Bioactive Glass Nanoparticles: From Synthesis to Materials Design for Biomedical Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Synthesis of Bioactive Glass Nanoparticles
2.1. From Melt-Derived Glass to Sol-Gel Chemistry
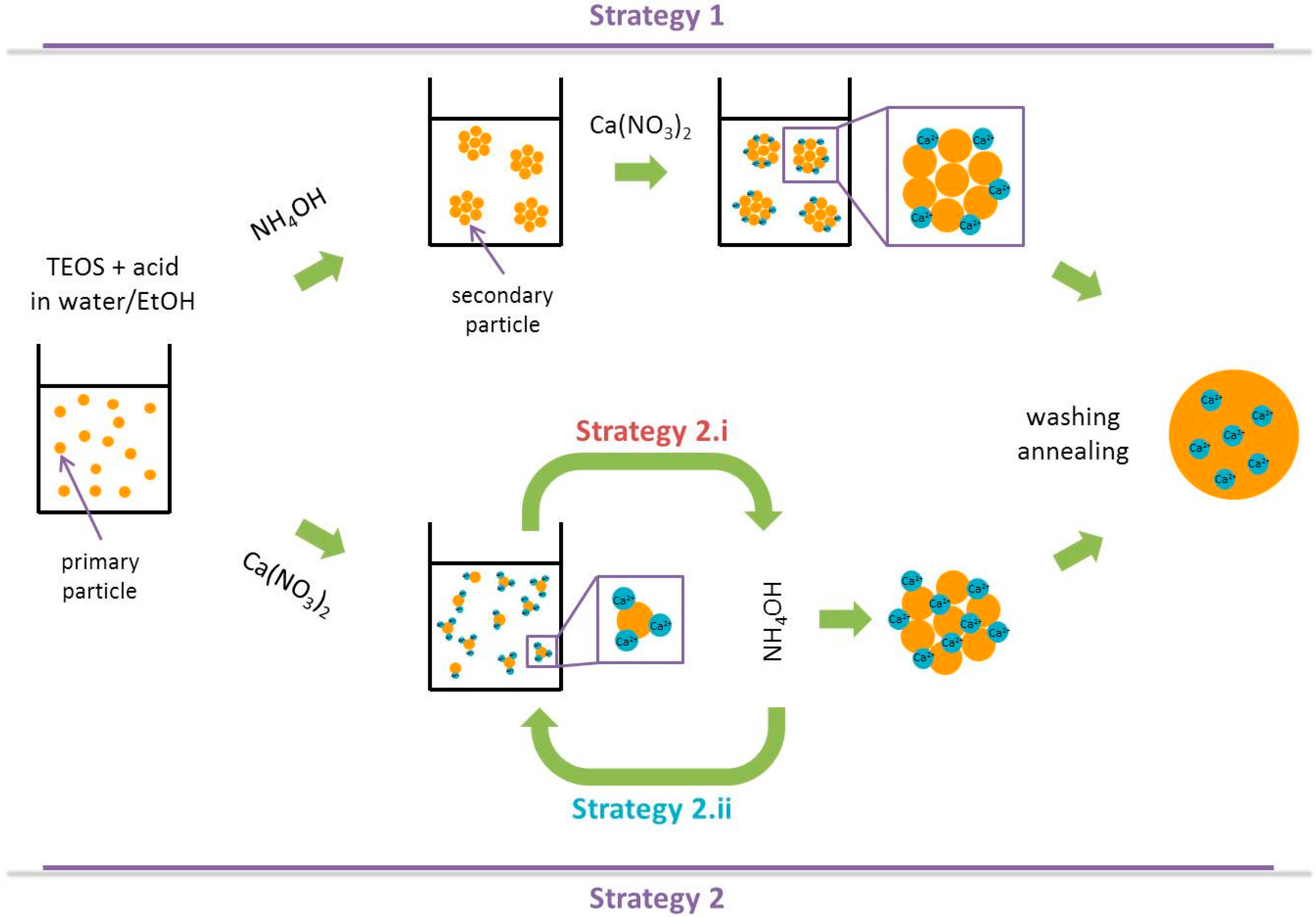
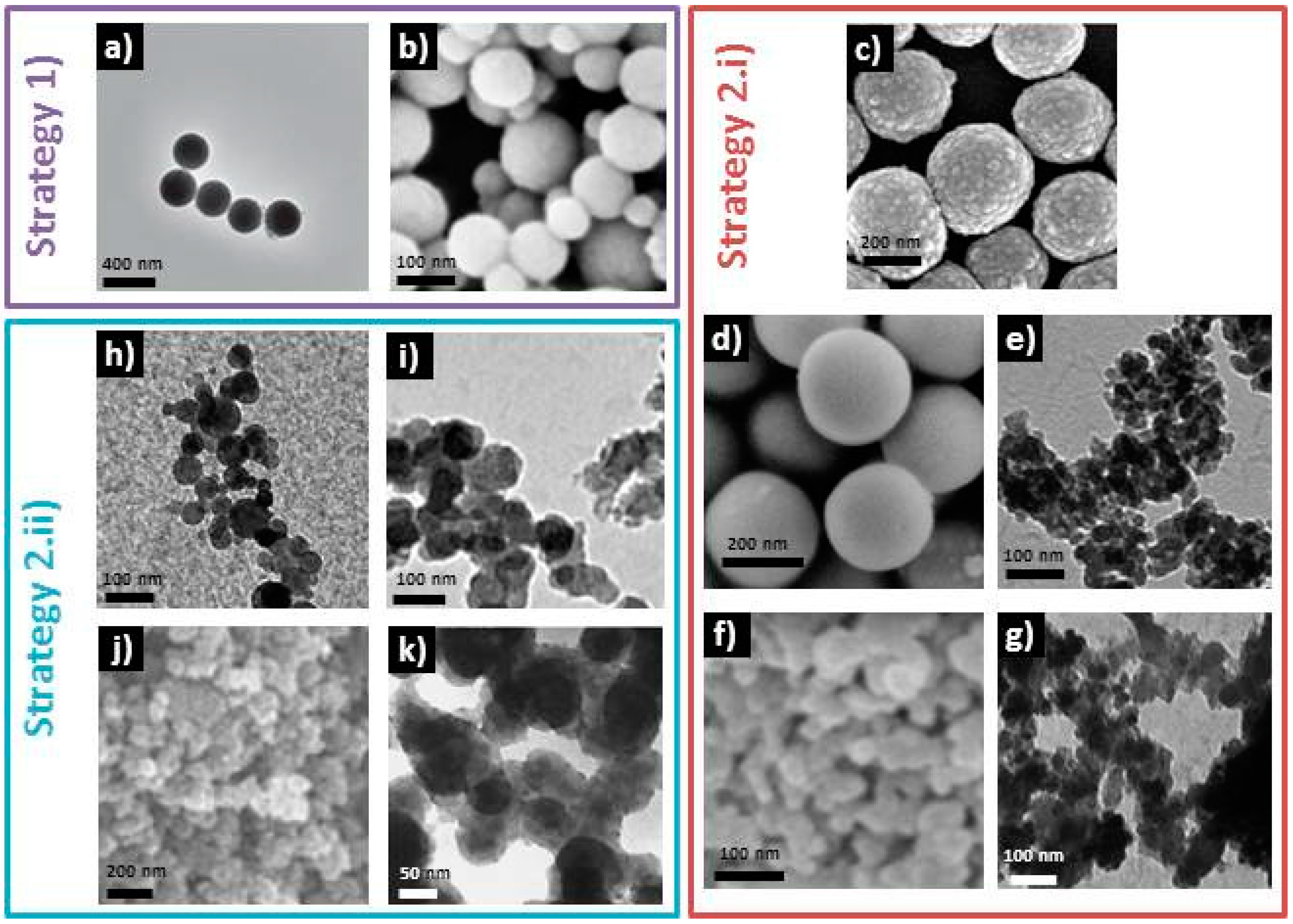
2.2. Looking into the Core of Sol-Gel Strategies
- The second one introduces calcium (and phosphate) ions along with the silica precursor prior to increase the pH in order to form the particles. In the latter strategy:
- (i)
- (ii)
2.3. Of the Use of Additives and Surfactants
3. Materials Design for Biomedical Applications
3.1. Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery and Ionic Therapy
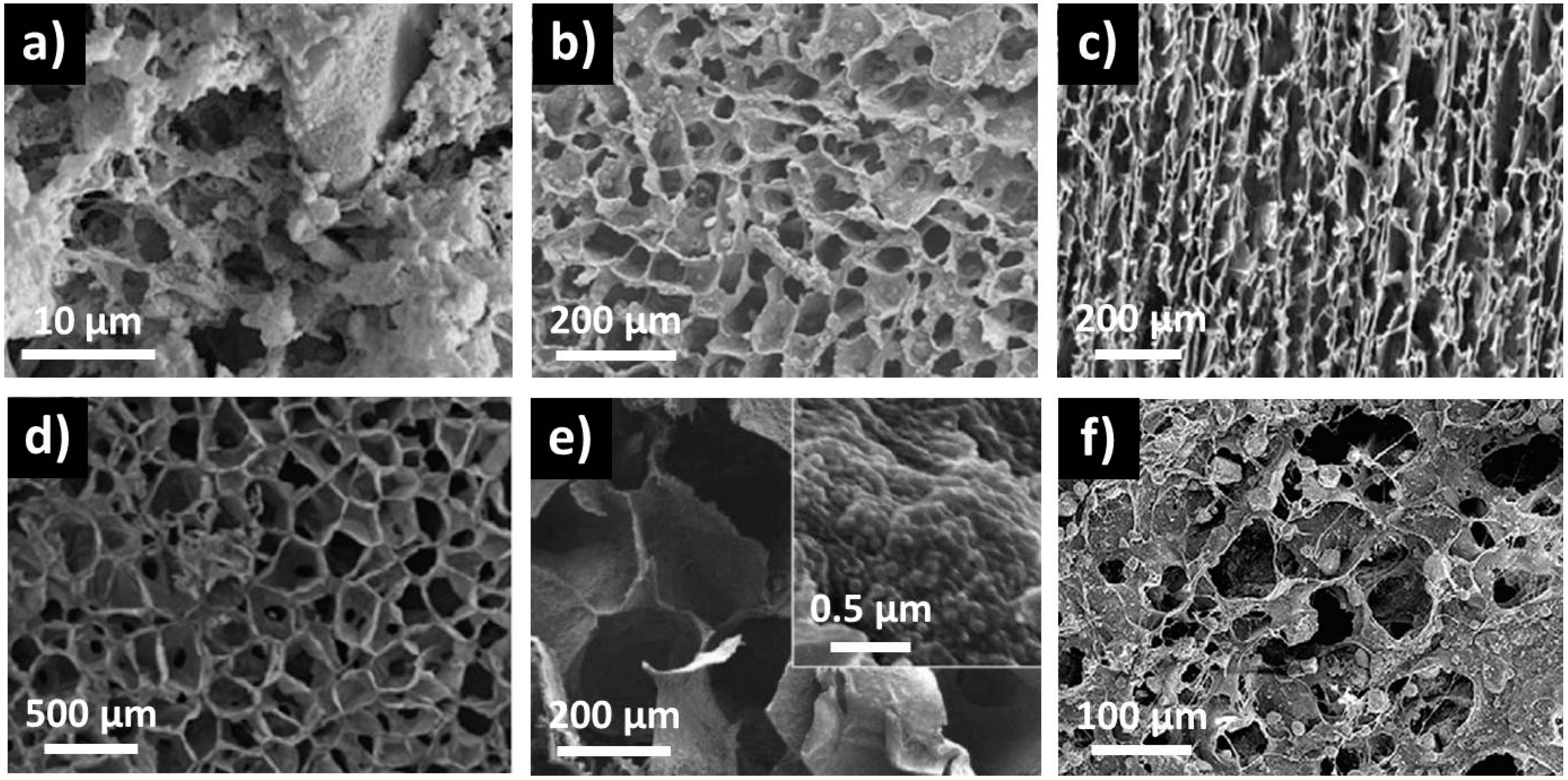
3.2. Polymer-Nanoparticles Composite Scaffolds
3.3. Implants Coating
3.4. Dispersed Nanoparticles for Dentistry and Wound Healing
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jones, J.R. Review of bioactive glass: From Hench to hybrids. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 4457–4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, P.; Serra, J.; Liste, S.; Chiussi, S.; León, B.; Pérez-Amor, M. Raman spectroscopic study of bioactive silica based glasses. J. Non Cryst. Solids 2003, 320, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hench, L.L. Bioceramics: From concept to clinic. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1991, 74, 1487–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawidjaja, P.N.; Lo, A.Y.H.; Izquierdo-Barba, I.; García, A.; Arcos, D.; Stevensson, B.; Grins, J.; Vallet-Regí, M.; Edén, M. Biomimetic apatite mineralization mechanisms of mesoporous bioactive glasses as probed by multinuclear 31P, 29Si, 23Na and 13C solid-state NMR. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 19345–19356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Gong, W.; Dong, Y.; Hu, Q.; Chen, X.; Gao, X. The effect of submicron bioactive glass particles on in vitro osteogenesis. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 38830–38836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, S.K.; Mohn, D.; Brunner, T.J.; Stark, W.J.; Philip, S.E.; Roy, I.; Salih, V.; Knowles, J.C.; Boccaccini, A.R. Comparison of nanoscale and microscale bioactive glass on the properties of P(3HB)/Bioglass® composites. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 1750–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hench, L.L. The story of Bioglass®. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2006, 17, 967–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunner, T.J.; Grass, R.N.; Stark, W.J. Glass and bioglass nanopowders by flame synthesis. Chem. Commun. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stöber, W.; Fink, A.; Bohn, E. Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micron size range. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1968, 26, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Ionescu, C.; Pike, K.J.; Smith, M.E.; Jones, J.R. Nanostructure evolution and calcium distribution in sol-gel derived bioactive glass. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 1276–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepulveda, P.; Jones, J.R.; Hench, L.L. Characterization of melt-derived 45S5 and sol-gel-derived 58S bioactive glasses. