Homoserine Lactones Influence the Reaction of Plants to Rhizobia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. S. meliloti Rm2011 Produces N-3-Oxo-Tetradecanoyl-l-Homoserine Lactone (oxo-C14-HSL)
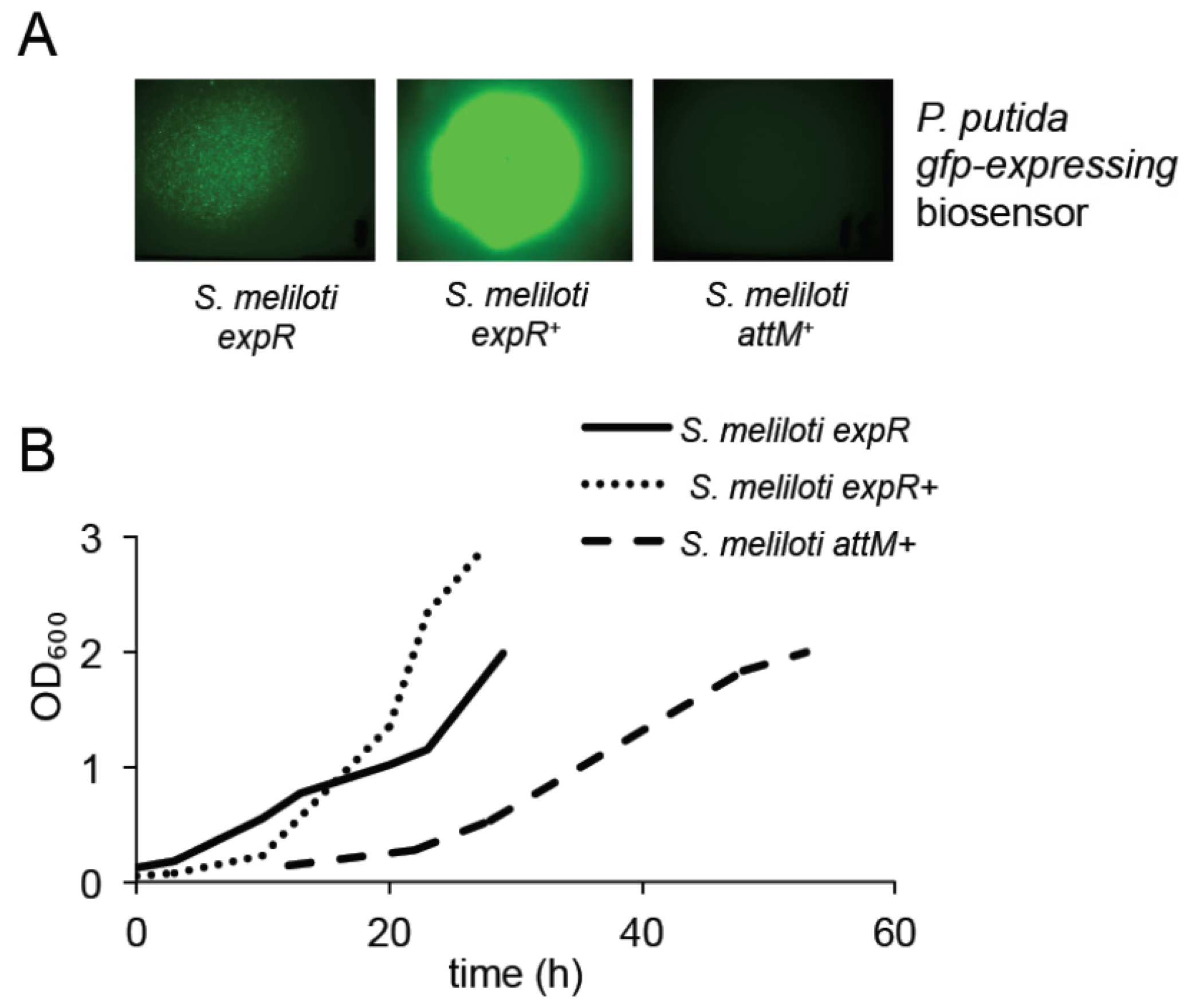
2.2. Expression of the AttM Lactonase Abolishes AHL Accumulation in S. meliloti
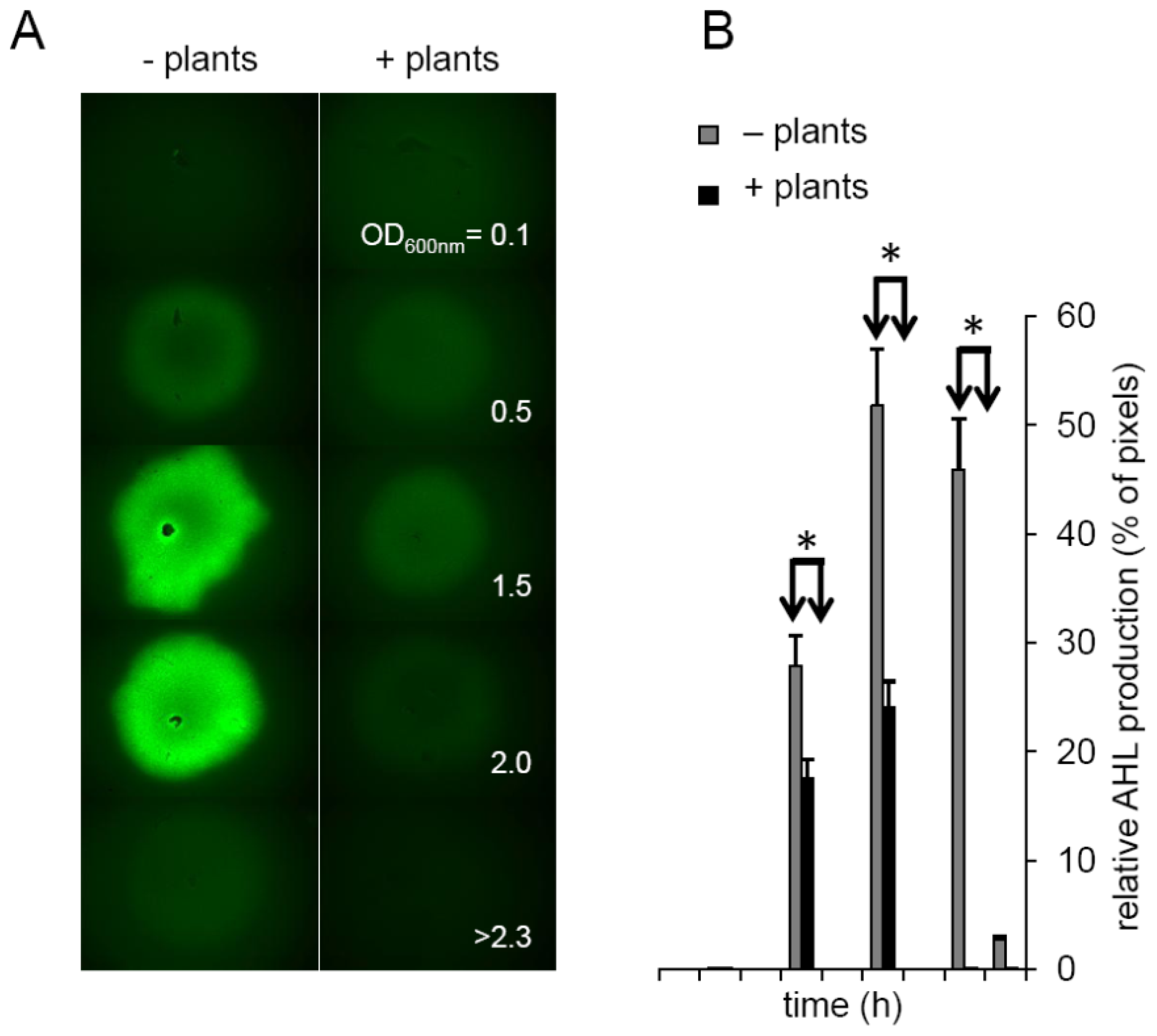
