Recent Advances in Bacteria Identification by Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Mass Spectrometry Using Nanomaterials as Affinity Probes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Bacterial Identification Using MALDI-MS
3. Nanoparticles Used as Affinity Probes
3.1. Magnetic Nanoparticles
3.2. Silver (Ag) Nanoparticles
3.3. Cadmium Sulfide (CdS) Quantum Dots (QDs)
3.4. Platinum (Pt) Nanoparticles
3.5. Other Nanomaterials
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ivnitski, D.; Abdel-Hamid, I.; Atanasov, P.; Wilkins, E. Biosensors for detection of pathogenic bacteria. Biosens. Bioelectron 1999, 14, 599–624. [Google Scholar]
- WHO Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality. Available online: http://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/dwq/guidelines/en/ accessed on 7 May 2014.
- Jahid, I.K.; Ha, S.-D. A review of microbial biofilms of produce: Future challenge to food safety. Food Sci. Biotechnol 2012, 21, 299–316. [Google Scholar]
- Velusamy, V.; Arshak, K.; Korostynska, O.; Oliwa, K.; Adley, C. An overview of foodborne pathogen detection: In the perspective of biosensors. Biotechnol. Adv 2010, 28, 232–254. [Google Scholar]
- Tallury, P.; Malhotra, A.; Byrne, L.M.; Santra, S. Nanobioimaging and sensing of infectious diseases. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev 2010, 62, 424–437. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Yoon, M.-Y. Recent advances in rapid and ultrasensitive biosensors for infectious agents: Lesson from Bacillus anthracis diagnostic sensors. Analyst 2010, 135, 1182–1190. [Google Scholar]
- Sekhon, S.S.; Kim, S.-G.; Lee, S.-H.; Jang, A.; Min, J.; Ahn, J.-Y.; Kim, Y.-H. Advances in pathogen-associated molecules detection using aptamer based biosensors. Mol. Cell. Toxicol 2013, 9, 311–317. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, H.; Mutharasan, R. Review of biosensors for foodborne pathogens and toxins. Sens. Actuators B 2013, 183, 535–549. [Google Scholar]
- Quilliam, R.S.; Williams, A.P.; Avery, L.M.; Malham, S.K.; Jones, D.L. Unearthing human pathogens at the agricultural–environment interface: A review of current methods for the detection of Escherichia coli O157 in freshwater ecosystems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ 2011, 140, 354–360. [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch, J.; Siltanen, C.; Zhou, Q.; Revzin, A.; Simonian, A. Biosensor technology: Recent advances in threat agent detection and medicine. Chem. Soc. Rev 2013, 42, 8733–8768. [Google Scholar]
- Bridle, H.; Miller, B.; Desmulliez, M.P.Y. Application of microfluidics in waterborne pathogen monitoring: A review. Water Res 2014, 55, 256–271. [Google Scholar]
- Biswas, S.; Rolain, J.-M. Use of MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry for identification of bacteria that are difficult to culture. J. Microbiol. Methods 2013, 92, 14–24. [Google Scholar]
- Sandrin, T.R.; Goldstein, J.E.; Schumaker, S. MALDI TOF MS profiling of bacteria at the strain level: A review. Mass Spectrom. Rev 2013, 32, 188–217. [Google Scholar]
