Bioassay-Guided Isolation and Identification of Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitory Constituents from the Leaves of Perilla frutescens
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Hypouricemic Activities of Extract in Potassium Oxonate-Induced Hyperuricemic Mice
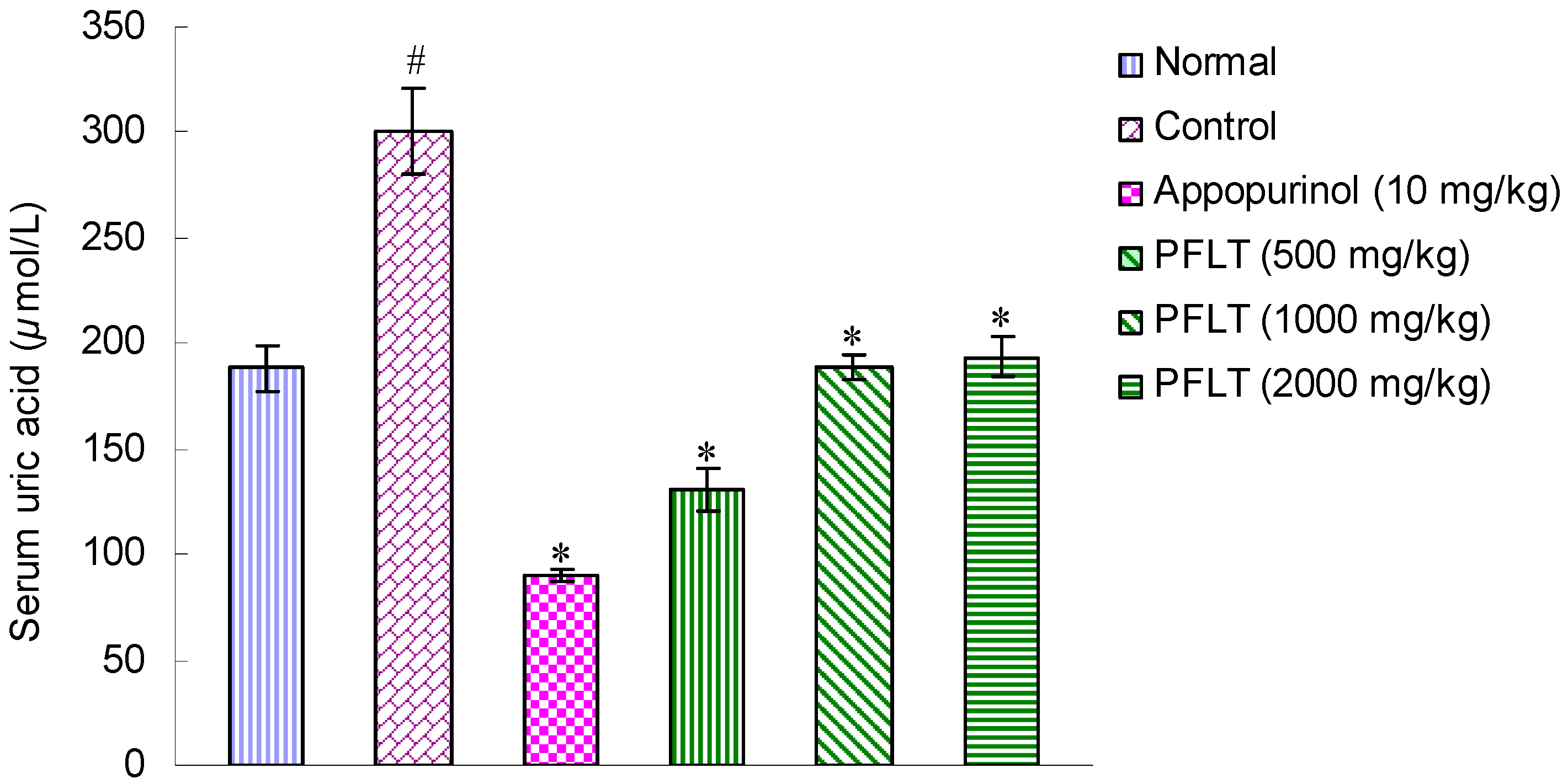
2.2. Bioassay-Guided Isolation of Compounds

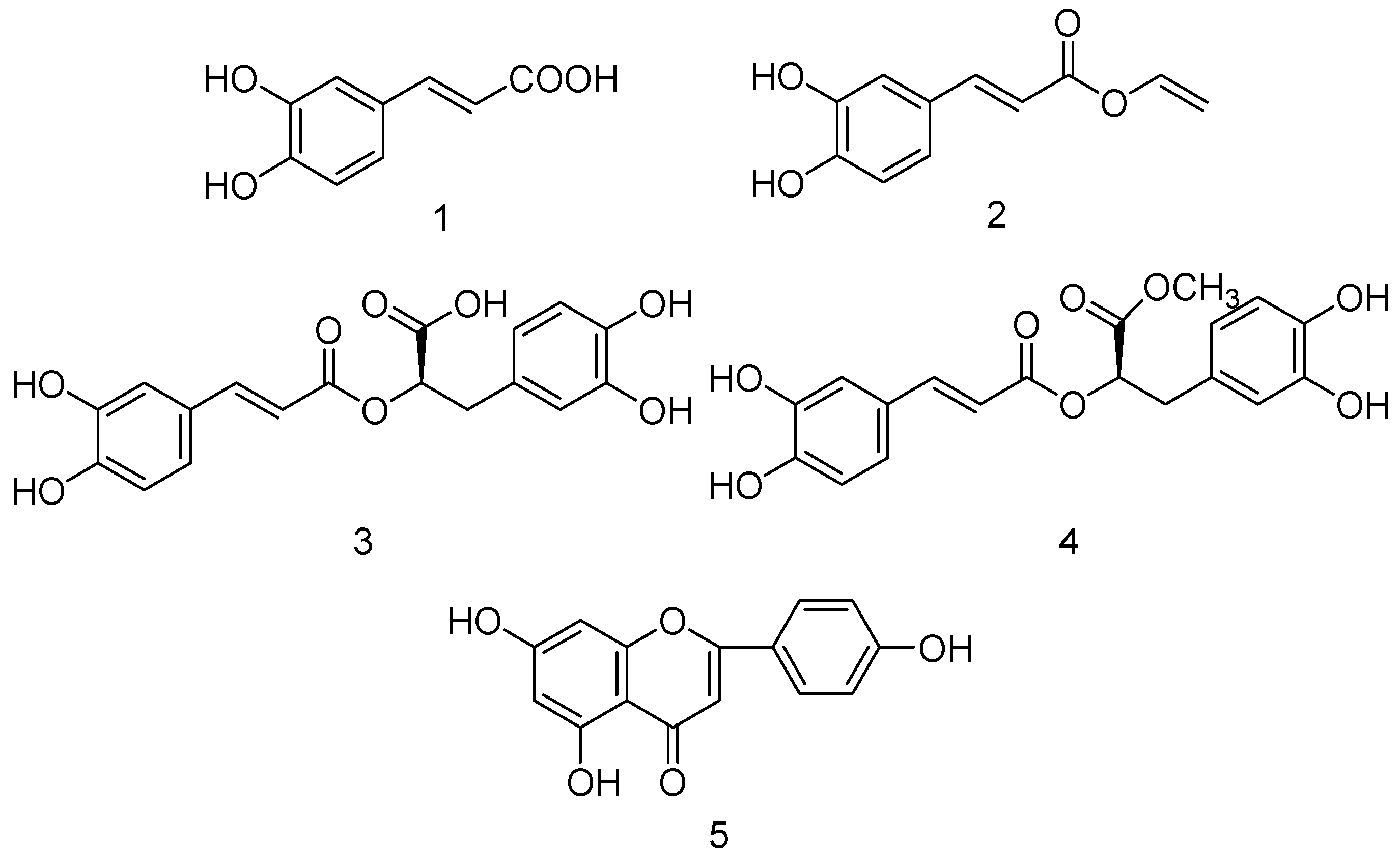
2.3. Effect of Five Compounds on XO Activity and Inhibitory Modes of Action in Vitro
2.3.1. Effect on XO Activity
| Compound | IC50 (μM) | Ki (μM) | Mode of Inhibition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Caffeic acid | 121.22 | 9.22 | Competitive |
| Vinyl caffeate | 31.26 | 5.05 | Competitive |
| Rosmarinic acid | 91.72 | 26.22 | Competitive |
| Methyl rosmarinate | 26.59 | 2.85 | Competitive |
| Apigenin | 0.44 | 0.11 | Mixed |
| Allopurinol | 2.07 | 2.42 | Competitive |
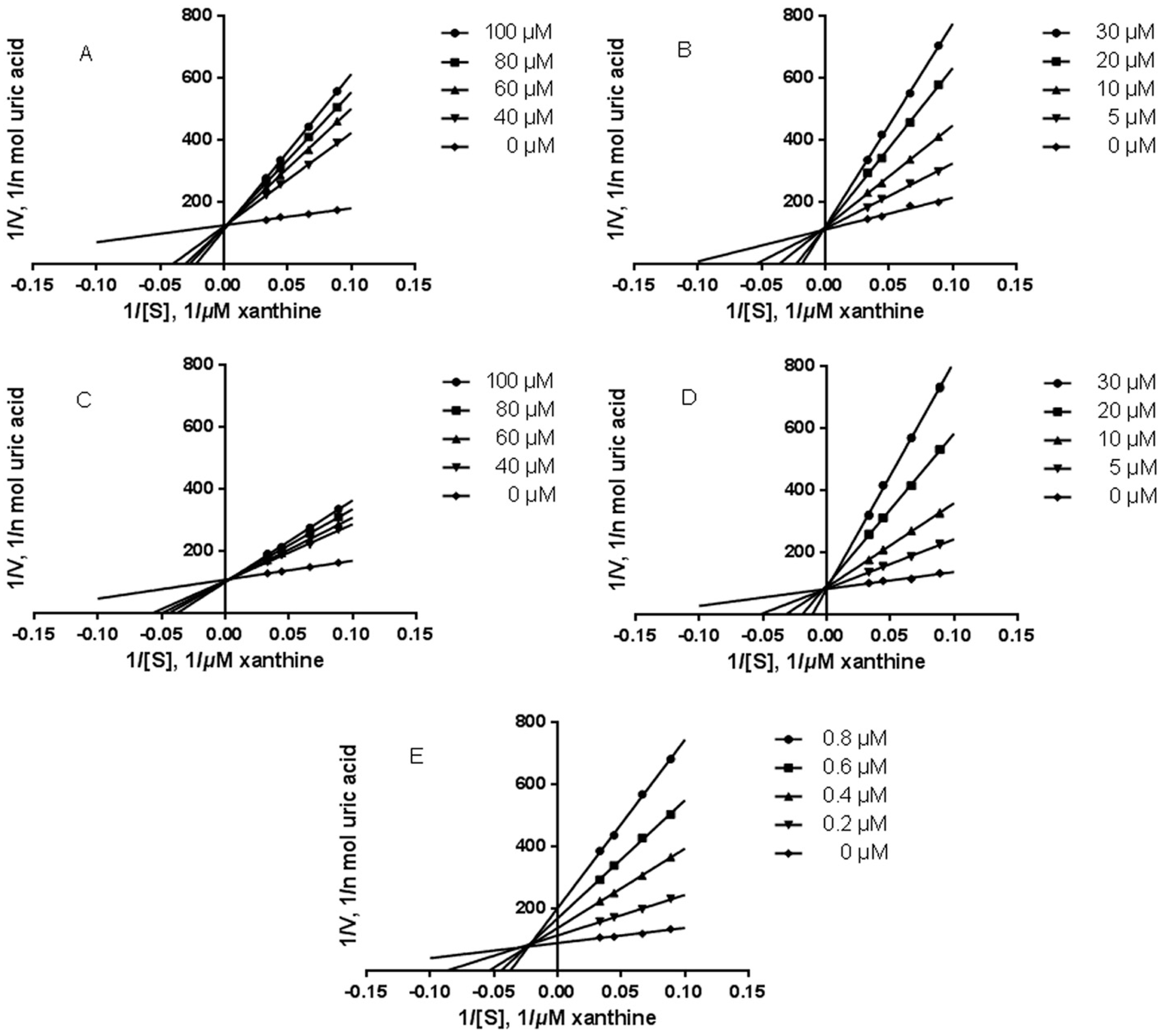
2.3.2. Inhibition Kinetic Analysis
2.4. HPLC Analysis

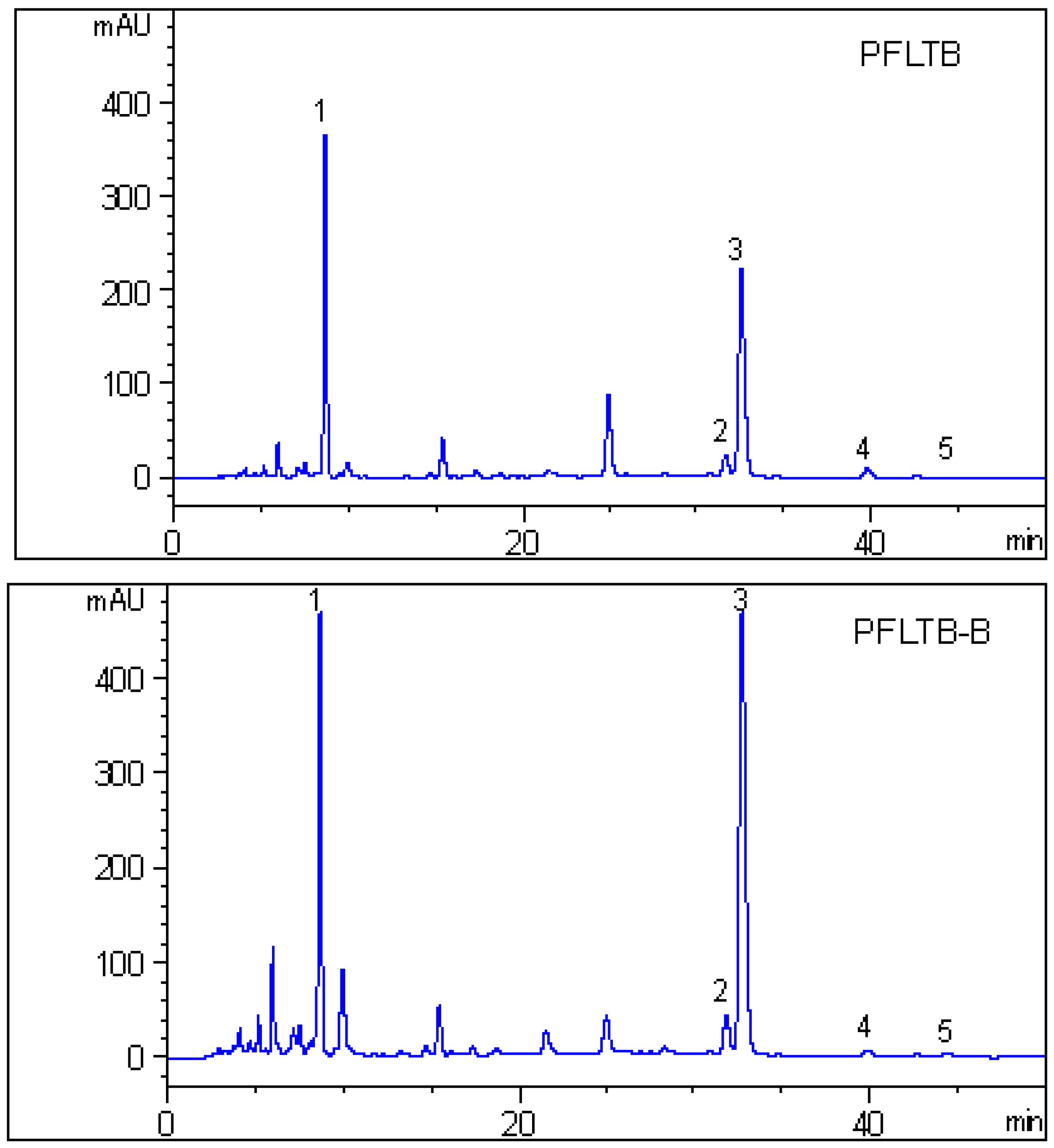
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Procedures
3.2. Plant Materials
3.3. Animals
3.4. Extraction and Isolation of Bioactive Compounds
3.5. Mice Model of Hyperuricemia and Drug Administration
3.6. Assay of XO Activity and Inhibitory Mode of Action in Vitro
3.6.1. Assay of XO Activity
3.6.2. Assay of XO Inhibitory Modes of Action
3.7. HPLC Analysis
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Punzi, L.; So, A. Serum uric acid and gout: From the past to molecular biology. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2013, 29, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puddu, P.; Puddu, G.M.; Cravero, E.; Vizioli, L.; Muscari, A. The relationship among hyperuricemia, endothelial dysfunction, and cardiovascular diseases: Molecular mechanisms and clinical implications. J. Cardiol. 