Appl. Sci. 2021, 11(21), 10369; https://doi.org/10.3390/app112110369 - 4 Nov 2021
Cited by 14 | Viewed by 4713
Abstract
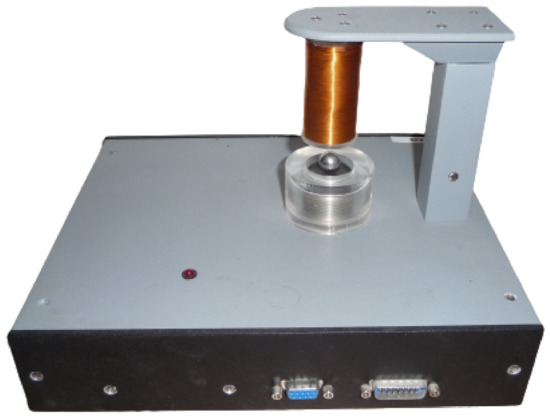
This paper contributes toward research on the control of the magnetic levitation plant, representing a typical nonlinear unstable system that can be controlled by various methods. This paper shows two various approaches to the solution of the controller design based on different closed
[...] Read more.
This paper contributes toward research on the control of the magnetic levitation plant, representing a typical nonlinear unstable system that can be controlled by various methods. This paper shows two various approaches to the solution of the controller design based on different closed loop requirements. Starting from a known unstable linear plant model—the first method is based on the two-step procedure. In the first step, the transfer function of the controlled system is modified to get a stable non-oscillatory system. In the next step, the required first-order dynamic is defined and a model-based PI controller is proposed. The closed loop time constant of this first-order model-based approach can then be used as a tuning parameter. The second set of methods is based on a simplified ultra-local linear approximation of the plant dynamics by the double-integrator plus dead-time (DIPDT) model. Similar to the first method, one possible solution is to stabilize the system by a PD controller combined with a low-pass filter. To eliminate the offset, the stabilized system is supplemented by a simple static feedforward, or by a controller proposed by means of an internal model control (IMC). Another possible approach is to apply for the DIPDT model directly a stabilizing PID controller. The considered solutions are compared to the magnetic levitation system, controlled via the MATLAB/Simulink environment. It is shown that, all three controllers, with integral action, yield much slower dynamics than the stabilizing PD control, which gives one motivation to look for alternative ways of steady-state error compensation, guaranteeing faster setpoint step responses.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue New Trends in Automation Control Systems and Their Applications)
►
Show Figures