1
Department of Medicinal Botanicals and Health Applications, Da-Yeh University, Changhua 51591, Taiwan
2
Cheng Ching General Hospital, Taichung 42881, Taiwan
3
Horien International Co., Ltd., Taichung 42881, Taiwan
4
Pemay Biomedical Technology Corp, Taichung 41348, Taiwan
Molecules 2014, 19(4), 4681-4694; https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19044681 - 15 Apr 2014
Cited by 51 | Viewed by 8594
Abstract
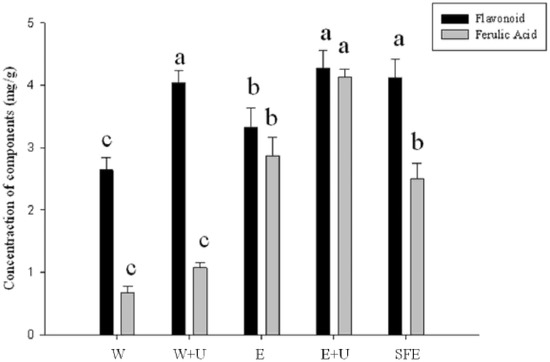
In this study, ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE) and other methods of extracting flavonoid compounds and ferulic acid (FA) from S. sinensis were investigated. Five different extraction methods, including water extraction (W), water extraction using UAE (W+U), 75% ethanol extraction (E), 75% ethanol extraction using
[...] Read more.
In this study, ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE) and other methods of extracting flavonoid compounds and ferulic acid (FA) from S. sinensis were investigated. Five different extraction methods, including water extraction (W), water extraction using UAE (W+U), 75% ethanol extraction (E), 75% ethanol extraction using UAE (E+U), and supercritical CO2 extraction (SFE) were applied in the extraction of bioactive compounds (flavonoids and ferulic acid) in order to compare their efficiency. The highest yield of flavonoids (4.28 mg/g) and ferulic acid (4.13 mg/g) content was detected in the E+U extract. Furthermore, S. sinensis extracts obtained by E+U show high antioxidant activity, and IC50 values of 0.47 mg/mL for DPPH radicals and 0.205 mg/mL for metal chelating activity. The total antioxidant assay shows superoxide radical scavenging capacity and in vitro mushroom tyrosinase inhibition in a dose-dependent manner, suggesting that E+U can be used for extraction of bioactive compounds from S. sinensis.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Natural Products Chemistry)
▼
Show Figures