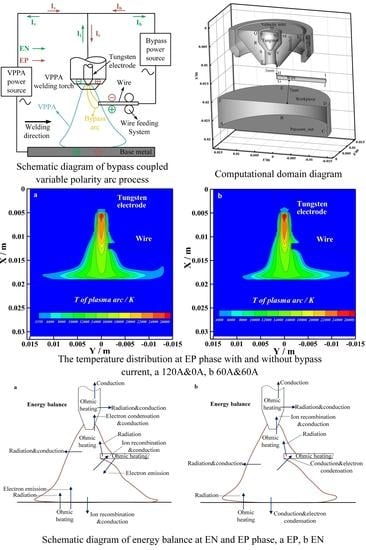
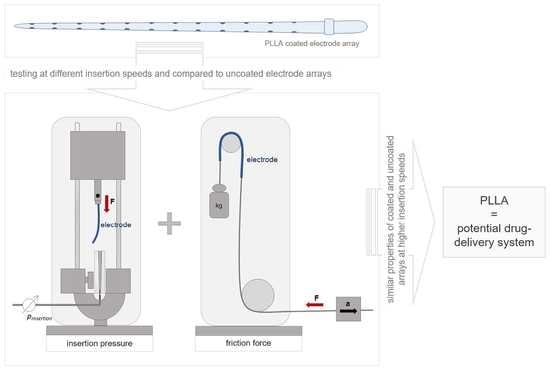
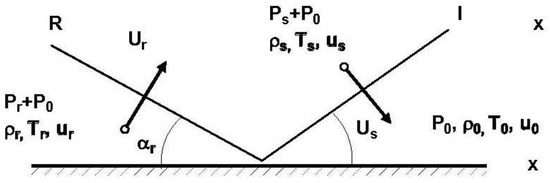
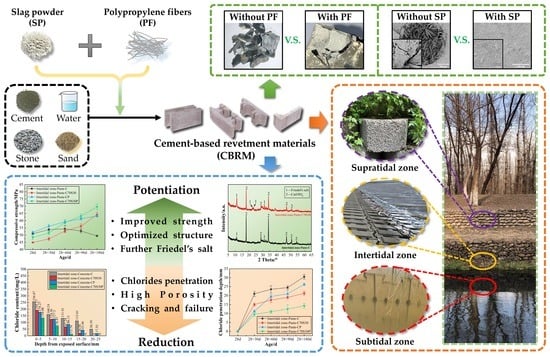
Materials 2022, 15(9), 2961; https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15092961 - 19 Apr 2022
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 2013
Abstract
►
Show Figures
Silicone rubber (SR) exhibits unique flame-retardant and fireproof properties and can be ceramized at high temperatures to cover the surface of an object that needs fire protection. In this paper, the influence of low-melting-point frit content on the expandable performance of SR has
[...] Read more.
Silicone rubber (SR) exhibits unique flame-retardant and fireproof properties and can be ceramized at high temperatures to cover the surface of an object that needs fire protection. In this paper, the influence of low-melting-point frit content on the expandable performance of SR has been investigated, and a decrease in the ceramization temperature with an increase in the frit content has been observed. The sample began to expand at 850 °C, and an expansion of 157% and compressive strength of 1.99 MPa were attained at 950 °C. The increased frit content resulted in a larger liquid phase, which covered the surface of the matrix owing to surface tension. This made the escape of small-molecule gaseous substances generated by decomposition difficult: this resulted in the expansion of the SR matrix. The relationships between composite compositions and expansibility as well as the degree of ceramization were also explored through performance tests. It was found that the formation of eutectic substances between frits and the matrix resulted in a decrease in the temperature of ceramization, which in turn contributed to the formation of highly intumescent ceramifiable SR.
Full article