Appl. Sci. 2019, 9(3), 389; https://doi.org/10.3390/app9030389 - 23 Jan 2019
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 8616
Abstract
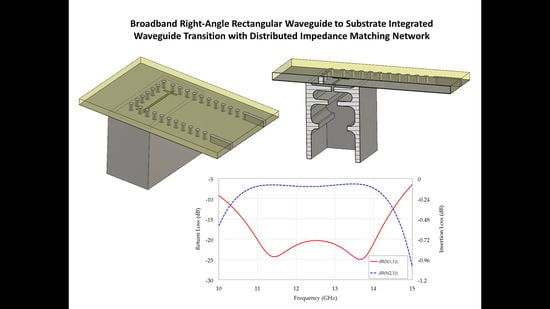
A broadband right-angle rectangular waveguide to substrate integrated waveguide transition for hybrid RWG-SIW (rectangular waveguide–substrate integrated waveguide) feeding networks is presented. The narrower return loss bandwidth issue with respect to in-line configurations is addressed with the introduction of a multi-section matching network consisting
[...] Read more.
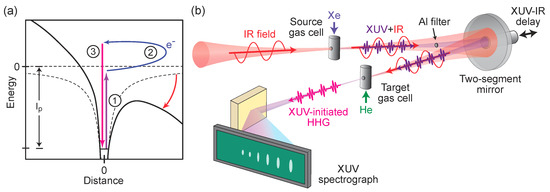
A broadband right-angle rectangular waveguide to substrate integrated waveguide transition for hybrid RWG-SIW (rectangular waveguide–substrate integrated waveguide) feeding networks is presented. The narrower return loss bandwidth issue with respect to in-line configurations is addressed with the introduction of a multi-section matching network consisting of a number of symmetric E-plane irises in the rectangular waveguide section. A hybrid design procedure based on circuit simulation and full-wave optimization is outlined and adopted to synthesize three matching networks with respectively one, two, and three irises, according to the bandwidth to be covered. The design procedure is experimentally validated with a proof-of-concept prototype.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Substrate Integrated Waveguide (SIW) and Its Applications)
►
Show Figures