Coatings 2022, 12(11), 1704; https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12111704 - 9 Nov 2022
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 3493
Abstract
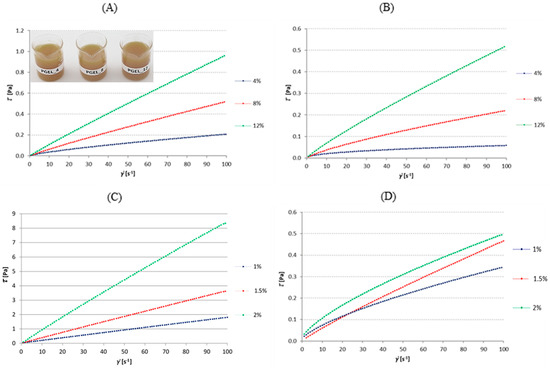
Film-forming solutions based on four types of biopolymers were prepared and their rheological properties were determined. High methylated apple pectin and sodium alginate were used at the concentrations 1%, 1.5%, and 2%, whereas soy protein isolate and pork gelatin were obtained at 4%,
[...] Read more.
Film-forming solutions based on four types of biopolymers were prepared and their rheological properties were determined. High methylated apple pectin and sodium alginate were used at the concentrations 1%, 1.5%, and 2%, whereas soy protein isolate and pork gelatin were obtained at 4%, 8%, and 12%. The parameters determining the production of the appropriate type of packaging film or edible coating are the setting time on the substrate, regardless of its type, and the gelation temperature, which were analyzed in the study by determination of flow curves and rheological parameters of prepared dispersions. The Newtonian model was used to describe the flow curves of the gelatin and sodium alginate solutions, while the Ostwald–de Waele model was used to describe the flow curves of the soy protein isolate and high methylated apple pectin solutions. The apparent viscosity of all solutions increased with increasing biopolymer concentrations, from 0.0042 to 0.0061 Pa·s and from 0.0187 to 0.0884 Pa·s for high-methylated apple pectin and sodium alginate, respectively; whereas, for a protein-based solution the viscosity increase was from 0.024 to 0.100 Pa·s and from 0.0018 to 0.0056 Pa·s for soy and gelatin, respectively. Modulus of elasticity curves appeared only at the highest concentrations, which means that the formation of the continuous structure of film or coating occurs by different mechanisms depending on the biopolymer type and its amount dispersed in aqueous solutions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Innovations in Active Food Packaging during the Pandemic and into the 'New Normal')
►
Show Figures