- Bakry, R.; Rainer, M.; Huck, C.W.; Bonn, G.K. Protein profiling for cancer biomarker discovery using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry and infrared imaging: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 690, 26–34. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, Y.-T.; Su, H.; Huang, T.-L.; Chen, H.-C.; Wu, W.-J.; Wu, P.-C.; Wu, D.-C.; Shiea, J. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization/time-of-flight mass spectrometry for clinical diagnosis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2013, 415, 266–275. [Google Scholar]
- Bergman, N.; Shevchenko, D.; Bergquist, J. Approaches for the analysis of low molecular weight compounds with laser desorption/ionization techniques and mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem 2014, 406, 49–61. [Google Scholar]
- Karas, M.; Hillenkamp, F. Laser desorption ionization of proteins with molecular masses exceeding 10,000 daltons. Anal. Chem 1988, 60, 2299–2301. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, K.; Waki, H.; Ido, Y.; Akita, S.; Yoshida, Y.; Yoshida, T. Protein and polymer analyses up to m/z 100,000 by laser ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom 1988, 2, 151–153. [Google Scholar]
- Dingle, T.C.; Butler-Wu, S.M. MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry for microorganism identification. Clin. Lab. Med 2013, 33, 589–609. [Google Scholar]
- Chalupová, J.; Raus, M.; Sedlářová, M.; Šebela, M. Identification of fungal microorganisms by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Biotechnol. Adv 2014, 32, 230–241. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y.-P.; Reddy, P.M. Advances in mass spectrometry for the identification of pathogens. Mass Spectrom. Rev 2011, 30, 1203–1224. [Google Scholar]
- Wieser, A.; Schneider, L.; Jung, J.; Schubert, S. MALDI-TOF MS in microbiological diagnostics—Identification of microorganisms and beyond (mini review). Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol 2012, 93, 965–974. [Google Scholar]
- Krásný, L.; Hynek, R.; Hochel, I. Identification of bacteria using mass spectrometry techniques. Int. J. Mass Spectrom 2013, 353, 67–79. [Google Scholar]
- Lartigue, M.-F. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry for bacterial strain characterization. Infect. Genet. Evol 2013, 13, 230–235. [Google Scholar]
- Kostrzewa, M.; Sparbier, K.; Maier, T.; Schubert, S.; MALDI-TOF, M.S. An upcoming tool for rapid detection of antibiotic resistance in microorganisms. Proteomics Clin. Appl 2013, 7, 767–778. [Google Scholar]
- Havlicek, V.; Lemr, K.; Schug, K.A. Current trends in microbial diagnostics based on mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem 2013, 85, 790–797. [Google Scholar]
- Del Chierico, F.; Petrucca, A.; Vernocchi, P.; Bracaglia, G.; Fiscarelli, E.; Bernaschi, P.; Muraca, M.; Urbani, A.; Putignani, L. Proteomics boosts translational and clinical microbiology. J. Proteomics 2014, 97, 69–87. [Google Scholar]
- Welker, M.; Moore, E.R.B. Applications of whole-cell matrix-assisted laser-desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry in systematic microbiology. Syst. Appl. Microbiol 2011, 34, 2–11. [Google Scholar]
