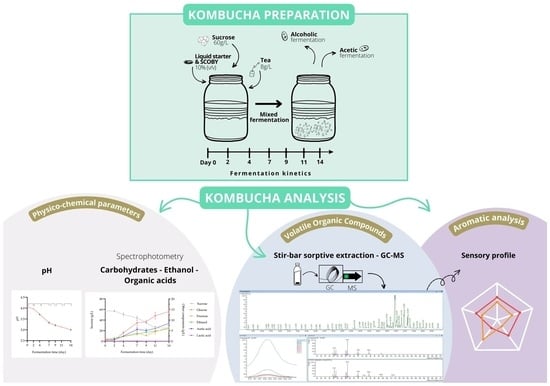
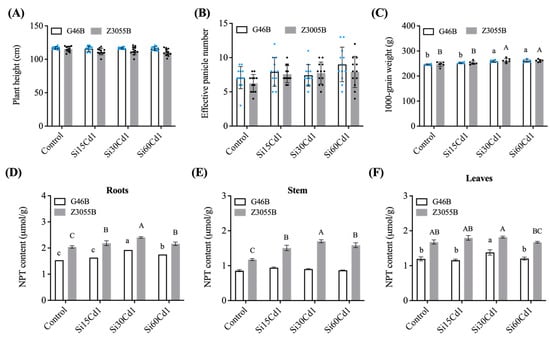
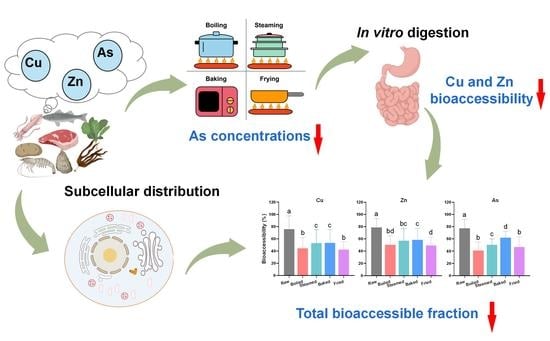
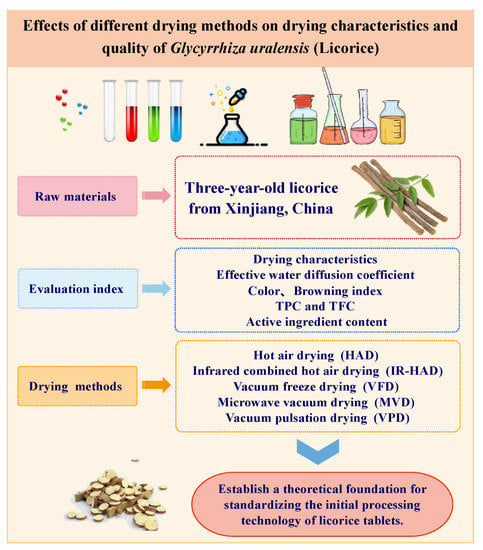
Foods 2023, 12(8), 1661; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12081661 - 16 Apr 2023
Cited by 27 | Viewed by 10492
Abstract
The aim of the research is to investigate whether purchasing decisions about bakery products (bread, snacks and biscuits) are influenced by concerns about health, climate change, biodiversity loss and food waste. The exploratory survey was carried out in two successive moments before and
[...] Read more.
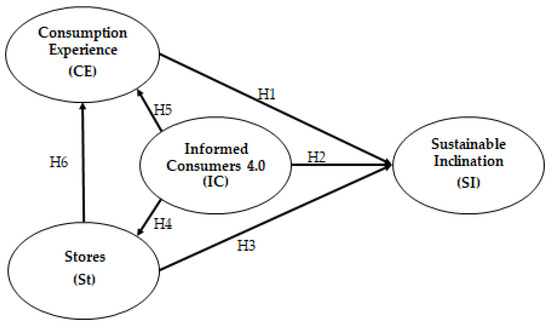
The aim of the research is to investigate whether purchasing decisions about bakery products (bread, snacks and biscuits) are influenced by concerns about health, climate change, biodiversity loss and food waste. The exploratory survey was carried out in two successive moments before and during the health emergency from COVID-19. Before the health emergency, face-to-face interviews were carried out using a structured questionnaire. Data were analyzed by factor analysis, reliability tests and descriptive analysis. Structural equation modeling (SEM) was employed to test the research hypotheses. The results of the modeling analysis of the structural equations highlighted that health and the environment represent an important background in the consumer experience of the respondents and influence the attitude and intention to purchase safe and environmentally friendly bakery products. Furthermore, the results suggest that informed, modern and aware consumers have direct and indirect effects on the intentions to adopt sustainable attitudes. On the contrary, the perception relating to the shops where consumers buy bakery products does not always show a significant influence on the propensity for sustainability. During the health emergency, the interviews were conducted online. Families confined to their homes, buying less in stores, have prepared many baked goods manually at home. The descriptive analysis of this group of consumers shows a growing attention to points of sale and the tendency to use online shopping. Furthermore, the changes in the type of purchases and the importance attributed to the need to reduce food waste emerge.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in the Quality of the Food Supply Chain for Bakery Products)
►
Show Figures