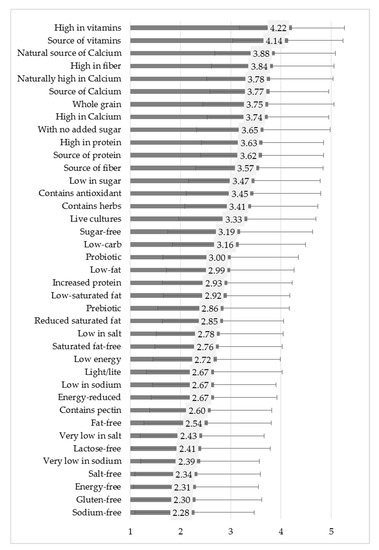
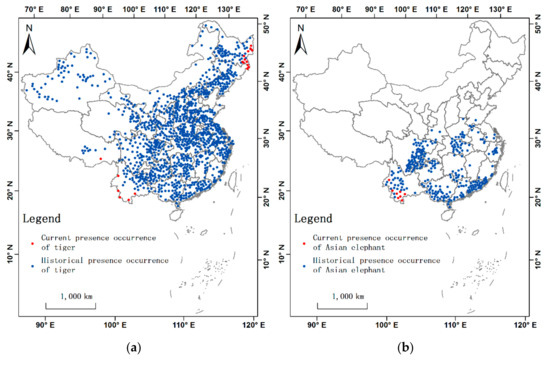
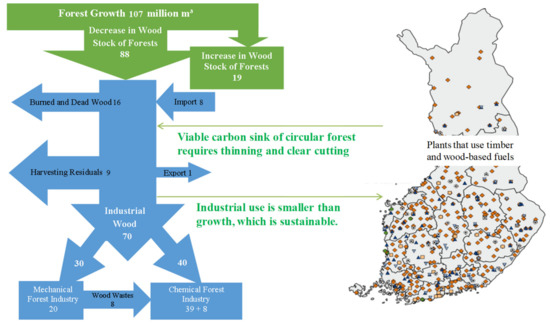
Sustainability 2020, 12(7), 2752; https://doi.org/10.3390/su12072752 - 1 Apr 2020
Cited by 48 | Viewed by 4943
Abstract
►
Show Figures
By exploring the cooling potential of tree quantity, ground albedo, green roofs and their combinations in local climate zone (LCZ)-4, LCZ-5, and LCZ-6, this study focuses on the optimum cooling level that can be achieved in open residential regions in Changsha. It designs
[...] Read more.
By exploring the cooling potential of tree quantity, ground albedo, green roofs and their combinations in local climate zone (LCZ)-4, LCZ-5, and LCZ-6, this study focuses on the optimum cooling level that can be achieved in open residential regions in Changsha. It designs and models 39 scenarios by integrating in situ measurement and ENVI-met numerical simulation and further compares cooling effects of various combinations of the cooling factors. The results show that (1) an increased number of trees and higher albedo are more effective compared to green roofs in reducing summer potential temperatures at street level (2 m high) in three LCZs. Negative correlations are observed in the pedestrian air temperature with trees and ground albedo; (2) the effects of cooling factors vary among different LCZ classes, with the increased 60% more trees leading to lower outdoor temperatures for LCZ-4 (0.28 °C), LCZ-5 (0.39 °C), and LCZ-6 (0.54 °C), while higher albedo of asphalt surface (increased by 0.4) is more effective in LCZ-4 (reaches to 0.68 °C) 14:00, compare to LCZ-5 (0.49 °C) and LCZ-6 (0.38 °C); (3) applying combined cooling methods can provoke air temperature reduction (up to 0.96 °C), especially when higher levels of tree quantities (increased by 60%) are coupled with cool ground materials (albedo increased by 0.4). The results can contribute useful information for improving thermal environment in existing residential regions and future residential planning.
Full article