- Intelicato-Young, J.; Fox, A. Mass spectrometry and tandem mass spectrometry characterization of protein patterns, protein markers and whole proteomes for pathogenic bacteria. J. Microbiol. Methods 2013, 92, 381–386. [Google Scholar]
- Chiu, T.-C.; Huang, L.-S.; Lin, P.-C.; Chen, Y.-C.; Chen, Y.-J.; Lin, C.-C.; Chang, H.-T. Nanomaterials based affinity matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry for biomolecules and pathogenic bacteria. Recent Pat. Nanotechnol 2007, 1, 99–111. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, F.-H.; Gopal, J.; Manikandan, M. Future perspective of nanoparticle interaction-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry for rapid, simple, direct and sensitive detection of microorganisms. J. Mass Spectrom 2012, 47, 355–363. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.-T.; Tomalová, I.; Preisler, J.; Chang, H.-T. Analysis of biomolecules through surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry employing nanomaterials. J. Chin. Chem. Soc 2011, 58, 769–778. [Google Scholar]
- Rainer, M.; Qureshi, M.N.; Bonn, G.K. Matrix-free and material-enhanced laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry for the analysis of low molecular weight compounds. Anal. Bioanal. Chem 2011, 400, 2281–2288. [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, C.-K.; Chen, W.-T.; Chang, H.-T. Nanoparticle-based mass spectrometry for the analysis of biomolecules. Chem. Soc. Rev 2011, 40, 1269–1281. [Google Scholar]
- Law, K.P.; Larkin, J.R. Recent advances in SALDI-MS techniques and their chemical and bioanalytical applications. Anal. Bioanal. Chem 2011, 399, 2597–2622. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, A.Y.; Ma, J.; Boey, Y.C.F. Development of nanomaterials for SALDI-MS analysis in forensics. Adv. Mater 2012, 24, 4211–4216. [Google Scholar]
- Sunner, J.; Dratz, E.; Chen, Y.-C. Graphite surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry of peptides and proteins from liquid solutions. Anal. Chem 1995, 67, 4335–4342. [Google Scholar]
- Han, M.; Sunner, J. An activated carbon substrate surface for laser desorption mass spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom 2000, 11, 644–649. [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, C.-K.; Lin, Y.-W.; Chen, W.-T.; Chang, H.-T. Accurate quantitation of glutathione in cell lysates through surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry using gold nanoaprticles. Nanomedicine 2010, 6, 530–537. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, Y.-T.; Chen, W.-T.; Tomalová, I.; Preisler, J.; Chang, H.-T. Detection of melamine in infant formula and grain powder by surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom 2012, 26, 1393–1398. [Google Scholar]
- Pilolli, R.; Ditaranto, N.; di Franco, C.; Palmisano, F.; Cioffi, N. Thermally annealed gold nanoparticles for surface-assisted laser desorption ionisation–mass spectrometry of low molecular weight analytes. Anal. Bioanal. Chem 2012, 404, 1703–1711. [Google Scholar]
