Languages 2023, 8(1), 54; https://doi.org/10.3390/languages8010054 - 12 Feb 2023
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 2307
Abstract
This study investigated language educators’ readiness in coping with language assessment during the global outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic and the enforced move to Emergency Remote Teaching (ERT). This pandemic prompted debates on language assessors’ roles in adjusting to a New Normal. While
[...] Read more.
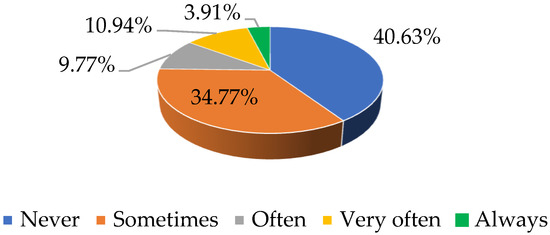
This study investigated language educators’ readiness in coping with language assessment during the global outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic and the enforced move to Emergency Remote Teaching (ERT). This pandemic prompted debates on language assessors’ roles in adjusting to a New Normal. While a good body of research has investigated the role of teacher assessment perceptions versus assessment behavior for many decades, little is known about the factors that may have impacted language educators’ assessment perceptions and practices during the recent crisis. To address this issue, an online survey was administered to 256 language educators. Pearson correlations and simple linear regression were utilized to determine if the language educators’ perceptions of (1) the official assessment measures, (2) purposes, and (3) their assessment self-efficacy were predictors of their assessment practices during this crisis. The results revealed a total absence of any correlations between these variables. The findings suggest that the assessment accommodations adopted by the teachers were not determined by their assessment perceptions. Other factors such as assessment policy and the assessment culture may have shaped their practices during this crisis.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Recent Developments in Language Testing and Assessment)
►
Show Figures