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2001, 58, 734–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hench, L.L.; West, J.K. The sol-gel process. Chem. Rev. 1990, 90, 33–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Guo, C.; Zhao, N. Preparation and characterization of the sol-gel nano-bioactive glasses modified by the coupling agent gamma-aminopropyltriethoxysilane. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 255, 466–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsigkou, O.; Labbaf, S.; Stevens, M.M.; Porter, A.E.; Jones, J.R. Monodispersed bioactive glass submicron particles and their effect on bone marrow and adipose tissue-derived stem cells. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2014, 3, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukowiak, A.; Lao, J.; Lacroix, J.; Nedelec, J.-M. Bioactive glass nanoparticles obtained through sol-gel chemistry. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 6620–6622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Z.; Luz, G.M.; Hampel, P.J.; Jin, M.; Liu, A.; Chen, X.; Mano, J.F. Mono-dispersed bioactive glass nanospheres: Preparation and effects on biomechanics of mammalian cells. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2010, 95A, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajita, J.; Saravanan, S.; Selvamurugan, N. Effect of size of bioactive glass nanoparticles on mesenchymal stem cell proliferation for dental and orthopedic applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 53, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.P.; Kalia, P.; Di Silvio, L.; Huang, J. In vitro response of human osteoblasts to multi-step sol-gel derived bioactive glass nanoparticles for bone tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 36, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luz, G.M.; Mano, J.F. Nanoengineering of bioactive glasses: Hollow and dense nanospheres. J. Nanopart. Res. 2013, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kady, A.M.; Ali, A.F.; Farag, M.M. Development, characterization, and in vitro bioactivity studies of sol-gel bioactive glass/poly(l-lactide) nanocomposite scaffolds. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2010, 30, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kady, A.M.; Ali, A.F.; Rizk, R.A.; Ahmed, M.M. Synthesis, characterization and microbiological response of silver doped bioactive glass nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 2012, 38, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delben, J.R.J.; Pimentel, O.M.; Coelho, M.B.; Candelorio, P.D.; Furini, L.N.; dos Santos, F.A.; de Vicente, F.S.; Delben, A.A.S.T. Synthesis and thermal properties of nanoparticles of bioactive glasses containing silver. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2009, 97, 433–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Chang, J. Preparation and characterization of nano-bioactive-glasses (NBG) by a quick alkali-mediated sol-gel method. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 3251–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, H.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.; Song, I. Synthesis of high surface area mesoporous bioactive glass nanospheres. Mater. Lett. 2010, 64, 1850–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Turdean-Ionescu, C.A.; Martin, R.A.; Newport, R.J.; Hanna, J.V.; Smith, M.E.; Jones, J.R. Effect of calcium source on structure and properties of sol-gel derived bioactive glasses. Langmuir 2012, 28, 17465–17476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.-S.; Li, A.-L.; Xu, F.-J.; Qiu, D. A low-temperature sol-gel route for the synthesis of bioactive calcium silicates. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2013, 24, 170–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doostmohammadi, A.; Monshi, A.; Salehi, R.; Fathi, M.H.; Golniya, Z.; Daniels, A.U. Bioactive glass nanoparticles with negative zeta potential. Ceram. Int. 2011, 37, 2311–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labbaf, S.; Tsigkou, O.; Müller, K.H.; Stevens, M.M.; Porter, A.E.; Jones, J.R. Spherical bioactive glass particles and their interaction with human mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 1010–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.; Du, Y.; Yan, J.; Liu, Z.; Ma, P.X.; Chen, X.; Lei, B. Monodisperse photoluminescent and highly biocompatible bioactive glass nanoparticles for controlled drug delivery and cell imaging. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 3831–3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Ning, C.; Yuan, B.; Hu, Q. Facile synthesis of mesoporous bioactive glasses with controlled shapes. Mater. Lett. 2015, 161, 605–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhao, N.; Ning, C.; Chen, X. Facile synthesis of hollow mesoporous bioactive glass sub-micron spheres with a tunable cavity size. Mater. Lett. 2014, 134, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Bastakoti, B.P.; Yamauchi, Y. Smart soft-templating synthesis of hollow mesoporous bioactive glass spheres. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 8038–8042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Q.; Hu, Q.; Miao, G.; Yuan, B.; Chen, X. A facile synthesis of novel mesoporous bioactive glass nanoparticles with various morphologies and tunable mesostructure by sacrificial liquid template method. Mater. Lett. 2015, 148, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Yu, C.; Zhou, X.; Tang, J.; Zhao, D. Highly ordered mesoporous bioactive glasses with superior in vitro bone-forming bioactivities. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 5980–5984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Chang, J. Mesoporous bioactive glasses: Structure characteristics, drug/growth factor delivery and bone regeneration application. Interface Focus 2012, 2, 292–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcos, D.; López-Noriega, A.; Ruiz-Hernández, E.; Terasaki, O.; Vallet-Regí, M. Ordered mesoporous microspheres for bone grafting and drug delivery. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 1000–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Ke, X.; Xie, Y.; Zhu, H.; Crawford, R.; Xiao, Y. Bioactive mesopore-glass microspheres with controllable protein-delivery properties by biomimetic surface modification. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2010, 95A, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, L.; Yan, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, L.; Wang, H.; Tang, J.; Yu, C. Mesoporous bioactive glasses for controlled drug release. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 109, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Fiqi, A.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, H.-W. Osteoinductive fibrous scaffolds of biopolymer/mesoporous bioactive glass nanocarriers with excellent bioactivity and long-term delivery of osteogenic drug. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 1140–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, T.; Zhang, Y.S.; Pang, B.; Hyun, D.C.; Yang, M.; Xia, Y. Engineered nanoparticles for drug delivery in cancer therapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 12320–12364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcos, D.; Vallet-Regí, M. Bioceramics for drug delivery. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 890–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, D.S.; Hong, Z.; Mano, J.F. Development of bioactive and biodegradable chitosan-based injectable systems containing bioactive glass nanoparticles. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, C.D.F.; Carvalho, S.M.; Mansur, H.S.; Pereira, M.M. Thermogelling chitosan-collagen-bioactive glass nanoparticle hybrids as potential injectable systems for tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 58, 1207–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leite, Á.J.; Caridade, S.G.; Mano, J.F. Synthesis and characterization of bioactive biodegradable chitosan composite spheres with shape memory capability. J. Non Cryst. Solids 2016, 432, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, I.; Newman, H.; Wilson, M. Antibacterial activity of particulate Bioglass® against supra- and subgingival bacteria. Biomaterials 2001, 22, 1683–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppe, A.; Güldal, N.S.; Boccaccini, A.R. A review of the biological response to ionic dissolution products from bioactive glasses and glass-ceramics. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 2757–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, Y.-F.; Alshemary, A.Z.; Akram, M.; Abdul Kadir, M.R.; Hussain, R. In vitro study of nano-sized zinc doped bioactive glass. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2013, 137, 1031–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xynos, I.D.; Edgar, A.J.; Buttery, L.D.K.; Hench, L.L.; Polak, J.M. Gene-expression profiling of human osteoblasts following treatment with the ionic products of Bioglass® 45S5 dissolution. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2001, 55, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effah Kaufmann, E.A.B.; Ducheyne, P.; Shapiro, I.M. Evaluation of osteoblast response to porous bioactive glass (45S5) substrates by RT-PCR analysis. Tissue Eng. 2000, 6, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jell, G.; Notingher, I.; Tsigkou, O.; Notingher, P.; Polak, J.M.; Hench, L.L.; Stevens, M.M. Bioactive glass-induced osteoblast differentiation: A noninvasive spectroscopic study. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2008, 86A, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bielby, R.C.; Christodoulou, I.S.; Pryce, R.S.; Radford, W.J.P.; Hench, L.L.; Polak, J.M. Time- and concentration-dependent effects of dissolution products of 58S sol-gel bioactive glass on proliferation and differentiation of murine and human osteoblasts. Tissue Eng. 2004, 10, 1018–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christodoulou, I.; Buttery, L.D.K.; Tai, G.; Hench, L.L.; Polak, J.M. Characterization of human fetal osteoblasts by microarray analysis following stimulation with 58S bioactive gel-glass ionic dissolution products. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2006, 77B, 431–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, L.; Wang, W.; Jin, D.; Zhou, S.; Song, X. In vitro bioactivity and mechanical properties of bioactive glass nanoparticles/polycaprolactone composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 46, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonor, I.B.; Sousa, R.A.; Cunha, A.M.; Reis, R.L.; Zhong, Z.P.; Greenspan, D. Novel starch thermoplastic/bioglass composites: Mechanical properties, degradation behavior and in vitro bioactivity. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2002, 13, 939–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niemelä, T.; Niiranen, H.; Kellomäki, M.; Törmälä, P. Self-reinforced composites of bioabsorbable polymer and bioactive glass with different bioactive glass contents. Part I: Initial mechanical properties and bioactivity. Acta Biomater. 2005, 1, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, Y.; Hillmyer, M.A.; Francis, L.F. Processing and properties of porous poly(l-lactide)/bioactive glass composites. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 2489–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sowmya, S.; Kumar, P.T.S.; Chennazhi, K.P.; Nair, S.V.; Tamura, H.; Rangasamy, J. Biocompatible β-chitin hydrogel/nanobioactive glass ceramic nanocomposite scaffolds for periodontal bone regeneration. Trends Biomater. Artif. Organs 2011, 25, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Peter, M.; Binulal, N.S.; Nair, S.V.; Selvamurugan, N.; Tamura, H.; Jayakumar, R. Novel biodegradable chitosan-gelatin/nano-bioactive glass ceramic composite scaffolds for alveolar bone tissue engineering. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 158, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Shen, H.; Tian, Y.; Xie, Y.; Li, A.; Ji, L.; Niu, Z.; Wu, D.; Qiu, D. Bioactive nanoparticle-gelatin composite scaffold with mechanical performance comparable to cancellous bones. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 13061–13068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maquet, V.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Pravata, L.; Notingher, I.; Jérôme, R. Porous poly(α-hydroxyacid)/Bioglass® composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. I: Preparation and in vitro characterisation. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 4185–4194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boccaccini, A.R.; Maquet, V. Bioresorbable and bioactive polymer/Bioglass® composites with tailored pore structure for tissue engineering applications. