Treatment with the Hyaluronic Acid Synthesis Inhibitor 4-Methylumbelliferone Suppresses SEB-Induced Lung Inflammation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
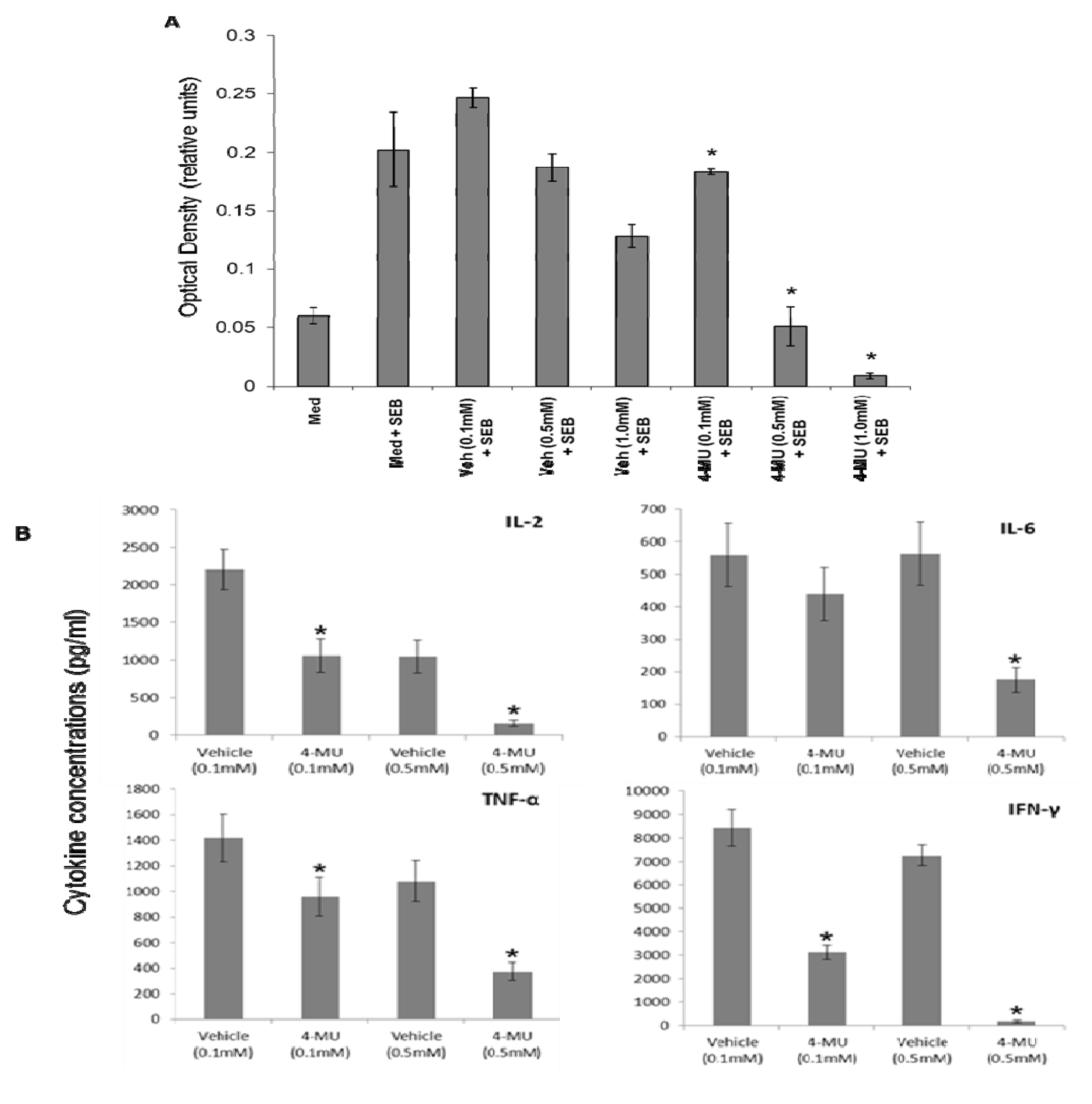
2.1. 4-MU Inhibits SEB-Induced Leukocyte Proliferation and Cytokine Production in Vitro
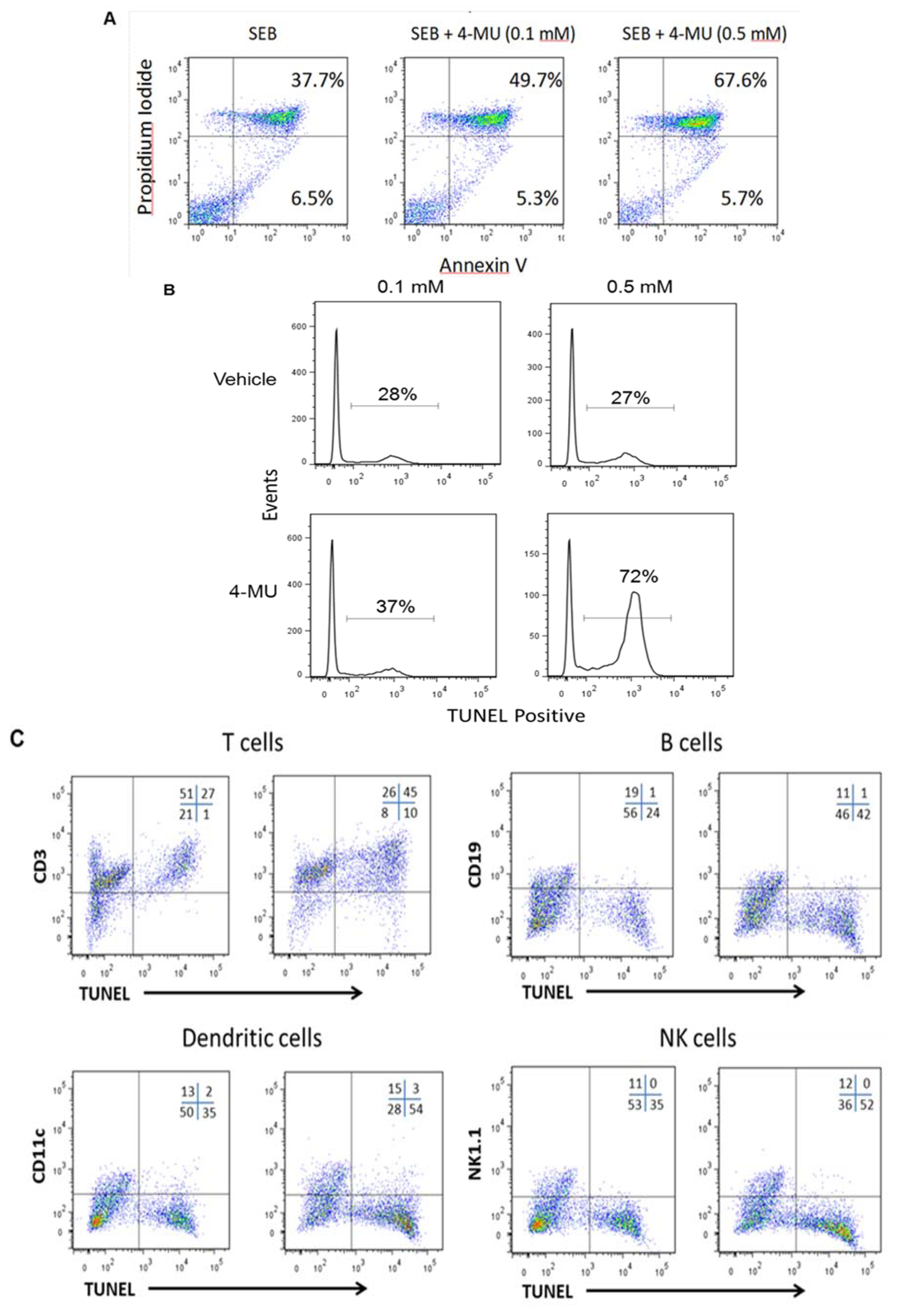
2.2. 4-MU Treatment Leads to Increased Apoptosis in SEB-Exposed T lymphocytes in Vitro
2.3. 4-MU Treatment Suppresses SEB-Induced Hyaluronic Acid Synthase Expression and Accumulation of Soluble HA in the Lungs

2.4. 4-MU Treatment Protects Mice from SEB-Induced Acute Lung Injury
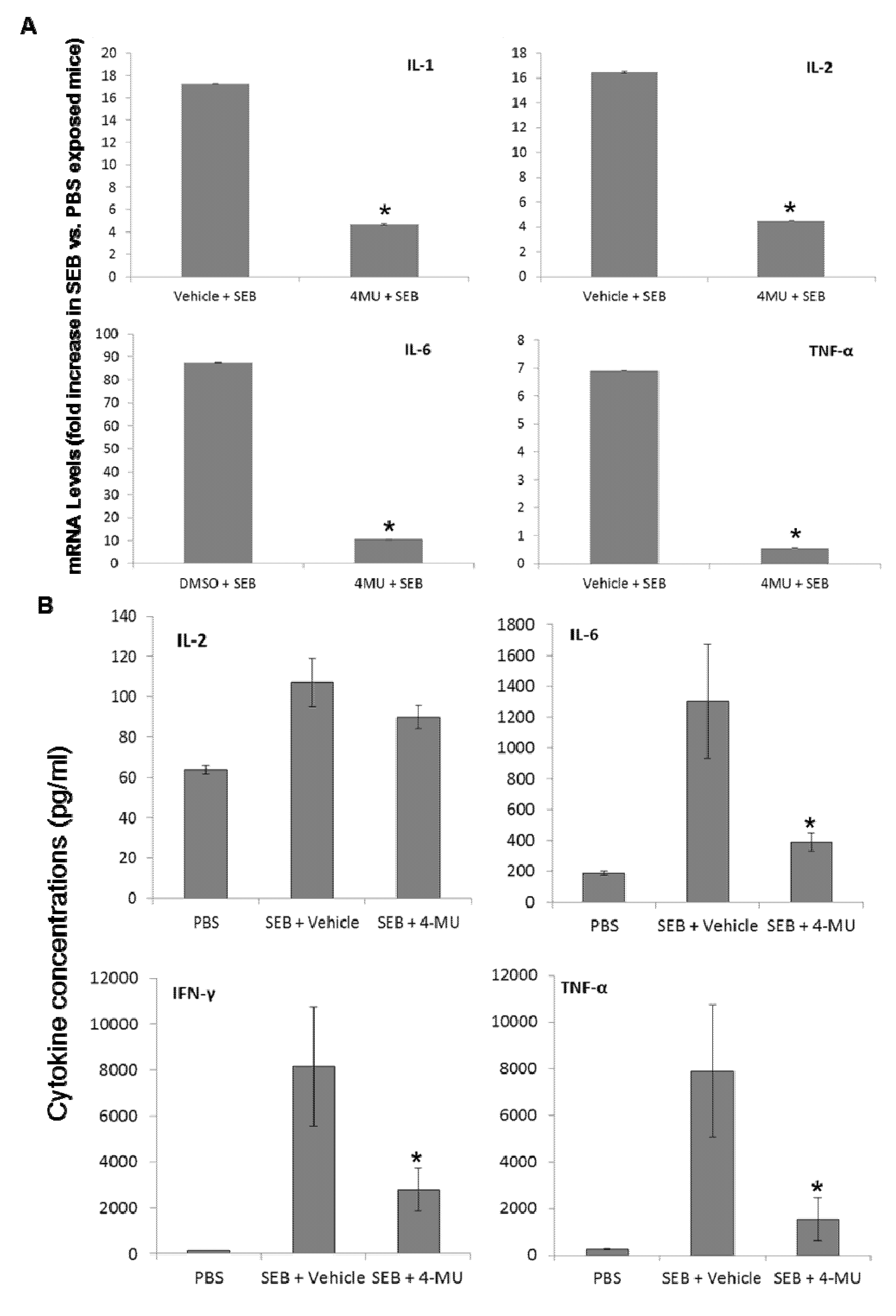
2.5. 4-MU Treatment Suppresses SEB-Induced Inflammatory Cytokine Production in the Lungs
3. Experimental Section
3.1. In Vitro Proliferation Assay
3.2. Bead Array Analysis of Cytokine Levels
3.3. Quantification of Apoptosis
3.4. Hyaluronic Acid Quantification
3.5. RNA Isolation and Real-Time RT-PCR Analysis
3.6. Quantification of Vascular Permeability
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marrack, P.; Kappler, J. The staphylococcal enterotoxins and their relatives. Science 1990, 248, 705–711. [Google Scholar]
- McKallip, R.J.; Do, Y.; Fisher, M.T.; Robertson, J.L.; Nagarkatti, P.S.; Nagarkatti, M. Role of CD44 in activation-induced cell death: CD44-deficient mice exhibit enhanced T cell response to conventional and superantigens. Int. Immunol. 2002, 14, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopalan, G.; Sen, M.M.; Singh, M.; Murali, N.S.; Nath, K.A.; Iijima, K.; Kita, H.; Leontovich, A.A.; Gopinathan, U.; Patel, R.; et al. Intranasal exposure to staphylococcal enterotoxin B elicits an acute systemic inflammatory response. Shock 2006, 25, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayworth, J.L.; Mazzuca, D.M.; Maleki Vareki, S.; Welch, I.; McCormick, J.K.; Haeryfar, S.M. CD1d-independent activation of mouse and human iNKT cells by bacterial superantigens. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2012, 90, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schramm, R.; Thorlacius, H. Staphylococcal enterotoxin B-induced acute inflammation is inhibited by dexamethasone: important role of CXC chemokines KC and macrophage inflammatory protein 2. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 2542–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strandberg, K.L.; Rotschafer, J.H.; Vetter, S.M.; Buonpane, R.A.; Kranz, D.M.; Schlievert, P.M. Staphylococcal superantigens cause lethal pulmonary disease in rabbits. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202, 1690–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKallip, R.J.; Fisher, M.; Do, Y.; Szakal, A.K.; Gunthert, U.; Nagarkatti, P.S.; Nagarkatti, M. Targeted deletion of CD44v7 exon leads to decreased endothelial cell injury but not tumor cell killing mediated by interleukin-2-activated cytolytic lymphocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 43818–43830. [Google Scholar]
- Hayworth, J.L.; Kasper, K.J.; Leon-Ponte, M.; Herfst, C.A.; Yue, D.; Brintnell, W.C.; Mazzuca, D.M.; Heinrichs, D.E.; Cairns, E.; Madrenas, J.; et al. Attenuation of massive cytokine response to the staphylococcal enterotoxin B superantigen by the innate immunomodulatory protein lactoferrin. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2009, 157, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, A.; Liang, L.; Li, F.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, X. Consequences of acute ozone exposure imposed on the culminated allergic pulmonary inflammation in an established murine model of asthma. Front. Biosci. 