2.3. Plants Impact on AHL Concentration
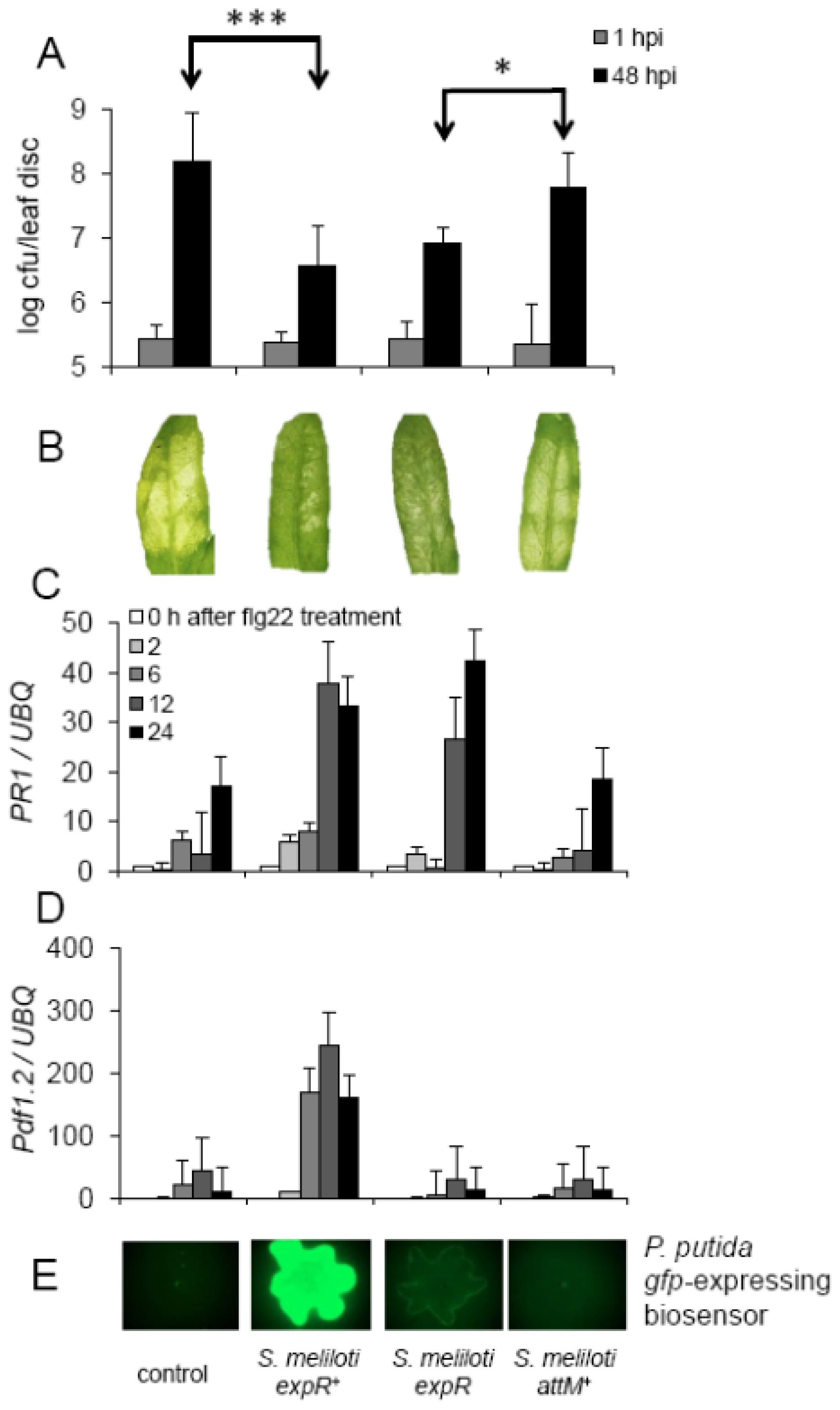
2.4. Oxo-C14-HSL Produced by S. meliloti Enhances Resistance of Arabidopsis Plants
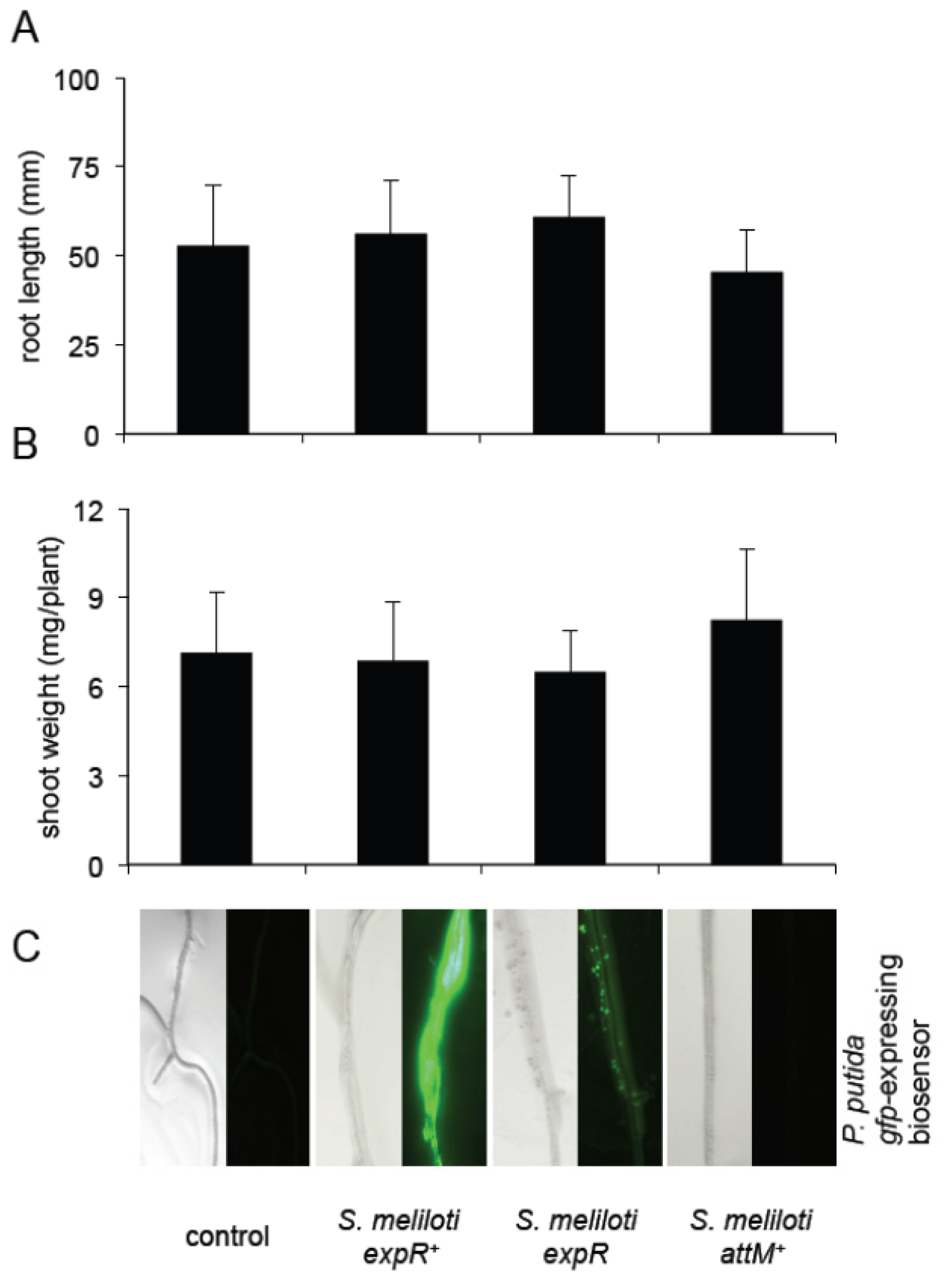
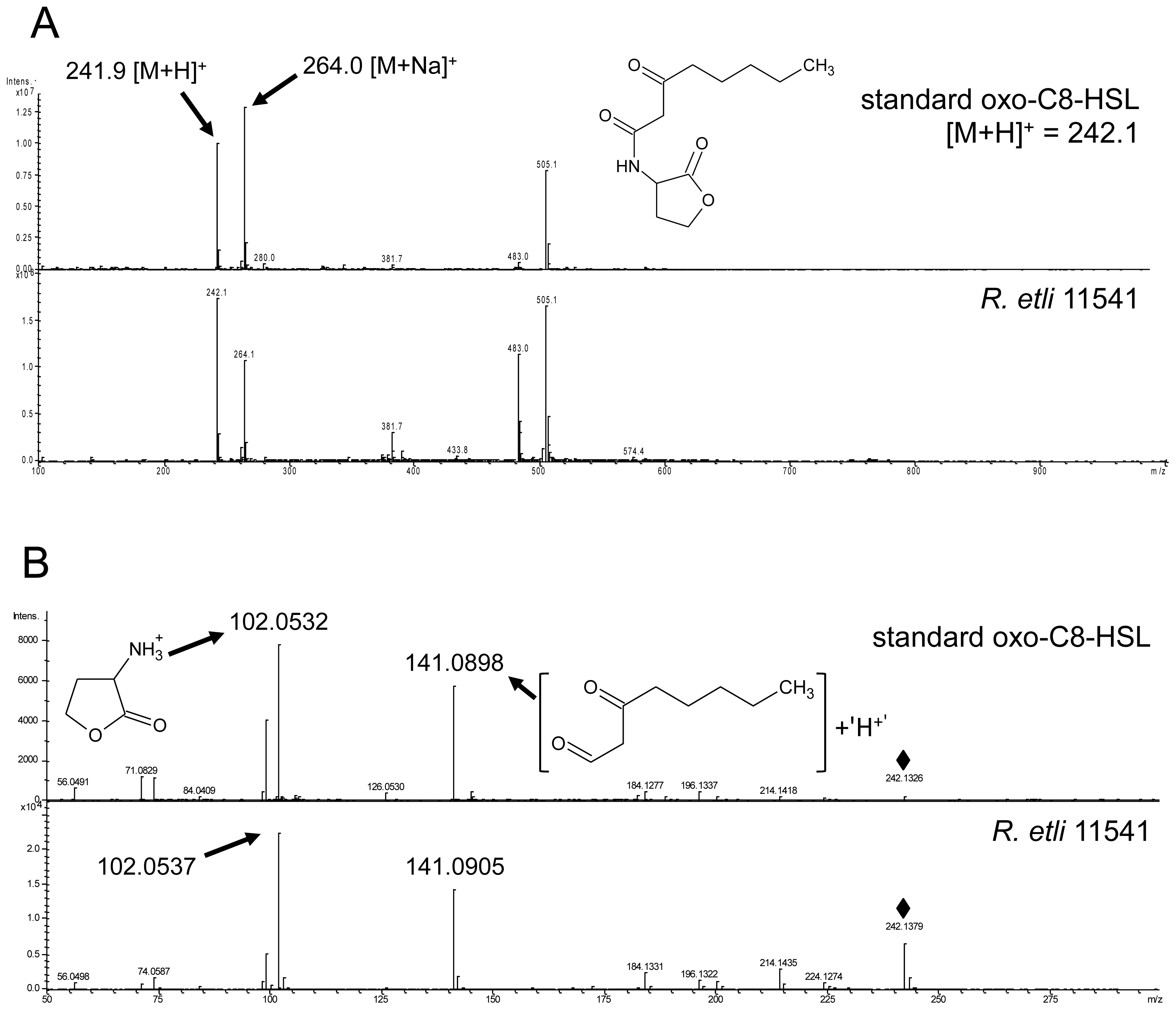
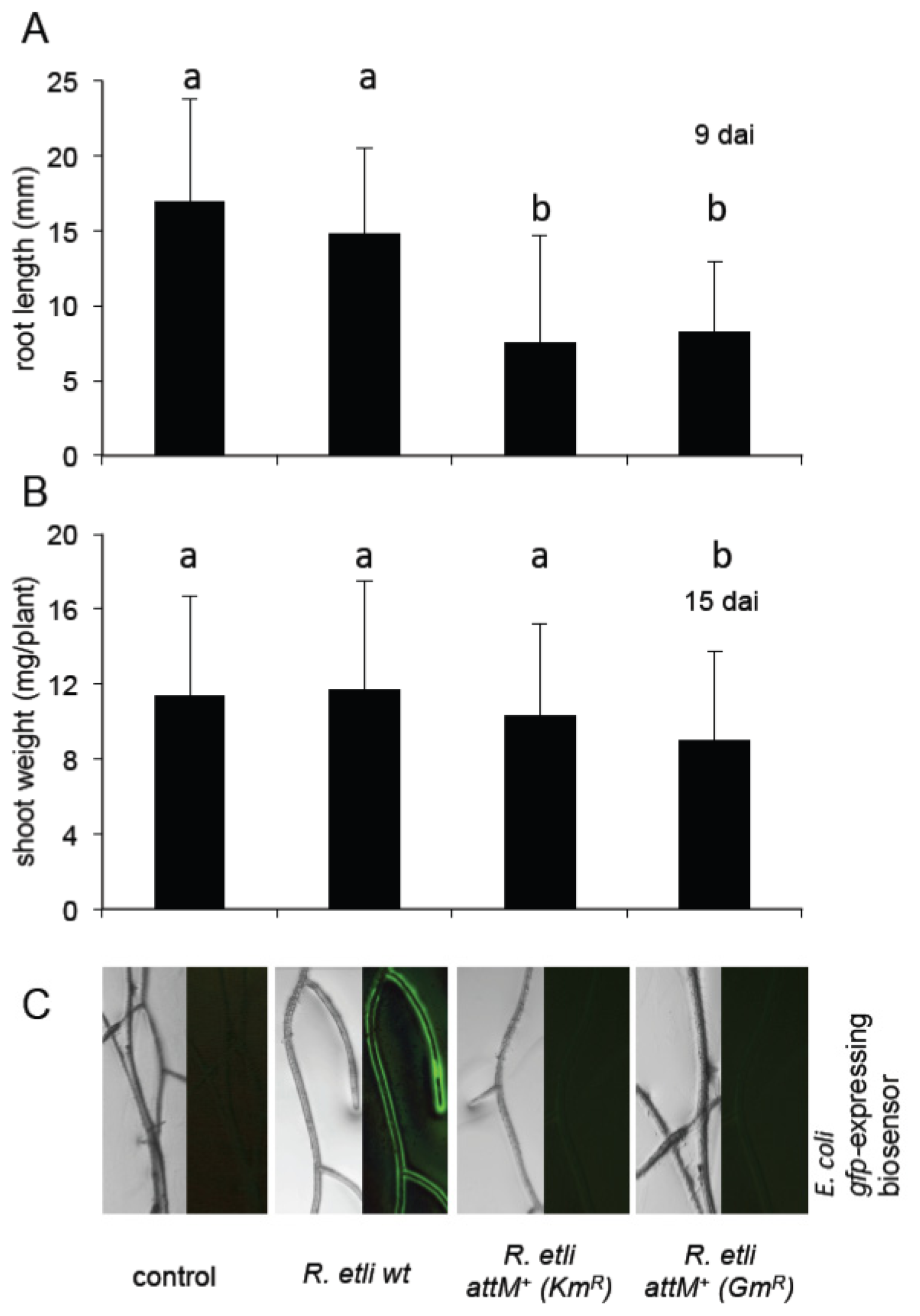
2.5. Oxo-C8-HSL Produced by R. etli Has only Moderate Impact on Arabidopsis Growth
3. Discussion
3.1. AHL Production in S. meliloti and R. etli
3.2. Systemic Induction of Arabidopsis Resistance by S. meliloti Treatment
3.3. Growth Inducing Capacities
3.4. Impact of Plant on AHL Production
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Plant
4.2. Bacterial Strains and Growth Conditions
4.3. AHL Detection and Quantification
4.3.1. Chemicals
4.3.2. HPLC/MS-MS
4.3.3. AHL Detection Using Biosensor Bacteria
4.4. Segmentation Algorithm
4.5. Growth Promotion Assay
4.6. Pathogenicity Assays
4.7. Gene Expression Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Information
Detection and quantification of standard AHLs using the bacterial biosensor strains P. putida KS35 and E. coli E. coli MT102 (pJBA89). (a) The GFP-based system using the P. putida KS35 and E. coli MT102 (pJBA89) strains. AHLs were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, resuspended in Me2CO at concentrations as indicated and 5 μL of the solution were applied onto bacterial lawns; (b) Quantification of the GFP photographs using the segmentation algorithm [40].