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 2417–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Su, P.; Chen, X.; Meng, Y.; Yu, W.; Xiang, A.P.; Wang, Y. Biocompatibility and osteogenesis of biomimetic bioglass-collagen-phosphatidylserine composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 1051–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Z.; Reis, R.L.; Mano, J.F. Preparation and in vitro characterization of scaffolds of poly(l-lactic acid) containing bioactive glass ceramic nanoparticles. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 1297–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, A.; Hong, Z.; Zhuang, X.; Chen, X.; Cui, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jing, X. Surface modification of bioactive glass nanoparticles and the mechanical and biological properties of poly(l-lactide) composites. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 1005–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palin, E.; Liu, H.; Webster, T.J. Mimicking the nanofeatures of bone increases bone-forming cell adhesion and proliferation. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguez-Pacheco, V.; Hench, L.L.; Boccaccini, A.R. Bioactive glasses beyond bone and teeth: Emerging applications in contact with soft tissues. Acta Biomater. 2015, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Jin, L.; Cook, W.D.; Mohn, D.; Lagerqvist, E.L.; Elliott, D.A.; Haynes, J.M.; Boyd, N.; Stark, W.J.; Pouton, C.W.; et al. Elastomeric nanocomposites as cell delivery vehicles and cardiac support devices. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 4715–4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, R.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Knowles, J.C.; Locke, I.C.; Gordge, M.P.; McCormick, A.; Salih, V.; Mordon, N.; Keshavarz, T.; Roy, I. Fabrication of a novel poly(3-hydroxyoctanoate)/nanoscale bioactive glass composite film with potential as a multifunctional wound dressing. In AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing: Melville, NY, USA, 2010; Volume 1255, pp. 126–128. [Google Scholar]
- Day, R.M.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Shurey, S.; Roether, J.A.; Forbes, A.; Hench, L.L.; Gabe, S.M. Assessment of polyglycolic acid mesh and bioactive glass for soft-tissue engineering scaffolds. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 5857–5866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koudehi, M.F.; Fooladi, A.A.I.; Mansoori, K.; Jamalpoor, Z.; Amiri, A.; Nourani, M.R. Preparation and evaluation of novel nano-bioglass/gelatin conduit for peripheral nerve regeneration. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2013, 25, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verrier, S.; Blaker, J.J.; Maquet, V.; Hench, L.L.; Boccaccini, A.R. PDLLA/Bioglass® composites for soft-tissue and hard-tissue engineering: An in vitro cell biology assessment. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 3013–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pishbin, F.; Simchi, A.; Ryan, M.P.; Boccaccini, A.R. A study of the electrophoretic deposition of Bioglass® suspensions using the Taguchi experimental design approach. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2010, 30, 2963–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlotte Schausten, M.; Meng, D.; Telle, R.; Boccaccini, A.R. Electrophoretic deposition of carbon nanotubes and bioactive glass particles for bioactive composite coatings. Ceram. Int. 2010, 36, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhitomirsky, D.; Roether, J.A.