- Chiu, T.-C.; Chang, L.-C.; Chiang, C.-K.; Chang, H.-T. Determining estrogens using surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry with silver nanoparticles as the matrix. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom 2008, 19, 1343–1346. [Google Scholar]
- Nizioł, J.; Rode, W.; Zieliński, Z.; Ruman, T. Matrix-free laser desorption–ionization with silver nanoparticle-enhanced steel targets. Int. J. Mass Spectrom 2013, 335, 22–32. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, P.-C.; Yu, C.-C.; Wu, H.-T.; Lu, Y.-W.; Han, C.-L.; Su, A.-K.; Chen, Y.-J.; Lin, C.-C. A chemically functionalized magnetic nanoplatform for rapid and specific biomolecular recognition and separation. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 160–168. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.-Y.; Chen, Y.-C. Magnetic nanoparticle-based platform for characterization of histidine-rich proteins and peptides. Anal. Chem 2013, 85, 3347–3354. [Google Scholar]
- Chiu, T.-C. Steroid hormones analysis with surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry using catechin-modified titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Talanta 2011, 86, 415–420. [Google Scholar]
- Radisavljević, M.; Kamčeva, T.; Vukićević, I.; Radoičić, M.; Šaponjić, Z.; Petković, M. Colloidal TiO2 nanoparticles as substrates for M(S)ALDI mass spectrometry of transition metal complexes. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom 2012, 26, 2041–2050. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, W.-Y.; Lin, W.-D.; Hwu, W.-L.; Lai, C.-C.; Tsai, F.-J. Screening assay of very long chain fatty acids in human plasma with multiwalled carbon nanotube-based surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem 2010, 82, 6814–6820. [Google Scholar]
- Cegłowski, M.; Schroeder, G. Laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometric analysis of surfactants on functionalized carbon nanotubes. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom 2012, 27, 258–264. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, E.W.Y.; Lam, H.S.; Ng, P.C.; Poon, T.C.W. Quantification of citrulline by parallel fragmentation monitoring—A novel method using graphitized carbon nanoparticles and MALDI-TOF/TOF mass spectrometry. Clin. Chim. Acta 2013, 420, 121–127. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, L.-M.; Shen, Q.; Lu, H.-J.; Yang, P.-Y. Pretreatment of low-abundance peptides on detonation nanodiamond for direct analysis by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2009, 877, 3631–3637. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Deng, C.; Zhang, X. Graphene and graphene oxide: Two ideal choices for the enrichment and ionization of long-chain fatty acids free from matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization matrix interference. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom 2011, 25, 3223–3234. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, L.; Sánchez-Juanes, F.; González-Ávila, M.; Cembrero-Fuciños, D.; Herrero-Hernández, A.; González-Buitrago, J.M.; Muñoz-Bellido, J.L. Direct identification of urinary tract pathogens from urine samples by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry. J. Clin. Microbiol 2010, 48, 2110–2115. [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson, L.G.; Drake, S.K.; Murray, P.R. Rapid identification of bacteria in positive blood culture broths by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry. J. Clin. Microbiol 2010, 48, 444–447. [Google Scholar]
