1255–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gudavicius, G.; Dilworth, D.; Serpa, J.J.; Sessler, N.; Petrotchenko, E.V.; Borchers, C.H.; Nelson, C.J. The prolyl isomerase, FKBP25, interacts with RNA-engaged nucleolin and the pre-60S ribosomal subunit. RNA 2014, 20, 1014–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litchfield, D.W.; Shilton, B.H.; Brandl, C.J.; Gyenis, L. Pin1: Intimate involvement with the regulatory protein kinase networks in the global phosphorylation landscape. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.P.; Hanes, S.D.; Hunter, T. A human peptidyl-prolyl isomerase essential for regulation of mitosis. Nature 1996, 380, 544–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liou, Y.C.; Zhou, X.Z.; Lu, K.P. Prolyl isomerase Pin1 as a molecular switch to determine the fate of phosphoproteins. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2011, 36, 501–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrell, A.S.; Pelz, C.; Wang, X.; Daniel, C.J.; Wang, Z.; Su, Y.; Janghorban, M.; Zhang, X.; Morgan, C.; Impey, S.; et al. Pin1 regulates the dynamics of c-Myc DNA binding to facilitate target gene regulation and oncogenesis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2013, 33, 2930–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wulf, G.M.; Ryo, A.; Wulf, G.G.; Lee, S.W.; Niu, T.; Petkova, V.; Lu, K.P. Pin1 is overexpressed in breast cancer and cooperates with ras signaling in increasing the transcriptional activity of c-Jun towards cyclin D1. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 3459–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; You, H.; Zhou, X.Z.; Murray, S.A.; Uchida, T.; Wulf, G.; Gu, L.; Tang, X.; Lu, K.P.; Xiao, Z.X.; et al. The prolyl isomerase Pin1 is a regulator of p53 in genotoxic response. Nature 2002, 419, 849–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girardini, J.E.; Napoli, M.; Piazza, S.; Rustighi, A.; Marotta, C.; Radaelli, E.; Capaci, V.; Jordan, L.; Quinlan, P.; Thompson, A.; et al. A Pin1/mutant p53 axis promotes aggressiveness in breast cancer. Cancer Cell 2011, 20, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, K.; Kosugi, I.; Lee, D.Y.; Hafner, A.; Sinclair, D.A.; Ryo, A.; Lu, K.P. Prolyl isomerase Pin1 regulates neuronal differentiation via beta-catenin. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2012, 32, 2966–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dougherty, M.K.; Muller, J.; Ritt, D.A.; Zhou, M.; Zhou, X.Z.; Copeland, T.D.; Conrads, T.P.; Veenstra, T.D.; Lu, K.P.; Morrison, D.K.; et al. Regulation of Raf-1 by direct feedback phosphorylation. Mol. Cell 2005, 17, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, E.S.; Lew, B.O.; Means, A.R. The loss of Pin1 deregulates cyclin E and sensitizes mouse embryo fibroblasts to genomic instability. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.Z.; Liu, B.G.; Zhang, Y. Pin1-based diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for breast cancer. Pharmacol. Res. 2015, 93, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rustighi, A.; Zannini, A.; Tiberi, L.; Sommaggio, R.; Piazza, S.; Sorrentino, G.; Nuzzo, S.; Tuscano, A.; Eterno, V.; Benvenuti, F.; et al. Prolyl-isomerase Pin1 controls normal and cancer stem cells of the breast. EMBO Mol. Med. 2014, 6, 99–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, J.D.; Potter, A. Pin1 inhibitors: Pitfalls, progress and cellular pharmacology. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 4283–4291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.X.; Hirose, Y.; Zhou, X.Z.; Lu, K.P.; Manley, J.L. Pin1 modulates the structure and function of human RNA polymerase II. Genes Dev. 2003, 17, 2765–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.X.; Manley, J.L. Pinning down transcription: Regulation of RNA polymerase II activity during the cell cycle. Cell Cycle 2004, 3, 432–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanes, S.D. Prolyl isomerases in gene transcription. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Ma, Z.; Gemmill, T.; Wu, X.; Defiglio, H.; Rossettini, A.; Rabeler, C.; Beane, O.; Morse, R.H.; Palumbo, M.J.; et al. The Ess1 prolyl isomerase is required for transcription termination of small noncoding RNAs via the Nrd1 pathway. Mol. Cell 2009, 36, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnamurthy, S.; Ghazy, M.A.; Moore, C.; Hampsey, M. Functional interaction of the Ess1 prolyl isomerase with components of the RNA polymerase II initiation and termination machineries. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009, 29, 2925–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanes, S.D. The Ess1 prolyl isomerase: Traffic cop of the RNA polymerase II transcription cycle. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1839, 316–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hani, J.; Stumpf, G.; Domdey, H. Ptf1 encodes an essential protein in saccharomyces cerevisiae, which shows strong homology with a new putative family of PPIases. FEBS Lett. 1995, 365, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hani, J.; Schelbert, B.; Bernhardt, A.; Domdey, H.; Fischer, G.; Wiebauer, K.; Rahfeld, J.U. Mutations in a peptidylprolyl-cis/trans-isomerase gene lead to a defect in 3'-end formation of a pre-mRNA in saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Wilcox, C.B.; Devasahayam, G.; Hackett, R.L.; Arevalo-Rodriguez, M.; Cardenas, M.E.; Heitman, J.; Hanes, S.D. The Ess1 prolyl isomerase is linked to chromatin remodeling complexes and the general transcription machinery. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 3727–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, D.P.; Phatnani, H.P.; Greenleaf, A.L. Phospho-carboxyl-terminal domain binding and the role of a prolyl isomerase in pre-mRNA 3'-end formation. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 31583–31587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.X.; Manley, J.L. Pin1 modulates RNA polymerase II activity during the transcription cycle. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 2950–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meinhart, A.; Kamenski, T.; Hoeppner, S.; Baumli, S.; Cramer, P. A structural perspective of CTD function. Genes Dev. 2005, 19, 1401–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirose, Y.; Manley, J.L. RNA polymerase II and the integration of nuclear events. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 1415–1429. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maniatis, T.; Reed, R. An extensive network of coupling among gene expression machines. Nature 2002, 416, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartkowiak, B.; Liu, P.; Phatnani, H.P.; Fuda, N.J.; Cooper, J.J.; Price, D.H.; Adelman, K.; Lis, J.T.; Greenleaf, A.L. CDK12 is a transcription elongation-associated CTD kinase, the metazoan ortholog of yeast Ctk1. Genes Dev. 2010, 24, 2303–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keogh, M.C.; Podolny, V.; Buratowski, S. Bur1 kinase is required for efficient transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 7005–7018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komarnitsky, P.; Cho, E.J.; Buratowski, S. Different phosphorylated forms of RNA polymerase II and associated mRNA processing factors during transcription. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 2452–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, E.J.; Kobor, M.S.; Kim, M.; Greenblatt, J.; Buratowski, S. Opposing effects of Ctk1 kinase and Fcp1 phosphatase at Ser 2 of the RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 3319–3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnamurthy, S.; He, X.; Reyes-Reyes, M.; Moore, C.; Hampsey, M. Ssu72 is an RNA polymerase II CTD phosphatase. Mol. Cell 2004, 14, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sogaard, T.M.; Svejstrup, J.Q. Hyperphosphorylation of the C-terminal repeat domain of RNA polymerase II facilitates dissociation of its complex with mediator. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 14113–14120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perales, R.; Bentley, D. “Cotranscriptionality”: The transcription elongation complex as a nexus for nuclear transactions. Mol. Cell 2009, 36, 178–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drouin, S.; Laramee, L.; Jacques, P.E.; Forest, A.; Bergeron, M.; Robert, F. DSIF and RNA polymerase II CTD phosphorylation coordinate the recruitment of Rpd3s to actively transcribed genes. PLoS Genet. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govind, C.K.; Qiu, H.; Ginsburg, D.S.; Ruan, C.; Hofmeyer, K.; Hu, C.; Swaminathan, V.; Workman, J.L.; Li, B.; Hinnebusch, A.G.; et al. Phosphorylated Pol II CTD recruits multiple HDACs, including Rpd3C(S), for methylation-dependent deacetylation of ORF nucleosomes. Mol. Cell 2010, 39, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, H.H.; Robert, F.; Young, R.A.; Struhl, K. Targeted recruitment of Set1 histone methylase by elongating Pol II provides a localized mark and memory of recent transcriptional activity. Mol. Cell 2003, 11, 709–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.; Buratowski, S. Dimethylation of H3K4 by Set1 recruits the Set3 histone deacetylase complex to 5' transcribed regions. Cell 2009, 137, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bataille, A.R.; Jeronimo, C.; Jacques, P.E.; Laramee, L.; Fortin, M.E.; Forest, A.; Bergeron, M.; Hanes, S.D.; Robert, F. A universal RNA polymerase II CTD cycle is orchestrated by complex interplays between kinase, phosphatase, and isomerase enzymes along genes. Mol. Cell 2012, 45, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner-Allen, J.W.; Lee, C.J.; Liu, P.; Nicely, N.I.; Wang, S.; Greenleaf, A.L.; Zhou, P. Cis-proline-mediated Ser(p)5 dephosphorylation by the RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain phosphatase Ssu72. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 5717–5726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, X.J.; Chen, X.; Bowman, M.E.; Luo, Y.; Noel, J.P.; Ellington, A.D.; Etzkorn, F.A.; Zhang, Y. Structural and kinetic analysis of prolyl-isomerization/phosphorylation cross-talk in the CTD code. ACS Chem. Biol. 2012, 7, 1462–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranganathan, R.; Lu, K.P.; Hunter, T.; Noel, J.P. Structural and functional analysis of the mitotic rotamase Pin1 suggests substrate recognition is phosphorylation dependent. Cell 1997, 89, 875–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Daum, S.; Wildemann, D.; Zhou, X.Z.; Verdecia, M.A.; Bowman, M.E.; Lucke, C.; Hunter, T.; Lu, K.P.; Fischer, G.; et al. Structural basis for high-affinity peptide inhibition of human Pin1. ACS Chem. Biol. 2007, 2, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, K.A.; Bouchard, J.J.; Peng, J.W. Interdomain interactions support interdomain communication in human Pin1. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 6968–6981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, D.M.; Saxena, K.; Vogtherr, M.; Bernado, P.; Pons, M.; Fiebig, K.M. Peptide binding induces large scale changes in inter-domain mobility in human Pin1. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 26174–26182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daum, S.; Lucke, C.; Wildemann, D.; Schiene-Fischer, C. On the benefit of bivalency in peptide ligand/Pin1 interactions. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 374, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Z.J.; Esnault, S.; Malter, J.S. The peptidyl-prolyl isomerase Pin1 regulates the stability of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor mRNA in activated eosinophils. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 1280–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esnault, S.; Shen, Z.J.; Malter, J.S. Pinning down signaling in the immune system: The role of the peptidyl-prolyl isomerase Pin1 in immune cell function. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 28, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esnault, S.; Shen, Z.J.; Whitesel, E.; Malter, J.S. The peptidyl-prolyl isomerase Pin1 regulates granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor mRNA stability in t lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 6999–7006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nechama, M.; Peng, Y.; Bell, O.; Briata, P.; Gherzi, R.; Schoenberg, D.R.; Naveh-Many, T. KSRP-PMR1-exosome association determines parathyroid hormone mRNA levels and stability in transfected cells. BMC Cell Biol. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nechama, M.; Uchida, T.; mor Yosef-Levi, I.; Silver, J.; Naveh-Many, T. The peptidyl-prolyl isomerase Pin1 determines parathyroid hormone mRNA levels and stability in rat models of secondary hyperparathyroidism. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 3102–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Z.J.; Esnault, S.; Rosenthal, L.A.; Szakaly, R.J.; Sorkness, R.L.; Westmark, P.R.; Sandor, M.; Malter, J.S. Pin1 regulates tgf-beta1 production by activated human and murine eosinophils and contributes to allergic lung fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gherzi, R.; Chen, C.Y.; Trabucchi, M.; Ramos, A.; Briata, P. The role of KSRP in mRNA decay and microrna precursor maturation. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2010, 1, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R. Pin1 regulates parathyroid hormone mRNA stability. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 2887–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, N.; Titus, M.A.; Thapar, R. The prolyl isomerase Pin1 regulates mRNA levels of genes with short half-lives by targeting specific RNA binding proteins. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, N.; Lam, T.T.; Fritz, A.; Rempinski, D.; O’Loughlin, K.; Minderman, H.; Berezney, R.; Marzluff, W.F.; Thapar, R. The prolyl isomerase Pin1 targets stem-loop binding protein (SLBP) to dissociate the SLBP-histone mRNA complex linking histone mRNA decay with SLBP ubiquitination. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2012, 32, 4306–4322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borchers, C.H.; Thapar, R.; Petrotchenko, E.V.; Torres, M.P.; Speir, J.P.; Easterling, M.; Dominski, Z.; Marzluff, W.F. Combined top-down and bottom-up proteomics identifies a phosphorylation site in stem-loop-binding proteins that contributes to high-affinity RNA binding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 3094–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Lam, T.T.; Tonelli, M.; Marzluff, W.F.; Thapar, R. Interaction of the histone mRNA hairpin with stem-loop binding protein (SLBP) and regulation of the SLBP-RNA complex by phosphorylation and proline isomerization. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 3215–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, T.; Takamiya, M.; Takahashi, M.; Miyashita, H.; Ikeda, H.; Terada, T.; Matsuo, Y.; Shirouzu, M.; Yokoyama, S.; Fujimori, F.; et al. Pin1 and Par14 peptidyl prolyl isomerase inhibitors block cell proliferation. Chem. Biol. 2003, 10, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reimer, T.; Weiwad, M.; Schierhorn, A.; Ruecknagel, P.K.; Rahfeld, J.U.; Bayer, P.; Fischer, G. Phosphorylation of the N-terminal domain regulates subcellular localization and DNA binding properties of the peptidyl-prolyl cis/trans isomerase hPar14. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 330, 955–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekerina, E.; Rahfeld, J.U.; Muller, J.; Fanghanel, J.; Rascher, C.; Fischer, G.; Bayer, P. NMR solution structure of hPar14 reveals similarity to the peptidyl prolyl cis/trans isomerase domain of the mitotic regulator hPin1 but indicates a different functionality of the protein. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 301, 1003–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terada, T.; Shirouzu, M.; Fukumori, Y.; Fujimori, F.; Ito, Y.; Kigawa, T.; Yokoyama, S.; Uchida, T. Solution structure of the human parvulin-like peptidyl prolyl cis/trans isomerase, hPar14. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 305, 917–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, J.W.; Link, N.M.; Matena, A.; Hoppstock, L.; Ruppel, A.; Bayer, P.; Blankenfeldt, W. Crystallographic proof for an extended hydrogen-bonding network in small prolyl isomerases. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 20096–20099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heikkinen, O.; Seppala, R.; Tossavainen, H.; Heikkinen, S.; Koskela, H.; Permi, P.; Kilpelainen, I. Solution structure of the parvulin-type ppiase domain of staphylococcus aureus prsa—Implications for the catalytic mechanism of parvulins. BMC Struct. Biol. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rulten, S.; Thorpe, J.; Kay, J. Identification of eukaryotic parvulin homologues: A new subfamily of peptidylprolyl cis-trans isomerases. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 259, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorpe, J.R.; Rulten, S.L.; Kay, J.E. Binding of a putative and a known chaperone protein revealed by immunogold labeling transmission electron microscopy: A suggested use of chaperones as probes for the distribution of their target proteins. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1999, 47, 1633–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessler, D.; Papatheodorou, P.; Stratmann, T.; Dian, E.A.; Hartmann-Fatu, C.; Rassow, J.; Bayer, P.; Mueller, J.W. The DNA binding parvulin par17 is targeted to the mitochondrial matrix by a recently evolved prepeptide uniquely present in hominidae. BMC Biol. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surmacz, T.A.; Bayer, E.; Rahfeld, J.U.; Fischer, G.; Bayer, P. The N-terminal basic domain of human parvulin hPar14 is responsible for the entry to the nucleus and high-affinity DNA-binding. J. Mol. Biol. 2002, 321, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiyama-Nakamura, S.; Yoshikawa, H.; Homma, K.; Hayano, T.; Tsujimura-Takahashi, T.; Izumikawa, K.; Ishikawa, H.; Miyazawa, N.; Yanagida, M.; Miura, Y.; et al. Parvulin (Par14), a peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase, is a novel rRNA processing factor that evolved in the metazoan lineage. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2009, 8, 1552–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiyama, S.; Yanagida, M.; Hayano, T.; Miura, Y.; Isobe, T.; Fujimori, F.; Uchida, T.; Takahashi, N. Isolation and proteomic characterization of human parvulin-associating preribosomal ribonucleoprotein complexes. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 23773–23780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, K.P.; Suizu, F.; Zhou, X.Z.; Finn, G.; Lam, P.; Wulf, G. Targeting carcinogenesis: A role for the prolyl isomerase Pin1? Mol. Carcinog. 2006, 45, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driver, J.A.; Zhou, X.Z.; Lu, K.P. Pin1 dysregulation helps to explain the inverse association between cancer and alzheimer’s disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- High, K.P.; Handschumacher, R.E. Immunity, microbial pathogenesis, and immunophilins: Finding the keys, now where are the locks? Infect. Agents Dis. 1992, 1, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, S.; Gallay, P.A. The role of immunophilins in viral infection. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Hunter, T. Prolyl isomerase Pin1 in cancer. Cell Res. 2014, 24, 1033–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wulf, G.; Garg, P.; Liou, Y.C.; Iglehart, D.; Lu, K.P. Modeling breast cancer in vivo and ex vivo reveals an essential role of Pin1 in tumorigenesis. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 3397–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayala, G.; Wang, D.; Wulf, G.; Frolov, A.; Li, R.; Sowadski, J.; Wheeler, T.M.; Lu, K.P.; Bao, L. The prolyl isomerase Pin1 is a novel prognostic marker in human prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 6244–6251. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pastorino, L.; Ma, S.L.; Balastik, M.; Huang, P.; Pandya, D.; Nicholson, L.; Lu, K.P. Alzheimer’s disease-related loss of Pin1 function influences the intracellular localization and the processing of abetapp. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2012, 30, 277–297. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Simon, B.P.; Bennett, D.A.; Schneider, J.A.; Malter, J.S.; Wang, D.S. The significance of Pin1 in the development of alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2007, 11, 13–23. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann, H.; Schiene-Fischer, C. Functional aspects of extracellular cyclophilins. Biol. Chem. 2014, 395, 721–735. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Perrucci, G.L.; Gowran, A.; Zanobini, M.; Capogrossi, M.C.; Pompilio, G.; Nigro, P. Peptidyl-prolyl isomerases: A full cast of critical actors in cardiovascular diseases. Cardiovasc. Res. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erlejman, A.G.; Lagadari, M.; Galigniana, M.D. Hsp90-binding immunophilins as a potential new platform for drug treatment. Future Med. Chem. 2013, 5, 591–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galat, A. Functional diversity and pharmacological profiles of the FKBPs and their complexes with small natural ligands. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 3243–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Hou, X.; Dong, L.; Dagostino, E.; Greasley, S.; Ferre, R.; Marakovits, J.; Johnson, M.C.; Matthews, D.; Mroczkowski, B.; et al. Structure-based design of novel human Pin1 inhibitors (I). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 5613–5616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.; Marakovits, J.; Hou, X.; Guo, C.; Greasley, S.; Dagostino, E.; Ferre, R.; Johnson, M.C.; Kraynov, E.; Thomson, J.; et al. Structure-Based design of novel human Pin1 inhibitors (II). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 2210–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potter, A.; Oldfield, V.; Nunns, C.; Fromont, C.; Ray, S.; Northfield, C.J.; Bryant, C.J.; Scrace, S.F.; Robinson, D.; Matossova, N.; et al. Discovery of cell-active phenyl-imidazole Pin1 inhibitors by structure-guided fragment evolution. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 6483–6488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flisiak, R.; Feinman, S.V.; Jablkowski, M.; Horban, A.; Kryczka, W.; Pawlowska, M.; Heathcote, J.E.; Mazzella, G.; Vandelli, C.; Nicolas-Metral, V.; et al. The cyclophilin inhibitor debio 025 combined with peg IFNα2A significantly reduces viral load in treatment-naive hepatitis C patients. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1460–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, K.; Gwinn, W.M.; Bower, M.A.; Watson, A.; Okwumabua, I.; MacDonald, H.R.; Bukrinsky, M.I.; Constant, S.L. Extracellular cyclophilins contribute to the regulation of inflammatory responses. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damsker, J.M.; Okwumabua, I.; Pushkarsky, T.; Arora, K.; Bukrinsky, M.I.; Constant, S.L. Targeting the chemotactic function of CD147 reduces collagen-induced arthritis. Immunology 2009, 126, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thapar, R. Roles of Prolyl Isomerases in RNA-Mediated Gene Expression. Biomolecules 2015, 5, 974-999. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom5020974
Thapar R. Roles of Prolyl Isomerases in RNA-Mediated Gene Expression. Biomolecules. 2015; 5(2):974-999. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom5020974
Chicago/Turabian StyleThapar, Roopa. 2015. "Roles of Prolyl Isomerases in RNA-Mediated Gene Expression" Biomolecules 5, no. 2: 974-999. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom5020974
APA StyleThapar, R. (2015). Roles of Prolyl Isomerases in RNA-Mediated Gene Expression. Biomolecules, 5(2), 974-999. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom5020974





