Sustainability 2022, 14(23), 15693; https://doi.org/10.3390/su142315693 - 25 Nov 2022
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 2305
Abstract
Carbon-based conductive additives have been studied for their positive effects on anaerobic digestion (AD) using synthetic substrates, but their importance in wastewater sludge digestion has not been sufficiently explored. This research investigated and compared the effects of two conductive materials (graphene and petroleum
[...] Read more.
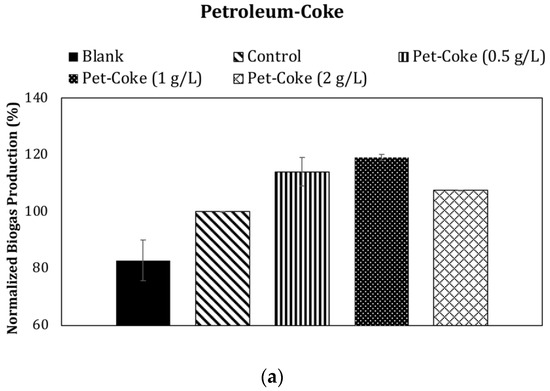
Carbon-based conductive additives have been studied for their positive effects on anaerobic digestion (AD) using synthetic substrates, but their importance in wastewater sludge digestion has not been sufficiently explored. This research investigated and compared the effects of two conductive materials (graphene and petroleum coke) with and without trace metal supplementation. The results indicated that supplementing reactors with graphene and petroleum coke could significantly improve biogas production. The supplementation of 1 g/L petroleum coke and 2 g/L graphene, without trace metal addition, led to an increase in the biogas production by 19.10 ± 1.04% and 16.97 ± 5.00%, respectively. Thus, it can be concluded that petroleum coke, which is an oil refinery by-product, can be used to enhance biogas production in a similar way to other carbon-based conductive materials that are currently available on the market. Moreover, using petroleum coke and graphene, the average chemical oxygen demand (COD) removal was 42.84 ± 1.23% and 42.80 ± 0.45%, respectively, without the addition of trace metals. On the other hand, supplementation of the reactors with trace elements resulted in a COD removal of 34.65 ± 0.43% and 34.05 ± 0.45% using petroleum coke and graphene, respectively.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Anaerobic Environmental Biotechnology and Sustainability II)
►
Show Figures