- Barreiro, J.R.; Braga, P.A.C.; Ferreira, C.R.; Kostrzewa, M.; Maier, T.; Wegemann, B.; Böettcher, V.; Eberlin, M.N.; dos Santos, M.V. Nonculture-based identification of bacteria in milk by protein fingerprinting. Proteomics 2012, 12, 2739–2745. [Google Scholar]
- Burda, C.; Chen, X.; Narayana, R.; El-Sayed, M.A. Chemistry and properties of nanocrystals of different shapes. Chem. Rev 2005, 105, 1025–1102. [Google Scholar]
- An, K.; Somorjai, G.A. Size and shape control of metal nanoparticles for reaction selectivity in catalysis. ChemCatChem 2012, 4, 1512–1524. [Google Scholar]
- Lohse, S.E.; Murphy, C.A. Applications of colloidal inorganic nanoparticles: From medicine to energy. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2012, 134, 15607–15620. [Google Scholar]
- Sanvicens, N.; Pastells, C.; Pascual, N.; Marco, M.-P. Nanoparticle-based biosensors for detection of pathogenic bacteria. Trends Anal. Chem 2009, 28, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar]
- Coto-García, A.M.; Sotelo-González, E.; Fernández-Argüelles, M.T.; Pereiro, R.; Costa-Fernández, J.M.; Sanz-Medel, A. Nanoparticles as fluorescent labels for optical imaging and sensing in genomics and proteomics. Anal. Bioanal. Chem 2011, 399, 29–42. [Google Scholar]
- Veerapandian, M.; Yun, K. Functionalization of biomolecules on nanoparticles: Specialized for antibacterial applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol 2011, 90, 1655–1667. [Google Scholar]
- Gilmartin, N.; O’Kennedy, R. Nanobiotechnologies for the detection and reduction of pathogens. Enzym. Microb. Technol 2012, 50, 87–95. [Google Scholar]
- Burris, K.P.; Stewart, C.N., Jr. Fluorescent nanoparticles: Sensing pathogens and toxins in foods and crops. Trends Food Sci. Technol 2012, 28, 143–152. [Google Scholar]
- Shinde, S.B.; Fernandes, C.B.; Patravale, V.B. Recent trends in in vitro nanodiagnostics for detection of pathogens. J. Control. Release 2012, 159, 164–180. [Google Scholar]
- Zamborini, F.P.; Bao, L.; Dasari, R. Nanoparticles in measurement science. Anal. Chem 2012, 84, 541–576. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, K.-C.; Tsai, P.-J.; Lin, Y.-S.; Chen, Y.-C. Using biofunctionalized nanoparticles to probe pathogenic bacteria. Anal. Chem 2004, 76, 7162–7168. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.-S.; Tsai, P.-J.; Weng, M.-F.; Chen, Y.-C. Affinity capture using vancomycin-bound magnetic nanoparticles for the MALDI-MS analysis of bacteria. Anal. Chem 2005, 77, 1753–1760. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Guo, Z.; Wu, H.-F.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Woo, C.H. Rapid analysis of Gram-positive bacteria in water via membrane filtration coupled with nanoprobe-based MALDI-MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem 2010, 397, 2465–2476. [Google Scholar]