2013, 18, 838–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Jiang, D.; Jung, Y.; Xie, T.; Ingram, J.; Church, T.; Degan, S.; Leonard, M.; Kraft, M.; Noble, P.W. Role of hyaluronan and hyaluronan-binding proteins in human asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 128, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.S.; Lee, H.J.; Choi, S.H.; Chang, E.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, E.J. Quercetin inhibits IL-1beta-induced inflammation, hyaluronan production and adipogenesis in orbital fibroblasts from Graves’ orbitopathy. PLoS One 2011, 6, e26261. [Google Scholar]
- Stern, R.; Asari, A.A.; Sugahara, K.N. Hyaluronan fragments: An information-rich system. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 85, 699–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchakina, O.N.; Castillejo, C.M.; Bridges, C.C.; McKallip, R.J. The role of hyaluronic acid in SEB-induced acute lung inflammation. Clin. Immunol. 2013, 146, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccioni, F.; Malvicini, M.; Garcia, M.G.; Rodriguez, A.; Atorrasagasti, C.; Kippes, N.; Piedra Buena, I.T.; Rizzo, M.M.; Bayo, J.; Aquino, J.; et al. Antitumor effects of hyaluronic acid inhibitor 4-methylumbelliferone in an orthotopic hepatocellular carcinoma model in mice. Glycobiology 2012, 22, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urakawa, H.; Nishida, Y.; Wasa, J.; Arai, E.; Zhuo, L.; Kimata, K.; Kozawa, E.; Futamura, N.; Ishiguro, N. Inhibition of hyaluronan synthesis in breast cancer cells by 4-methylumbelliferone suppresses tumorigenicity in vitro and metastatic lesions of bone in vivo. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 130, 454–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchakina, O.N.; Ban, H.; McKallip, R.J. Targeting hyaluronic acid production for the treatment of leukemia: Treatment with 4-methylumbelliferone leads to induction of MAPK-mediated apoptosis in K562 leukemia. Leuk. Res. 2013, 37, 1294–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baaten, B.J.; Li, C.R.; Deiro, M.F.; Lin, M.M.; Linton, P.J.; Bradley, L.M. CD44 regulates survival and memory development in Th1 cells. Immunity 2010, 32, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorchenko, O.; Stiefelhagen, M.; Peer-Zada, A.A.; Barthel, R.; Mayer, P.; Eckei, L.; Breuer, A.; Crispatzu, G.; Rosen, N.; Landwehr, T.; et al. CD44 regulates the apoptotic response and promotes disease development in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2013, 121, 4126–4136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kultti, A.; Pasonen-Seppanen, S.; Jauhiainen, M.; Rilla, K.J.; Karna, R.; Pyoria, E.; Tammi, R.H.; Tammi, M.I. 4-Methylumbelliferone inhibits hyaluronan synthesis by depletion of cellular UDP-glucuronic acid and downregulation of hyaluronan synthase 2 and 3. Exp. Cell Res. 2009, 315, 1914–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakizaki, I.; Kojima, K.; Takagaki, K.; Endo, M.; Kannagi, R.; Ito, M.; Maruo, Y.; Sato, H.; Yasuda, T.; Mita, S.; et al. A novel mechanism for the inhibition of hyaluronan biosynthesis by 4-methylumbelliferone. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 33281–33289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigetti, D.; Rizzi, M.; Viola, M.; Karousou, E.; Genasetti, A.; Clerici, M.; Bartolini, B.; Hascall, V.C.; De Luca, G.; Passi, A. The effects of 4-methylumbelliferone on