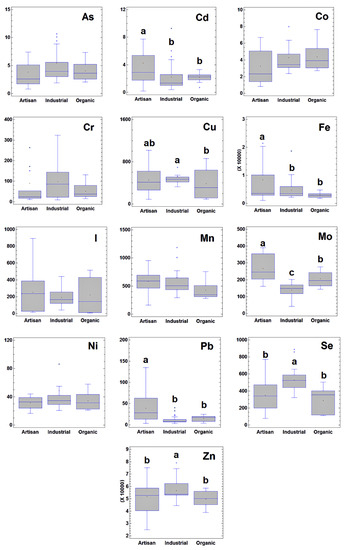
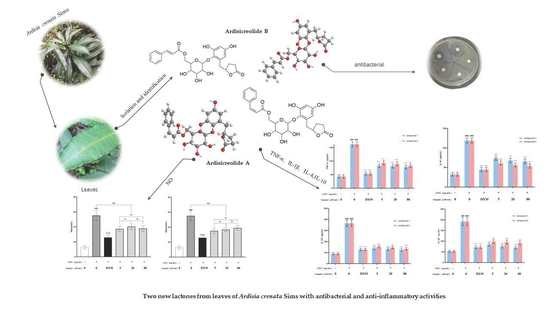
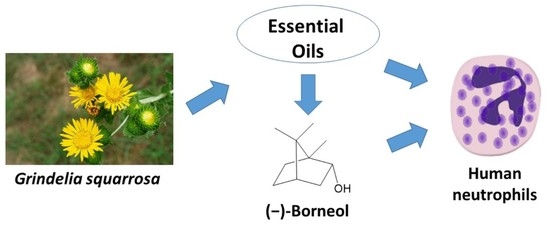
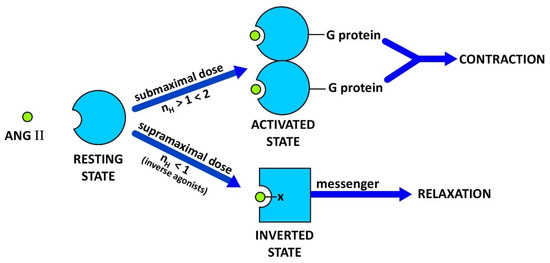
Molecules 2022, 27(15), 4956; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27154956 - 4 Aug 2022
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 2192
Abstract
►
Show Figures
In this work, the interactions between hyaluronic acid and bovine serum albumin were investigated. The film-forming properties of the mixture were proven, and the mechanical and surface properties of the films were measured. The results showed the interactions between hyaluronic acid and albumin,
[...] Read more.
In this work, the interactions between hyaluronic acid and bovine serum albumin were investigated. The film-forming properties of the mixture were proven, and the mechanical and surface properties of the films were measured. The results showed the interactions between hyaluronic acid and albumin, mainly by hydrogen bonds. Molecular docking was used for the visualization of the interactions. The films obtained from the mixture of hyaluronic acid possessed different properties to films obtained from the single component. The addition of bovine serum albumin to hyaluronic acid led to a decrease in the mechanical properties, and to an increase in the surface roughness of the film. The new materials that have been obtained by blending can form a new group of materials for biomedicine and cosmetology.
Full article