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Zhitomirsky, I. Electrophoretic deposition of bioactive glass/polymer composite coatings with and without HA nanoparticle inclusions for biomedical applications. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2009, 209, 1853–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rego, S.J.; Vale, A.C.; Luz, G.M.; Mano, J.F.; Alves, N.M. Adhesive bioactive coatings inspired by sea life. Langmuir 2016, 32, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roohani-Esfahani, S.I.; Nouri-Khorasani, S.; Lu, Z.F.; Appleyard, R.C.; Zreiqat, H. Effects of bioactive glass nanoparticles on the mechanical and biological behavior of composite coated scaffolds. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 1307–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esfahani, S.I.R.; Tavangarian, F.; Emadi, R. Nanostructured bioactive glass coating on porous hydroxyapatite scaffold for strength enhancement. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 3428–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostomel, T.A.; Shi, Q.; Tsung, C.-K.; Liang, H.; Stucky, G.D. Spherical bioactive glass with enhanced rates of hydroxyapatite deposition and hemostatic activity. Small 2006, 2, 1261–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillette, R.L.; Swaim, S.F.; Sartin, E.A.; Bradley, D.M.; Coolman, S.L. Effects of a bioactive glass on healing of closed skin wounds in dogs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2001, 62, 1149–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, G.; Xiao, L.; Tong, P.; Bi, D.; Wang, H.; Ma, H.; Zhu, G.; Liu, H. Antibacterial hemostatic dressings with nanoporous bioglass containing silver. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 2613–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Mao, C.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, X. Healing effect of bioactive glass ointment on full-thickness skin wounds. Biomed. Mater. 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoor, P.; Söderling, E.; Salonen, J.I. Antibacterial effects of a bioactive glass paste on oral microorganisms. Acta Odontol. Scand. 1998, 56, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waltimo, T.; Brunner, T.J.; Vollenweider, M.; Stark, W.J.; Zehnder, M. Antimicrobial effect of nanometric bioactive glass 45S5. J. Dent. Res. 2007, 86, 754–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vollenweider, M.; Brunner, T.J.; Knecht, S.; Grass, R.N.; Zehnder, M.; Imfeld, T.; Stark, W.J. Remineralization of human dentin using ultrafine bioactive glass particles. Acta Biomater. 2007, 3, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtis, A.R.; West, N.X.; Su, B. Synthesis of nanobioglass and formation of apatite rods to occlude exposed dentine tubules and eliminate hypersensitivity. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 3740–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Strategy | Reference | Acid | PO43− Precursor | Water:EtOH Vol. Ratio | Si:Ca(:P) | [Tetraethyl Orthosilicate (TEOS)] (mol/L) | Drying | Annealing |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | [14] | / | / | 0.11:1 | 0.43:0.57 | 0.045 | Not detailed | 680 °C |
