Electronics 2023, 12(6), 1328; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12061328 - 10 Mar 2023
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 2566
Abstract
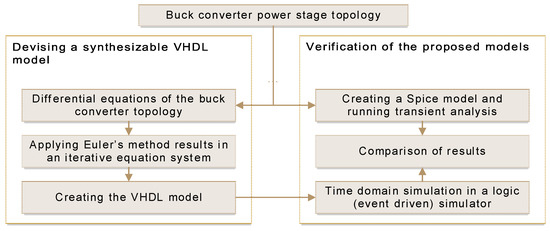
This paper proposes a methodology of delivering the emulation hardware of several step-down converter power stages. The generalized emulator design methodology follows these steps: first, the power stage is described using an ordinary differential equation system; second, the ordinary differential equation system is
[...] Read more.
This paper proposes a methodology of delivering the emulation hardware of several step-down converter power stages. The generalized emulator design methodology follows these steps: first, the power stage is described using an ordinary differential equation system; second, the ordinary differential equation system is solved using Euler’s method, and thus an accurate time-domain model is obtained; next, this time-domain model can be described using either general-purpose programming language (MATLAB, C, etc.) or hardware description language (VHDL, Verilog, etc.). As a result, the emulator has been created; validation of the emulator may be carried out by comparing it to SPICE transient simulations. Finally, the validated emulator can be implemented on the preferred target technology, either in a general-purpose processor or a field programmable gate array. As the emulator relies on the ordinary differential equation system of the power stage, it has better behavioral accuracy than the emulators based on average state space models. Moreover, this paper also presents the design methodology of a manually tuned proportional–integrative–derivative controller deployed on a field programmable gate array.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Hardware in the Loop, Real-Time Simulation and Digital Control of Power Electronics and Drives, 2nd Edition)
►
Show Figures