2012, 59, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoccali, C.; Mallamaci, F. Uric acid, hypertension, and cardiovascular and renal complications. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2013, 15, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.K.; Ford, E.S. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome in individuals with hyperuricemia. Am. J. Med. 2007, 120, 442–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behradmanesh, S.; Horestani, M.K.; Baradaran, A.; Nasri, H. Association of serum uric acid with proteinuria in type 2 diabetic patients. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2013, 18, 44–46. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Doghramji, P.P. Managing your patient with gout: A review of treatment options. Postgrad. Med. J. 2011, 123, 56–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.F.; Fong, W.P.; Cheng, C.H. The dual actions of morin (3,5,7,2′,4′-pentahydroxyflavone) as a hypouricemic agent: Uricosuric effect and xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 316, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.J.; Zhang, G.W.; Pan, J.H.; Gong, D.M. Novel insights into the inhibitory mechanism of kaempferol on xanthine oxidase. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.K.; Zhang, G.W.; Hu, Y.T.; Ma, Y.D. Effect of luteolin on xanthine oxidase: inhibition kinetic and interaction mechanism merging with docking simulation. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 3766–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- State Pharmacopoeia Committee. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; Medical Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2010; pp. 318–319. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, K.W.; Han, J.Y.; Suh, W.S.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, K.R. Two new chemical constituents from leaves of Perilla frutescens var. acuta. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2014, 35, 2151–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banno, N.; Akihisa, T.; Tokuda, H.; Yasukawa, K.; Higashihara, H.; Ukiya, M.; Watanabe, K.; Kimura, Y.; Hasegawa, J.; Nishino, H. Triterpene acids from the leaves of Perilla frutescens and their anti-inflammatory and antitumor-promoting effects. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2004, 68, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.J.; Yan, L.L.; Yin, P.P.; Shi, L.L.; Zhang, J.H.; Liu, Y.J.; Ma, C. Structural characterisation and antioxidant activity evaluation of phenolic compounds from cold-pressed Perilla frutescens var. arguta seed flour. Food Chem. 2014, 164, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.Y.; Hong, C.O.; Lee, H.; Park, S.Y.; Park, B.G.; Lee, K.W. Protective effect of extracts of Perilla frutescens treated with sucrose on tert-butyl hydroperoxide-induced oxidative hepatotoxicity in vitro and in vivo. Food Chem. 2012, 133, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.J.; Yu, C.H.; Ying, K.J.; Hua, J.A.; Dai, X.Y. Hypolipidemic and antioxidant effects of total flavonoids of Perilla Frutescens leaves in hyperlipidemia rats induced by high-fat diet. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.A.; Park, C.S.; Ahn, H.J.; Park, Y.S.; Kim, H.M. Effect of Perilla frutescens var. acuta Kudo and rosmarinic acid on allergic inflammatory reactions. Exp. Biol. Med. 2011, 236, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, Y.; Ju, J. Inhibitory activities of Perilla frutescens britton leaf extract against the growth, migration, and adhesion of human cancer cells. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2015, 9, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urushima, H.; Nishimura, J.; Mizushima, T.; Hayashi, N.; Maeda, K.; Ito, T. Perilla frutescens extract ameliorates DSS-induced colitis by suppressing proinflammatory cytokines and inducing anti-inflammatory cytokines. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2014, 308, G32–G41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, H.I.; Kim, B.T.; Song, G.S.; Kim, Y.S. Structural characterization of phenolic antioxidants from purple perilla (Perilla frutescens var. acuta) leaves. Food Chem. 2014, 148, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, T.; Nishi, M.; Inada, H.; Obata, H.; Abe, S.; Wakashiro, M. Two new potent inhibitors of xanthine oxidase from leaves of Perilla frutescens Britton var. acuta kudo. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1990, 38, 1772–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stavric, B.; Clayman, S.; Gradd, R.E.; Hebert, D. Some in vivo effects in the rat induced by chlorprothixene and potassium oxonate. Pharmacol. Res. Commun. 1975, 7, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.X.; He, M.T.; Tan, H.B.; Gu, W.; Yang, S.X.; Wang, Y.H.; Li, L.; Long, C.L. Xanthine oxidase inhibitors isolated from Piper nudibaccatum. Phytochem. Lett. 2015, 12, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Curtis-Long, M.J.; Yuk, H.J.; Wang, Y.; Song, Y.H.; Jeong, S.H.; Park, K.H. Quantitative analysis of phenolic metabolites from different parts of Angelica keiskei by HPLC–ESI MS/MS and their xanthine oxidase inhibition. Food Chem. 2014, 153, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, S.; Xu, N.Y.; Chu, C.J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, D.F. Chemical constituents of Rabdosia japonica var. glaucocalyx and their anti-complementary activity. Chin. J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2013, 38, 119–203. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.C.; Zheng, Q.X.; Wu, H.F.; Ma, G.X.; Xu, X.D.; Yang, J.S. Water-soluble constituents of Clerodendranthus spicatus. Chin. Pharm. J. 2014, 49, 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Park, K.H.; Lee, M.H.; Kim, H.T.; Seo, W.D.; Kim, J.Y.; Baek, I.Y.; Jang, D.S.; Ha, T.J. Identification, characterisation, and quantification of phenolic compounds in the antioxidant activity-containing fraction from the seed of Korean perilla (Perilla frutescens) cultivars. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flemmig, J.; Kuchta, K.; Arnhold, J.; Rauwald, H.W. Olea europaea leaf (Ph. Eur.) extract as well as several of its isolated phenolics inhibit the gout-related enzyme xanthine oxidase. Phytomedicine 2011, 18, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.Y.; Yin, H.F.; Lan, Z.; Ma, S.W.; Zhang, C.F.; Yang, C.L.; Li, P.; Lin, B.Q. Anti-hyperuricemic and nephroprotective effects of Smilax china L. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 135, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, H.C.; Lo, Y.J.; Lu, F.J. Xanthine-oxidase inhibitors from the leaves of Alsophila spinulosa (hook) tryon. J. Enzym. Inhib. 1994, 8, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.C.; Liu, X.H.; Gao, H.; Fan, M.L.; Liu, K.; Wang, W. Study on inhibition and enzyme kinetics of different solvent extractions from Polygonum cuspidatum on xanthine oxidase. China Pharm. 2015, 26, 494–496. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are available from the authors.
