Catalysts 2023, 13(4), 648; https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13040648 - 23 Mar 2023
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 3435
Abstract
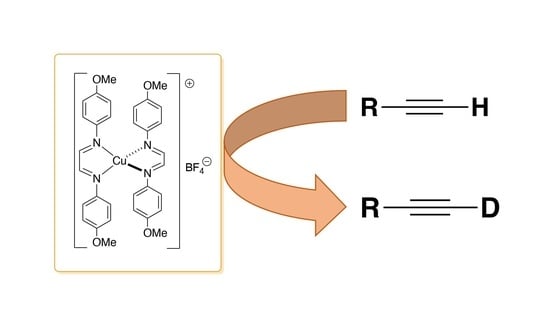
The mild and effective preparation of deuterated organic molecules is an active area of research due to their important applications. Herein, we report an air-stable and easy to access copper(I) complex as catalyst for the deuteration of mono-substituted alkynes. Reactions were carried out
[...] Read more.
The mild and effective preparation of deuterated organic molecules is an active area of research due to their important applications. Herein, we report an air-stable and easy to access copper(I) complex as catalyst for the deuteration of mono-substituted alkynes. Reactions were carried out in technical solvents and in the presence of air, to obtain excellent deuterium incorporation in a range of functionalised alkynes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Catalysis in Organic and Polymer Chemistry)
►
Show Figures