- Gopal, J.; Wu, H.-F.; Lee, C.-H. The biofunctional role of Ag nanoparticles on bacteria— A MALDI-MS perspective. Analyst 2011, 136, 5077–5083. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.-H.; Gopal, J.; Wu, F.-H. Ionic solution and nanoparticle assisted MALDI-MS as bacterial biosensors for rapid analysis of yogurt. Biosens. Bioelectron 2012, 31, 77–83. [Google Scholar]
- Gopal, J.; Wu, F.-H.; Gangaraju, G. Quantifying the degradation of extracellular polysaccharides of Escherichia coli by CdS quantum dots. J. Mater. Chem 2011, 21, 13445–13451. [Google Scholar]
- Manikandan, M.; Wu, H.-F. Probing the fungicidal properties of CdS quantum dots on Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Candida utilis using MALDI-MS. J. Nanopart. Res 2013, 15, 1728. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelhamid, H.N.; Wu, F.-H. Probing the interactions of chitosan capped CdS quantum dots with pathogenic bacteria and their biosensing application. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 6094–6106. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, F.; Wu, F.-H. Characterization of pathogenic bacteria using ionic liquid via single drop microextraction combined with MALDI-TOF MS. Analyst 2011, 136, 4020–4027. [Google Scholar]
- Amhad, F.; Siddiqui, M.A.; Babalola, O.O.; Wu, F.-H. Biofunctionalization of nanoparticle assisted mass spectrometry as biosensors for rapid detection of plant associated bacteria. Biosens. Bioelectron 2012, 35, 235–242. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, F.; Wu, F.-H. Rapid and sensitive detection of bacteria via platinum-labeled antibodies and on-particle ionization and enrichment prior to MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Microchim. Acta 2013, 180, 485–492. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, P.-H.; Wong, S.-Y.; Lin, S.-H.; Chen, Y.-C. Lysozyme-encapsulated gold nanocluster-based affinity mass spectrometry for pathogenic bacteria. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom 2013, 27, 2143–2148. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelhamid, H.N.; Wu, H.-F. Multifunctional graphene magnetic nanosheet decorated with chitosan for highly sensitive detection of pathogenic bacteria. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 3950–3961. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, N.; Ahmad, F.; Wu, F.-H. Monitoring the heat stress response of Escherichia coli via NiO nanoparticle assisted MALDI–TOF mass spectrometry. Talanta 2013, 103, 38–46. [Google Scholar]
- Gopal, J.; Narayana, J.L.; Wu, F.-H. TiO2 nanoparticle assisted mass spectrometry as biosensors of Staphylococcus aureus, key pathogen in nosocomial infections from air, skin surface and human nasal passage. Biosens. Bioelectron 2011, 27, 201–206. [Google Scholar]
- Gopal, J.; Wu, F.-H.; Lee, Y.-H. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time-of-flight mass spectrometry as a rapid and reliable technique for directly evaluating bactericidal activity: Probing the critical concentration of ZnO nanoparticles as affinity probes. Anal. Chem 2010, 82, 9617–9621. [Google Scholar]