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fuqua, W.C.; Winans, S.C. A LuxR-LuxI type regulatory system activates Agrobacterium Ti plasmid conjugal transfer in the presence of a plant tumor metabolite. J. Bacteriol 1994, 176, 2796–2806. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, H.B.; Greenberg, E.P. Diffusion of autoinducer is involved in regulation of the Vibrio fischeri luminescence system. J. Bacteriol 1985, 163, 1210–1214. [Google Scholar]
- Schuhegger, R.; Ihring, A.; Gantner, S.; Bahnweg, G.; Knappe, C.; Vogg, G.; Hutzler, P.; Schmid, M.; van Breusegem, F.; Eberl, L.; et al. Induction of systemic resistance in tomato by N-acyl-l-homoserine lactone-producing rhizosphere bacteria. Plant Cell Environ 2006, 29, 909–918. [Google Scholar]
- Gantner, S.; Schmid, M.; Durr, C.; Schuhegger, R.; Steidle, A.; Hutzler, P.; Langebartels, C.; Eberl, L.; Hartmann, A.; Dazzo, F.B. In situ quantitation of the spatial scale of calling distances and population density-independent N-acylhomoserine lactone-mediated communication by rhizobacteria colonized on plant roots. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol 2006, 56, 188–194. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, Y.; Liu, X.; Ma, Y.; Chernin, L.; Berg, G.; Gao, K. Induction of systemic resistance, root colonisation and biocontrol activities of the rhizospheric strain of Serratia plymuthica are dependent on N-acyl homoserine lactones. Eur. J. Plant Pathol 2009, 124, 261–268. [Google Scholar]
- Von Rad, U.; Klein, I.; Dobrev, P.I.; Kottova, J.; Zazimalova, E.; Fekete, A.; Hartmann, A.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P.; Durner, J. Response of Arabidopsis thaliana to N-hexanoyl-dl-homoserine-lactone, a bacterial quorum sensing molecule produced in the rhizosphere. Planta 2008, 229, 73–85. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Bian, Z.; Jia, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Song, S. The GCR1 and GPA1 participate in promotion of Arabidopsis primary root elongation induced by N-Acyl-homoserine lactones, the bacterial quorum-sensing signals. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact 2012, 25, 677–683. [Google Scholar]
- Schenk, S.T.; Stein, E.; Kogel, K.H.; Schikora, A. Arabidopsis growth and defense are modulated by bacterial quorum sensing molecules. Plant Signal. Behav 2012, 7, 178–181. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, X.; Todd, C.D.; Desikan, R.; Yang, Y.; Hu, X. N-3-oxo-decanoyl-l-homoserine-lactone activates auxin-induced adventitious root formation via hydrogen peroxide- and nitric oxide-dependent cyclic GMP signaling in mung bean. Plant Physiol 2012, 158, 725–736. [Google Scholar]
- Schikora, A.; Schenk, S.T.; Stein, E.; Molitor, A.; Zuccaro, A.; Kogel, K.H. N-acyl-homoserine lactone confers resistance towards biotrophic and hemibiotrophic pathogens via altered activation of AtMPK6. Plant Physiol 2011, 157, 1407–1418. [Google Scholar]
- Teplitski, M.; Eberhard, A.; Gronquist, M.R.; Gao, M.; Robinson, J.B.; Bauer, W.D. Chemical identification of N-acyl homoserine lactone quorum-sensing signals produced by Sinorhizobium meliloti strains in defined medium. Arch. Microbiol 2003, 180, 494–497. [Google Scholar]
- Pellock, B.J.; Teplitski, M.; Boinay, R.P.; Bauer, W.D.; Walker, G.C. A LuxR homolog controls production of symbiotically active extracellular polysaccharide II by Sinorhizobium meliloti. J. Bacteriol 2002, 184, 5067–5076. [Google Scholar]
- Beringer, J.E. R factor transfer in Rhizobium leguminosarum. J. Gen. Microbiol 1974, 84, 188–198. [Google Scholar]
- Simon, R.; Priefer, U.; Pühler, A. A broad host range mobilization system for in vivo genetic engineering: Transposon mutagenesis in gram negative bacteria. Nat. Biotechnol 1983, 1, 784–791. [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh, M. University of Marburg: Marburg, Germany, Unpublished observation; 2013.
- Schikora, A. Justus Liebig University Giessen: Giessen, Germany, Unpublished oberservation; 2013.
- Ortiz-Castro, R.; Martinez-Trujillo, M.; Lopez-Bucio, J. N-acyl-l-homoserine lactones: A class of bacterial quorum-sensing signals alter post-embryonic root development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Environ 2008, 31, 1497–1509. [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Montano, F.; Guasch-Vidal, B.; Gonzalez-Barroso, S.; Lopez-Baena, F.J.; Cubo, T.; Ollero, F.J.; Gil-Serrano, A.M.; Rodriguez-Carvajal, M.A.; Bellogin, R.A.; Espuny, M.R. Nodulation-gene-inducing flavonoids increase overall production of autoinducers and expression of N-acyl homoserine lactone synthesis genes in Rhizobia. Res. Microbiol 2011, 162, 715–723. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Fraile, P.; Carro, L.; Robledo, M.; Ramirez-Bahena, M.H.; Flores-Felix, J.D.; Fernandez, M.T.; Mateos, P.F.; Rivas, R.; Igual, J.M.; Martinez-Molina, E.; et al. Rhizobium promotes non-legumes growth and quality in several production steps: Towards a biofertilization of edible raw vegetables healthy for humans. PLoS One 2012, 7, e38122. [Google Scholar]
- Marketon, M.M.; Gonzalez, J.E. Identification of two quorum-sensing systems in Sinorhizobium meliloti. J. Bacteriol 2002, 184, 3466–3475. [Google Scholar]
- Pozo, M.J.; van der Ent, S.; van Loon, L.C.; Pieterse, C.M. Transcription factor MYC2 is involved in priming for enhanced defense during rhizobacteria-induced systemic resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana. New Phytol 2008, 180, 511–523. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Ent, S.; Verhagen, B.W.; van Doorn, R.; Bakker, D.; Verlaan, M.G.; Pel, M.J.; Joosten, R.G.; Proveniers, M.C.; van Loon, L.C.; Ton, J.; et al. MYB72 is required in early signaling steps of rhizobacteria-induced systemic resistance in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 2008, 146, 1293–1304. [Google Scholar]
- Gurich, N.; Gonzalez, J.E. Role of quorum sensing in Sinorhizobium meliloti-Alfalfa symbiosis. J. Bacteriol 2009, 191, 4372–4382. [Google Scholar]
- Mathesius, U.; Mulders, S.; Gao, M.; Teplitski, M.; Caetano-Anolles, G.; Rolfe, B.G.; Bauer, W.D. Extensive and specific responses of a eukaryote to bacterial quorum-sensing signals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 1444–1449. [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann, A.; Schikora, A. Quorum sensing of bacteria and trans-kingdom interactions of N-acyl homoserine lactones with eukaryotes. J. Chem. Ecol 2012, 38, 704–713. [Google Scholar]
- Marketon, M.M.; Gronquist, M.R.; Eberhard, A.; Gonzalez, J.E. Characterization of the Sinorhizobium meliloti sinR/sinI locus and the production of novel N-acyl homoserine lactones. J. Bacteriol 2002, 184, 5686–5695. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, M.; Chen, H.; Eberhard, A.; Gronquist, M.R.; Robinson, J.B.; Rolfe, B.G.; Bauer, W.D. sinI- and expR-dependent quorum sensing in Sinorhizobium meliloti. J. Bacteriol 2005, 187, 7931–7944. [Google Scholar]
- Eberl, L.; Winson, M.K.; Sternberg, C.; Stewart, G.S.A.B.; Christiansen, G.; Chhabra, S.R.; Bycroft, B.; Williams, P.; Molin, S.; Givskov, M. Involvement of N-acyl-l-homoserine lactone autoinducers in controlling the multicellular behaviour of Serratia liquefaciens. Mol. Microbiol 1996, 20, 127–136. [Google Scholar]
- Schwachtje, J.; Karojet, S.; Thormahlen, I.; Bernholz, C.; Kunz, S.; Brouwer, S.; Schwochow, M.; Kohl, K.; van Dongen, J.T. A naturally associated rhizobacterium of Arabidopsis thaliana induces a starvation-like transcriptional response while promoting growth. PLoS One 2011, 6, e29382. [Google Scholar]
- Hense, B.A.; Muller, J.; Kuttler, C.; Hartmann, A. Spatial heterogeneity of autoinducer regulation systems. Sensors 2012, 12, 4156–4171. [Google Scholar]