hyaluronan synthesis, MMP2 activity, proliferation, and motility of human aortic smooth muscle cells. Glycobiology 2009, 19, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itano, N.; Sawai, T.; Yoshida, M.; Lenas, P.; Yamada, Y.; Imagawa, M.; Shinomura, T.; Hamaguchi, M.; Yoshida, Y.; Ohnuki, Y.; et al. Three isoforms of mammalian hyaluronan synthases have distinct enzymatic properties. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 25085–25092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Law, G.P.; Bridges, C.C.; McKallip, R.J. CD44 as a novel target for treatment of staphylococcal enterotoxin B-induced acute inflammatory lung injury. Clin. Immunol. 2012, 144, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udaka, K.; Takeuchi, Y.; Movat, H.Z. Simple method for quantitation of enhanced vascular permeability. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1970, 133, 1384–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
McKallip, R.J.; Hagele, H.F.; Uchakina, O.N. Treatment with the Hyaluronic Acid Synthesis Inhibitor 4-Methylumbelliferone Suppresses SEB-Induced Lung Inflammation. Toxins 2013, 5, 1814-1826. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins5101814
McKallip RJ, Hagele HF, Uchakina ON. Treatment with the Hyaluronic Acid Synthesis Inhibitor 4-Methylumbelliferone Suppresses SEB-Induced Lung Inflammation. Toxins. 2013; 5(10):1814-1826. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins5101814
Chicago/Turabian StyleMcKallip, Robert J., Harriet F. Hagele, and Olga N. Uchakina. 2013. "Treatment with the Hyaluronic Acid Synthesis Inhibitor 4-Methylumbelliferone Suppresses SEB-Induced Lung Inflammation" Toxins 5, no. 10: 1814-1826. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins5101814



