Appl. Sci. 2022, 12(16), 8074; https://doi.org/10.3390/app12168074 - 12 Aug 2022
Cited by 81 | Viewed by 16963
Abstract
Mushrooms are considered to be functional foods with high nutritional, culinary, and pharmacological values, and there has been an increase in their consumption, both through the diet and in the form of dietary supplements. The present study aimed to briefly review the nutritional
[...] Read more.
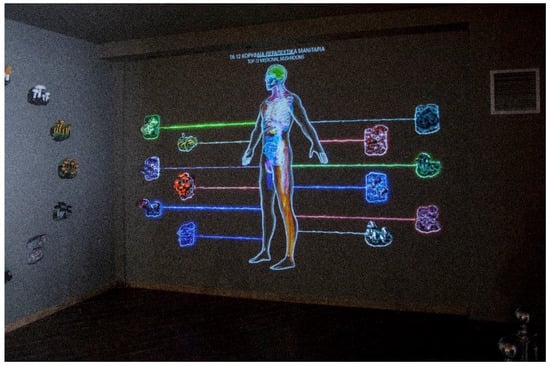
Mushrooms are considered to be functional foods with high nutritional, culinary, and pharmacological values, and there has been an increase in their consumption, both through the diet and in the form of dietary supplements. The present study aimed to briefly review the nutritional composition and biological properties of sixteen mushroom species, as well as to compare the mushrooms’ proximate composition to the analyses conducted at the University of Thessaly, Greece, in cooperation with the Natural History Museum of Meteora and Mushroom Museum. The macronutrient profile of each mushroom was analyzed according to the methods described in the Association of Official Analytical Chemists International, at the School of Agricultural Sciences of the University of Thessaly. The protein content of the mushrooms was found to range between 13.8 g/100 g and 38.5 g/100 g, carbohydrate content ranged between 32 g/100 g and 61.4 g/100 g, and fat content ranged between 0.4 g/100 g and 5.9 g/100 g. Additionally, a serving of 100 g of most species of mushrooms covers 15 to 30% of the daily recommendation of vitamins and trace elements. Based on their compositions, mushrooms were shown to constitute excellent food sources from a nutritional point of view, containing high amounts of dietary fiber and protein, low fat, and reasonable sources of phosphorus, although they were shown to be poor in vitamin C.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Bioactive Compounds from Natural Products - Volume II)
►
Show Figures