- Teplitski, M.; Chen, H.; Rajamani, S.; Gao, M.; Merighi, M.; Sayre, R.T.; Robinson, J.B.; Rolfe, B.G.; Bauer, W.D. Chlamydomonas reinhardtii secretes compounds that mimic bacterial signals and interfere with quorum sensing regulation in bacteria. Plant Physiol 2004, 134, 137–146. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, M.; Teplitski, M.; Robinson, J.B.; Bauer, W.D. Production of substances by Medicago truncatula that affect bacterial quorum sensing. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact 2003, 16, 827–834. [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Montano, F.; Jimenez-Guerrero, I.; Sanchez-Matamoros, R.C.; Lopez-Baena, F.J.; Ollero, F.J.; Rodriguez-Carvajal, M.A.; Bellogin, R.A.; Espuny, M.R. Rice and bean AHL-mimic quorum-sensing signals specifically interfere with the capacity to form biofilms by plant-associated bacteria. Res. Microbiol 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manefield, M.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Henzter, M.; Andersen, J.B.; Steinberg, P.; Kjelleberg, S.; Givskov, M. Halogenated furanones inhibit quorum sensing through accelerated LuxR turnover. Microbiology 2002, 148, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar]
- Keshavan, N.D.; Chowdhary, P.K.; Haines, D.C.; Gonzalez, J.E. l-Canavanine made by Medicago sativa interferes with quorum sensing in Sinorhizobium meliloti. J. Bacteriol 2005, 187, 8427–8436. [Google Scholar]
- Vandeputte, O.M.; Kiendrebeogo, M.; Rajaonson, S.; Diallo, B.; Mol, A.; El Jaziri, M.; Baucher, M. Identification of catechin as one of the flavonoids from Combretum albiflorum bark extract that reduces the production of quorum-sensing-controlled virulence factors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 2010, 76, 243–253. [Google Scholar]
- Kovach, M.E.; Phillips, R.W.; Elzer, P.H.; Roop, R.M., II; Peterson, K.M. pBBR1MCS: A broad-host-range cloning vector. BioTechniques 1994, 16, 800–802. [Google Scholar]
- Andersen, J.B.; Heydorn, A.; Hentzer, M.; Eberl, L.; Geisenberger, O.; Christensen, B.B.; Molin, S.; Givskov, M. gfp-based N-Acyl homoserine-lactone sensor systems for detection of bacterial communication. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 2001, 67, 575–585. [Google Scholar]
- Steidle, A.; Sigl, K.; Schuhegger, R.; Ihring, A.; Schmid, M.; Gantner, S.; Stoffels, M.; Riedel, K.; Givskov, M.; Hartmann, A.; et al. Visualization of N-acylhomoserine lactone-mediated cell-cell communication between bacteria colonizing the tomato Rhizosphere. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 2001, 67, 5761–5770. [Google Scholar]
- Schikora, M.; Hage, M.; Ruthotto, E.; Wild, K. A Convex Formulation for Color Image Segmentation in the Context of Passive Emitter Localization, Information Fusion, 2009. Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Information Fusion, 2009, FUSION 2009, Seattle, WA, USA, 6–9 July 2009; pp. 1424–1431.


© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Zarkani, A.A.; Stein, E.; Röhrich, C.R.; Schikora, M.; Evguenieva-Hackenberg, E.; Degenkolb, T.; Vilcinskas, A.; Klug, G.; Kogel, K.-H.; Schikora, A. Homoserine Lactones Influence the Reaction of Plants to Rhizobia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 17122-17146. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140817122
Zarkani AA, Stein E, Röhrich CR, Schikora M, Evguenieva-Hackenberg E, Degenkolb T, Vilcinskas A, Klug G, Kogel K-H, Schikora A. Homoserine Lactones Influence the Reaction of Plants to Rhizobia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2013; 14(8):17122-17146. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140817122
Chicago/Turabian StyleZarkani, Azhar A., Elke Stein, Christian R. Röhrich, Marek Schikora, Elena Evguenieva-Hackenberg, Thomas Degenkolb, Andreas Vilcinskas, Gabriele Klug, Karl-Heinz Kogel, and Adam Schikora. 2013. "Homoserine Lactones Influence the Reaction of Plants to Rhizobia" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 14, no. 8: 17122-17146. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140817122
APA StyleZarkani, A. A., Stein, E., Röhrich, C. R., Schikora, M., Evguenieva-Hackenberg, E., Degenkolb, T., Vilcinskas, A., Klug, G., Kogel, K.-H., & Schikora, A. (2013). Homoserine Lactones Influence the Reaction of Plants to Rhizobia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 14(8), 17122-17146. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms140817122



