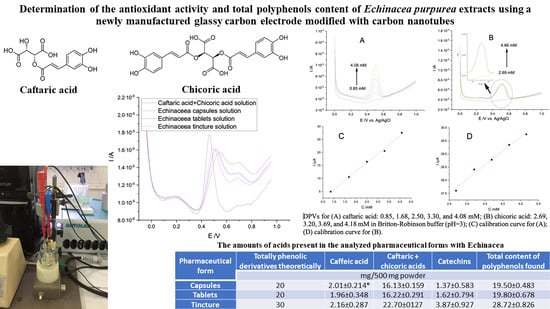
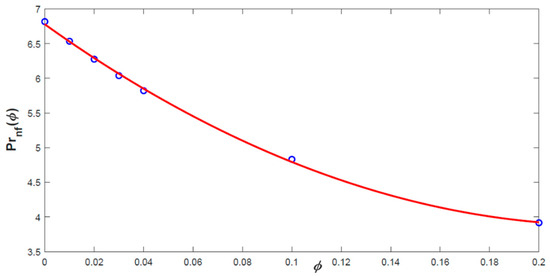
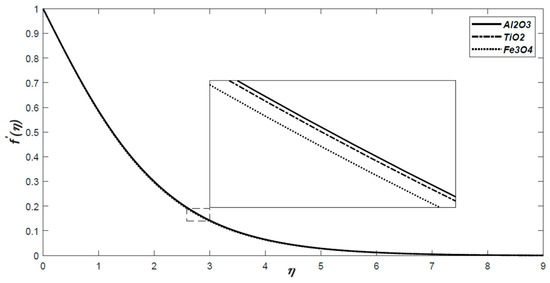
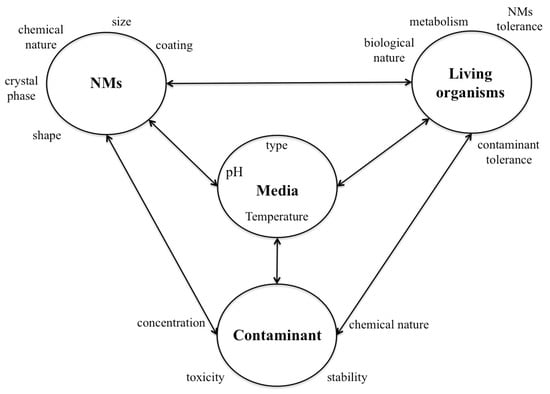
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Low-Carbon Composite Based on MOC, Silica Sand and Ground Porcelain Insulator Waste
by
Adam Pivák, Milena Pavlíková, Martina Záleská, Michal Lojka, Anna-Marie Lauermannová, Ondřej Jankovský and Zbyšek Pavlík
Cited by 22 | Viewed by 3223
Abstract
Magnesium oxychloride cement-based composites (MOC) with silica sand/porcelain waste blended fillers were designed and tested. The objective of the presented research was to design and test low carbon, eco-friendly and viable alternatives to Portland cement-based materials. To make new materials environmentally acceptable and
[...] Read more.
Magnesium oxychloride cement-based composites (MOC) with silica sand/porcelain waste blended fillers were designed and tested. The objective of the presented research was to design and test low carbon, eco-friendly and viable alternatives to Portland cement-based materials. To make new materials environmentally acceptable and sustainable, silica sand applied in the reference composite material was partially substituted by ground porcelain waste (PW) coming from used electrical insulators. The sand substitution ratio was 5, 10, and 15 vol.%. The chemical and mineralogical composition, morphology, and particle size distribution of porcelain waste were measured. For silica sand, porcelain waste, and MgO, specific density, loose bulk density, and Blaine fineness were determined. The effect of porcelain waste on the workability of fresh composite mixtures was characterized by spread diameter. The composites were characterized by their basic structural, mechanical, hygric, and thermal properties. The phase composition and thermal stability at high temperatures of MOC/porcelain waste pastes were also analyzed. Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) analysis helped to indicate main compounds formed within the precipitation of MOC phases and their reaction with porcelain waste. The usage of porcelain waste greatly decreased the porosity of composite matrix, which resulted in high mechanical resistance and reduced and decelerated water imbibition. The 10% sand substitution with porcelain waste brought the best mechanical resistance and the lowest water absorption due to the formation of amorphous phases, water-insoluble aluminosilicates. In case of the thermal performance of the examined composites, the low thermal conductivity of porcelain waste was the contradictory parameter to porosity and the high thermal stability of the phases present in porcelain slightly decreased the thermal decomposition of composites with porcelain waste dosage. Based on the results emerged from the experimental tests it was concluded that the partial substitution of silica sand in MOC composites enabled the development of materials possessing interesting and advanced function and technical parameters.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures