Sustainability 2022, 14(21), 13734; https://doi.org/10.3390/su142113734 - 23 Oct 2022
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 3502
Abstract
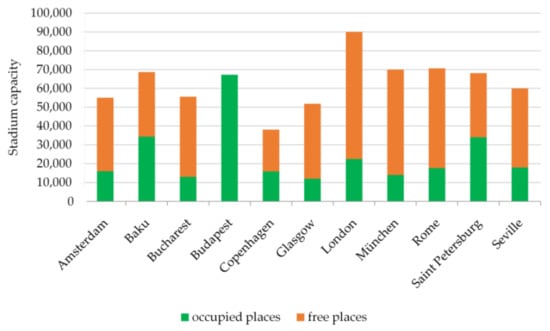
The People’s Republic of China (PRC) has appeared to be inattentive towards the globally lobbied Sport for Development and Peace (SDP) movement that endeavors to leverage sport for non-sporting development, currently subscribing to the United Nations’ 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). By adopting
[...] Read more.
The People’s Republic of China (PRC) has appeared to be inattentive towards the globally lobbied Sport for Development and Peace (SDP) movement that endeavors to leverage sport for non-sporting development, currently subscribing to the United Nations’ 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). By adopting the concept of ‘tiyu (体育)’—the supposed Chinese counterpart of ‘sport’—which also seeks to achieve wider objectives grounded on its premise of ‘body cultivation’, this paper proceeds with a text-based qualitative study incorporating document analysis and literature review to examine its current links to SDP. The findings suggest that: (1) While the national development foci of the PRC have demonstrated alignment with the SDGs, its tiyu policies have not. (2) Mainstream SDP projects have failed to be accommodated in the PRC, although some non-SDP tiyu practices have shown a commitment to SDP-desired outcomes. (3) The relative lack of interest in SDP in the PRC has not prevented some tiyu scholars from heeding this movement. Accordingly, this paper assesses the prospects of changing attitudes in the PRC toward SDP.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Contributions of the SDGs as Drivers of Sustainability through Physical Activity and Sport)