J. Fungi 2022, 8(9), 907; https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8090907 - 26 Aug 2022
Cited by 17 | Viewed by 4072
Abstract
In the present study, we report two new asexual fungal species (i.e., Discosia rhododendricola, Neopestalotiopsis rhododendricola (Sporocadaceae) and a new host for a previously described species (i.e., Diaporthe nobilis; Diaporthaceae). All species were isolated from Rhododendron spp. in
[...] Read more.
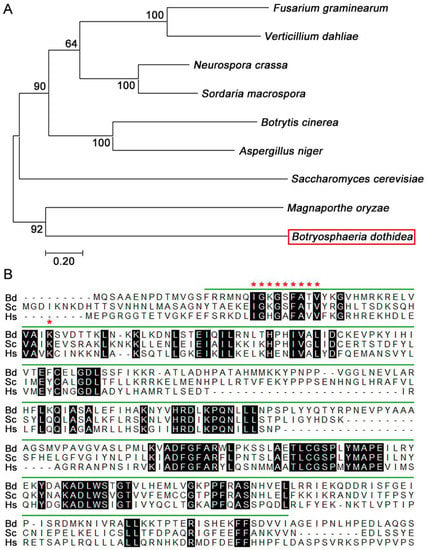
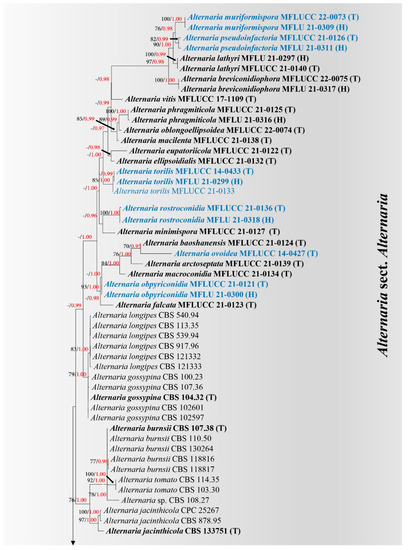
In the present study, we report two new asexual fungal species (i.e., Discosia rhododendricola, Neopestalotiopsis rhododendricola (Sporocadaceae) and a new host for a previously described species (i.e., Diaporthe nobilis; Diaporthaceae). All species were isolated from Rhododendron spp. in Kunming, Yunnan Province, China. All taxa are described based on morphology, and phylogenetic relationships were inferred using a multigenic approach (LSU, ITS, RPB2, TEF1 and TUB2). The phylogenetic analyses indicated that D. rhododendronicola sp. nov. is phylogenetically related to D. muscicola, and N. rhododendricola sp. nov is related to N. sonnaratae. Diaporthe nobilis is reported herein as a new host record from Rhododendron sp. for China, and its phylogeny is depicted based on ITS, TEF1 and TUB2 sequence data.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Ascomycota: Diversity, Taxonomy and Phylogeny)
►
Show Figures