© 2015 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huo, L.-N.; Wang, W.; Zhang, C.-Y.; Shi, H.-B.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.-H.; Guo, B.-H.; Zhao, D.-M.; Gao, H. Bioassay-Guided Isolation and Identification of Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitory Constituents from the Leaves of Perilla frutescens. Molecules 2015, 20, 17848-17859. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules201017848
Huo L-N, Wang W, Zhang C-Y, Shi H-B, Liu Y, Liu X-H, Guo B-H, Zhao D-M, Gao H. Bioassay-Guided Isolation and Identification of Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitory Constituents from the Leaves of Perilla frutescens. Molecules. 2015; 20(10):17848-17859. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules201017848
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuo, Li-Na, Wei Wang, Chun-Yu Zhang, Hai-Bo Shi, Yang Liu, Xiao-Hong Liu, Bing-Hua Guo, Dong-Mei Zhao, and Hua Gao. 2015. "Bioassay-Guided Isolation and Identification of Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitory Constituents from the Leaves of Perilla frutescens" Molecules 20, no. 10: 17848-17859. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules201017848
APA StyleHuo, L.-N., Wang, W., Zhang, C.-Y., Shi, H.-B., Liu, Y., Liu, X.-H., Guo, B.-H., Zhao, D.-M., & Gao, H. (2015). Bioassay-Guided Isolation and Identification of Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitory Constituents from the Leaves of Perilla frutescens. Molecules, 20(10), 17848-17859. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules201017848






