Foods 2022, 11(22), 3712; https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11223712 - 18 Nov 2022
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 5305
Abstract
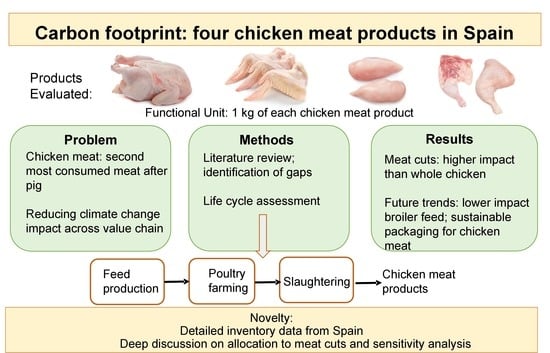
Despite its relatively low environmental impact within the livestock sector, the poultry sector still faces its own environmental challenges that need to be addressed. The present paper uses life cycle assessment to quantify greenhouse gas emissions, from cradle to slaughterhouse gate, of four
[...] Read more.
Despite its relatively low environmental impact within the livestock sector, the poultry sector still faces its own environmental challenges that need to be addressed. The present paper uses life cycle assessment to quantify greenhouse gas emissions, from cradle to slaughterhouse gate, of four chicken meat products: whole carcass, wings, breast fillets, and leg quarters. The main contribution of the present study is that it provides a detailed analysis of different chicken meat cuts, testing mass and economic allocation choices and showing that economic allocation better reflects the causality of the cutting process. We recommend that a distinction should be made between whole carcass and meat cuts, as there are significant differences in meat content and climate change results between these two categories. This is not so clear in the literature, nor in the LEAP guideline for the poultry sector. The study was performed by using disaggregated inventory data from Spain, for the first time. Results show that the major contributors to environmental impact are feed production (>70%), electricity use (10.2%), and fossil fuel combustion (8.1%). Packaging did not significantly contribute to the climate change impact of the chicken products evaluated (0.4–3.4% contribution, depending on the type of packaging and product considered).
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Foods: 10th Anniversary)
►
Show Figures