- Gopal, J.; Manikandan, M.; Hasan, N.; Lee, C.-H.; Wu, H.-F. A comparative study on the mode of interaction of different nanoparticles during MALDI-MS of bacterial cells. J. Mass Spectrom 2013, 48, 119–127. [Google Scholar]
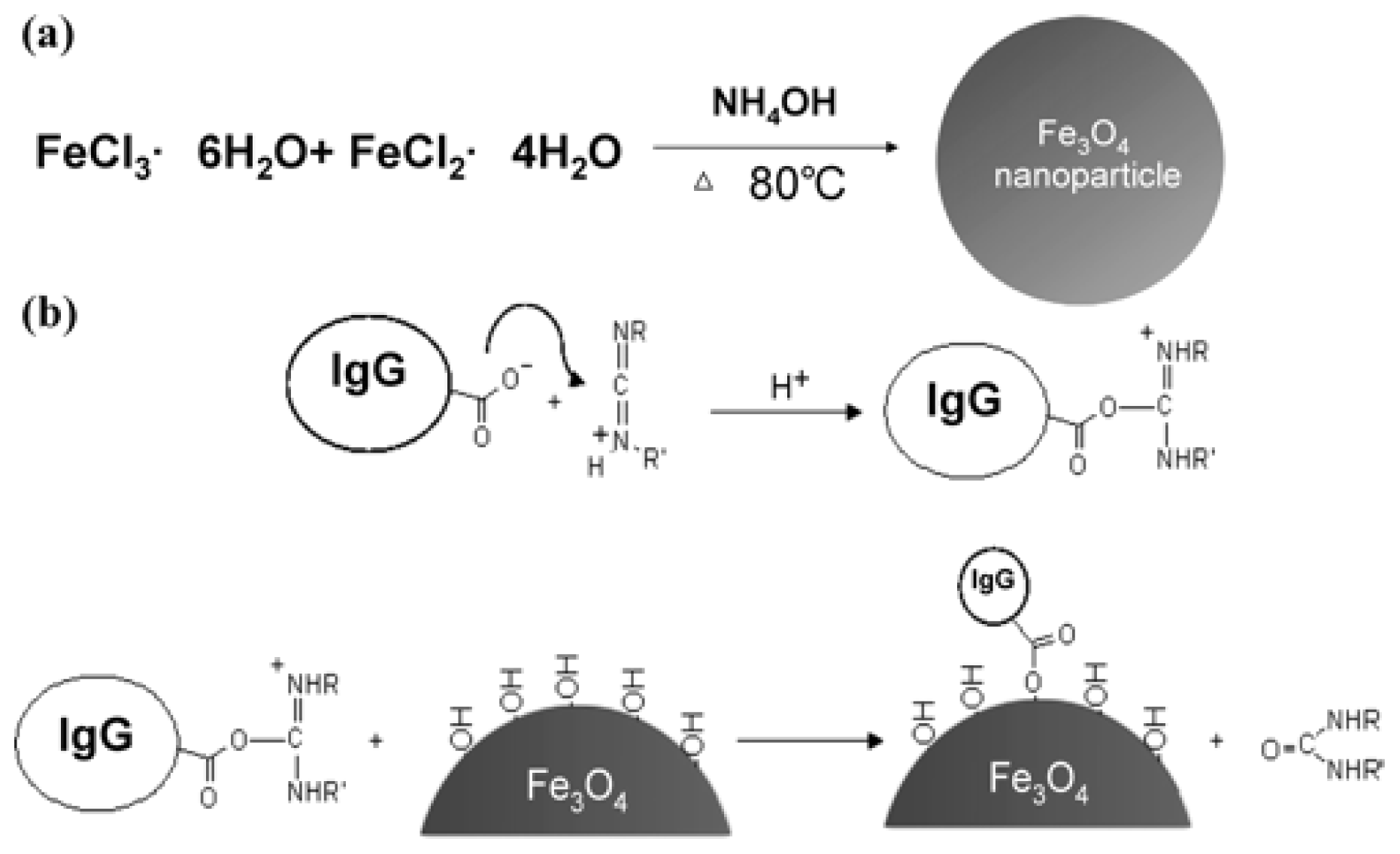
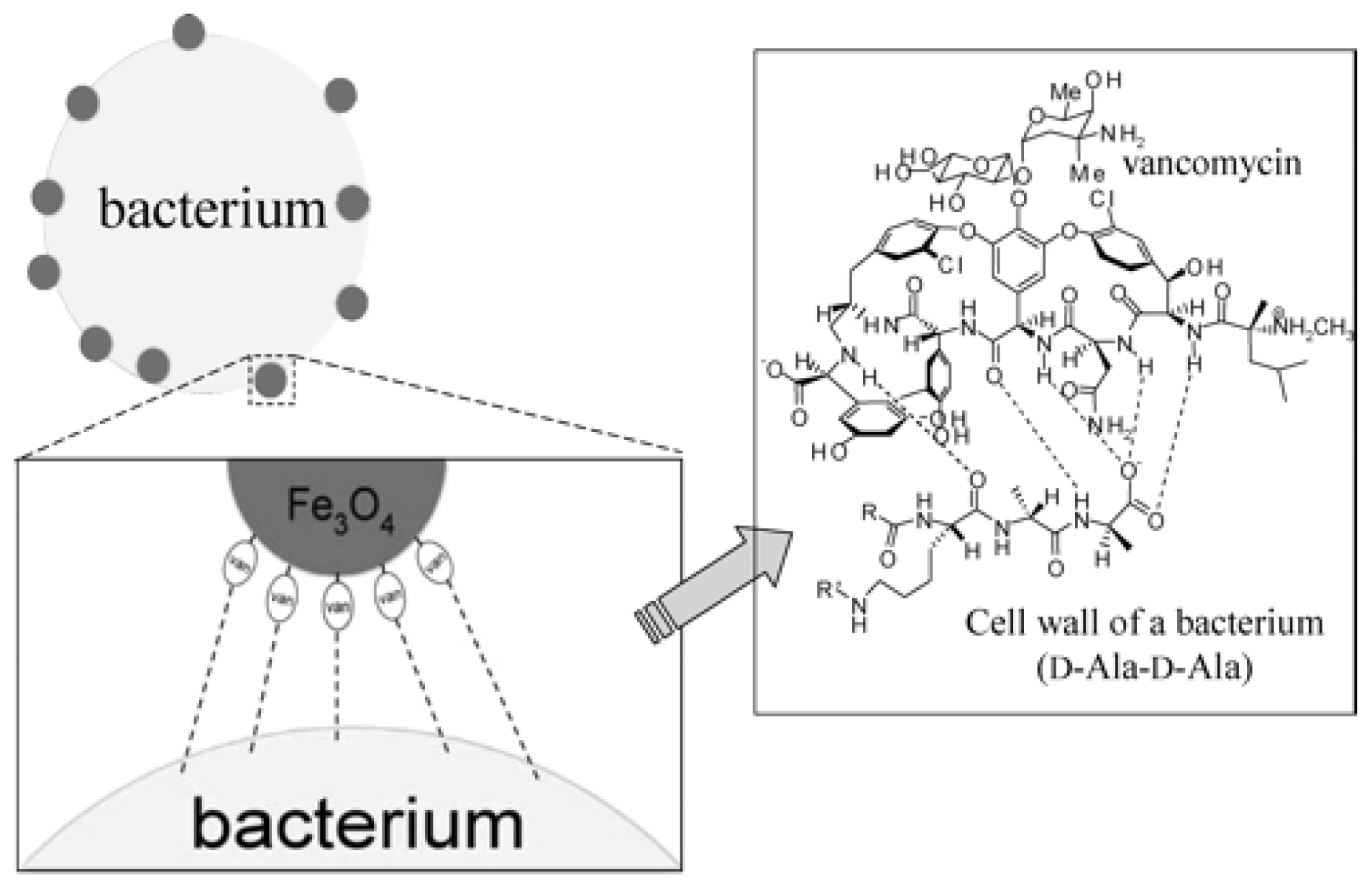


| Nanomaterials | Functionalized molecule | Pathogen | Application | LOD (cfu/mL) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe3O4 NPs | IgG | S. aureus; S. saprophyticus | 3.0 × 105 | [66] | |
| Fe3O4 NPs | IgG | S. saprophyticus | Urine | 3.0×107 | [66] |
| Fe3O4 NPs | Vancomycin | S. aureus; S. saprophyticus | Urine | 7.8 × 104; 7.4 × 104 | [67] |
| Fe3O4 NPs | Vancomycin | B. cereus; E. faecium; S. aureus | Tap water, reservoir water | 5.0 × 102 | [68] |
| Ag NPs | E. coli; S. marcescen | N.D. | [69] | ||
| Ag NPs | B. lactis; L. acidophilus; S. thermophilus; L. bulgaricus | Yogurt | N.D. | [70] | |
| Ag NPs | L. acidophilus; B. longum; L. bulgaricus; S. thermophilus | Yogurt | N.D. | [70] | |
| CdS QDs | E. coli | N.D. | [71] | ||
| CdS QDs | S. cerevisiae; C. utilis | N.D. | [72] | ||
| CdS QDs | Chitosan | P. aeruginosa; S. aureus | 2.0 × 102; 1.5 × 102 | [73] | |
| Pt NPs | Mixed with ionic liquid (1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate) | E. coli; S. marcescens | 106 | [74] | |
| Pt NPs | IgG | B. thuringiensis; B. subtilis | Rhizospheric soil and root | N.D. | [75] |
| Pt NPs | IgG | S. marcescens; E. coli | 105 | [76] | |
| AuNCs | Lysozyme | E. coli; K. pneumoniae; P. aeruginosa; pandrug-resistant A. baumannii; S. aureus; E. faecalis; vancomycin-resistant E. faecalis | Fetal bovine serum; urine | N.D.; 106 | [77] |
| Graphene magnetic nanosheets | Chitosan | P. aeruginosa; S. aureus | Blood | 6.0 × 102; 5.0 × 102 | [78] |
| NiO NPs | E. coli | 107 | [79] | ||
| TiO2 NPs | S. aureus | Human nasal passage | N.D. | [80] | |
| ZnO NPs | E. coli | N.D. | [81] | ||
| Ag, Pt, NiO, TiO2, ZnO NPs | S. aureus; P. saeruginosa | N.D. | [82] |
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Chiu, T.-C. Recent Advances in Bacteria Identification by Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Mass Spectrometry Using Nanomaterials as Affinity Probes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 7266-7280. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15057266
Chiu T-C. Recent Advances in Bacteria Identification by Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Mass Spectrometry Using Nanomaterials as Affinity Probes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2014; 15(5):7266-7280. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15057266
Chicago/Turabian StyleChiu, Tai-Chia. 2014. "Recent Advances in Bacteria Identification by Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Mass Spectrometry Using Nanomaterials as Affinity Probes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 15, no. 5: 7266-7280. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15057266