| [15] | HNO3 | / | 0.39:1 | 0.74:0.26 | 0.14 | 80 °C 24 h | 700 °C 2.5 h | |
| 2.i | [16] | citric acid | / | 12.7:1 | 0.70:0.30 | 0.043 | freeze-drying | 700 °C |
| [15] | citric acid | / | 13.2:1 | 0.74:0.26 | 0.043 | 80 °C 24 h | 700 °C 2.5 h | |
| [18] | HNO3 | (NH4)2HPO4 | 26.7:1 | 0.58:0.37:0.05 | 0.031 | 25 °C 24 h | 650 °C 3 h | |
| [19] | citric acid | (NH4)2HPO4 | 27.5:1 | 0.52:0.38:0.10 | 0.026 | Not detailed | 700 °C 3 h | |
| [17] | citric acid | (NH4)2HPO4 | 8.03:1 | 0.39:0.35:0.26 | Not detailed | 60 °C 8 h | 700 °C 6 h | |
| 2.ii | [20,21] | HNO3 | Et3PO4 | 0.33:1 | 0.61:0.36:0.03 | 1 | 80 °C 48 h | 700 °C 3 h |
| [22] | HNO3 | Et3PO4 | 1.2:1 | 0.55:0.38:0.07 | 0.96 | 130 °C 24 h | 600 °C 4 h | |
| [23] | HNO3 | Et3PO4 | 0.33:1 | 0.57:0.35:0.08 | 1.1 | 60 °C 24 h | 600 °C 2 h |
| Reference | Morphology | Size | Composition Si:Ca(:P) | Surfactant | Specific Surface Area (m2/g) | Pore Size (nm) | Pore Arrangement |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [37] | Microsphere | 1 mm | 0.80:0.15:0.05 | P123 9.2 mM | 336 | 5 | Hexagonal |
| [38] | Monoliths | / | 0.95:0.05 | P123 9.2 mM | 338 | 5.5 | Hexagonal |
| 0.84:0.16 | 229 | 5.2 | |||||
| 0.73:0.27 | 147 | 5.2 | |||||
| 0.63:0.37 | 159 | 4.6 | |||||
| [32] | Hollow nanoparticles 250 nm | 250 nm | 0.80:0.15:0.05 | Hexadecyl trimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) 6.9 mM | 949 | 2.6 | Vertical mesochanels in the shell |
| [36] | Polydispersed nanoparticles | Mean size of 400 nm | 0.82:0.09:0.09 | CTAB 28.1 mM | 484 | 1.1 + 3.7 | Defective order |
| P123 1.8 mM | 380 | 3.9 | |||||
| F127 0.8 mM | 275 | 3.5 | Hexagonal | ||||
| [31] | Hollow nanoparticles | 294 nm | 0.77:0.15:0.08 | CTAB 3.3 mM | 444 | 8.8 | Not detailed |
| Hollow nanoparticles | 264 nm | CTAB 4.6 mM | 600 | 5.6 | Not detailed | ||
| Dense nanoparticles | 187 nm | CTAB 5.9 mM | 972 | 4.6 | Not detailed | ||
| [30] | Nanoparticles | 150 nm | 0.77:0.15:0.08 | CTAB 1 mM | 318 | 3.7 | Worm-like |
| Nanorods | 150 × 380 nm | CTAB 3 mM | 388 | 3.7 | Worm-like | ||
| Nanorods | 150 × 550 nm | CTAB 6 mM | 455 | 3.7 | Hexagonal | ||
| [24] | Nanoparticles | 30 nm | 0.79:0.17:0.04 | CTAB 1.7 mM | 1040 | 2.2 | Worm-like |
| [33] | Nanoparticles | 133 nm | 0.58:0.35:0.08 | CTAB 35.6 mM | 684 | 5.1 | Radial mesostructure |
| Nanoparticles | 234 nm | 349 | 7.8 | ||||
| Nanoparticles | 254 nm | 259 | 11.2 | ||||
| Pineal particles | 28 nm | 151 | 9.9 | Lamellar mesostructure | |||
| Pineal particles | 161 nm | 280 | 10.5 | ||||
| Pineal particles | 193 nm | 192 | 14.0 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vichery, C.; Nedelec, J.-M. Bioactive Glass Nanoparticles: From Synthesis to Materials Design for Biomedical Applications. Materials 2016, 9, 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9040288
Vichery C, Nedelec J-M. Bioactive Glass Nanoparticles: From Synthesis to Materials Design for Biomedical Applications. Materials. 2016; 9(4):288. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9040288
Chicago/Turabian StyleVichery, Charlotte, and Jean-Marie Nedelec. 2016. "Bioactive Glass Nanoparticles: From Synthesis to Materials Design for Biomedical Applications" Materials 9, no. 4: 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9040288







