Effects of Wash-Out Dynamics on Nitrifying Bacteria in Aerobic Granular Sludge During Start-Up at Gradually Decreased Settling Time
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reactor Set-Up
2.2. Medium
2.3. Chemical Analysis and Microscopy
2.4. DNA Extraction and Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)
2.5. PCR Amplification and Terminal Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (T-RFLP)
3. Results and Discussion
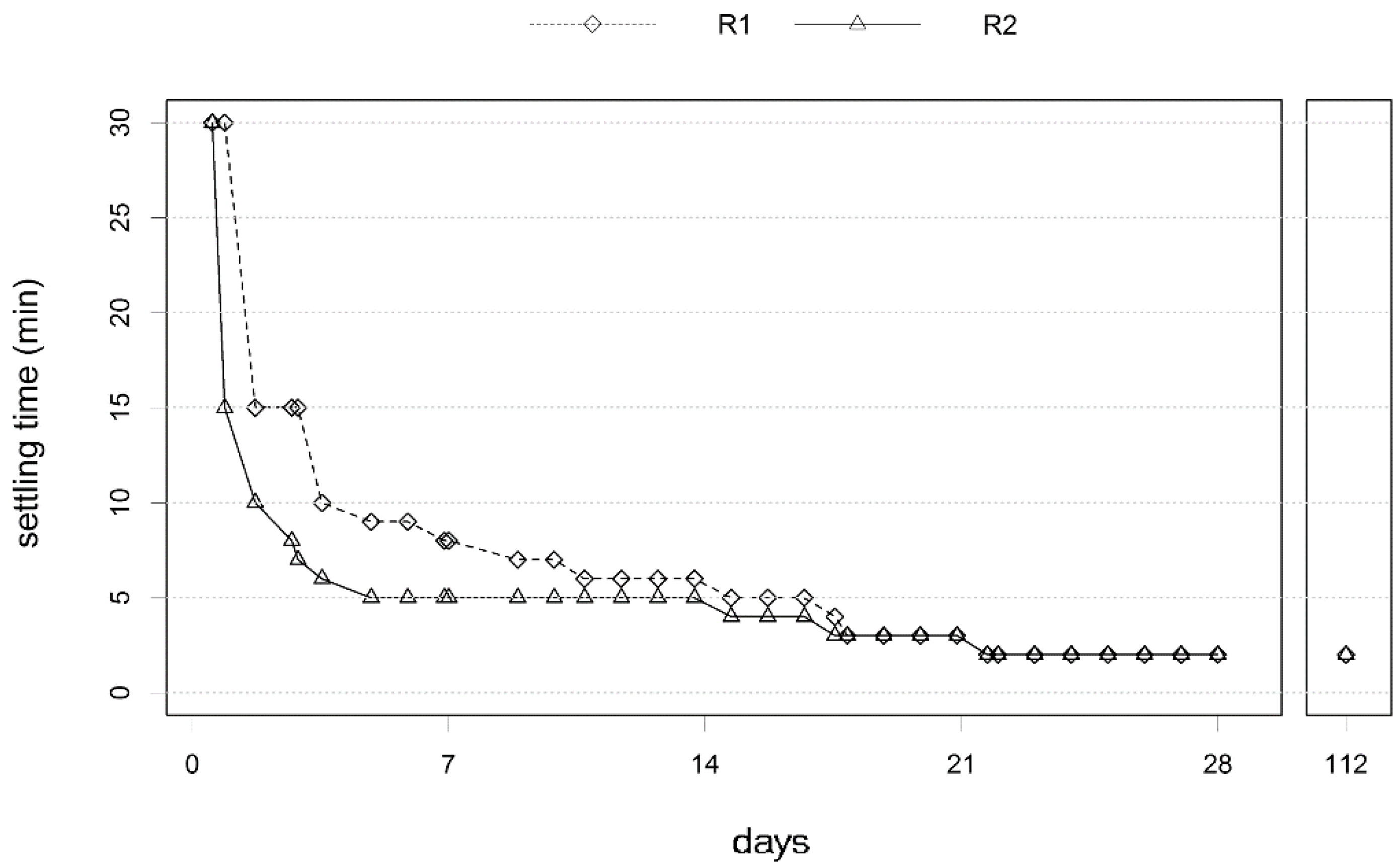
3.1. Biomass Retention and Granulation
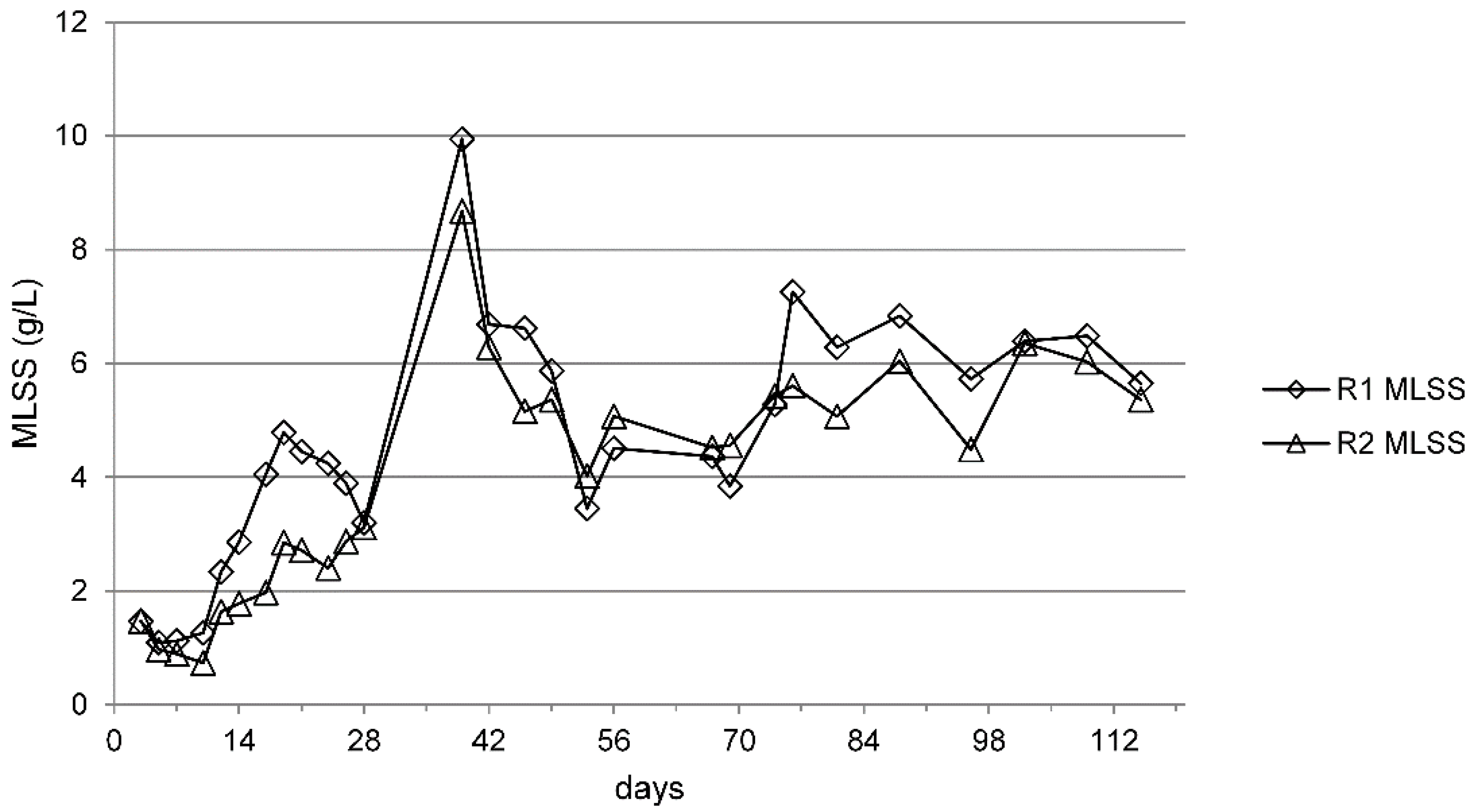
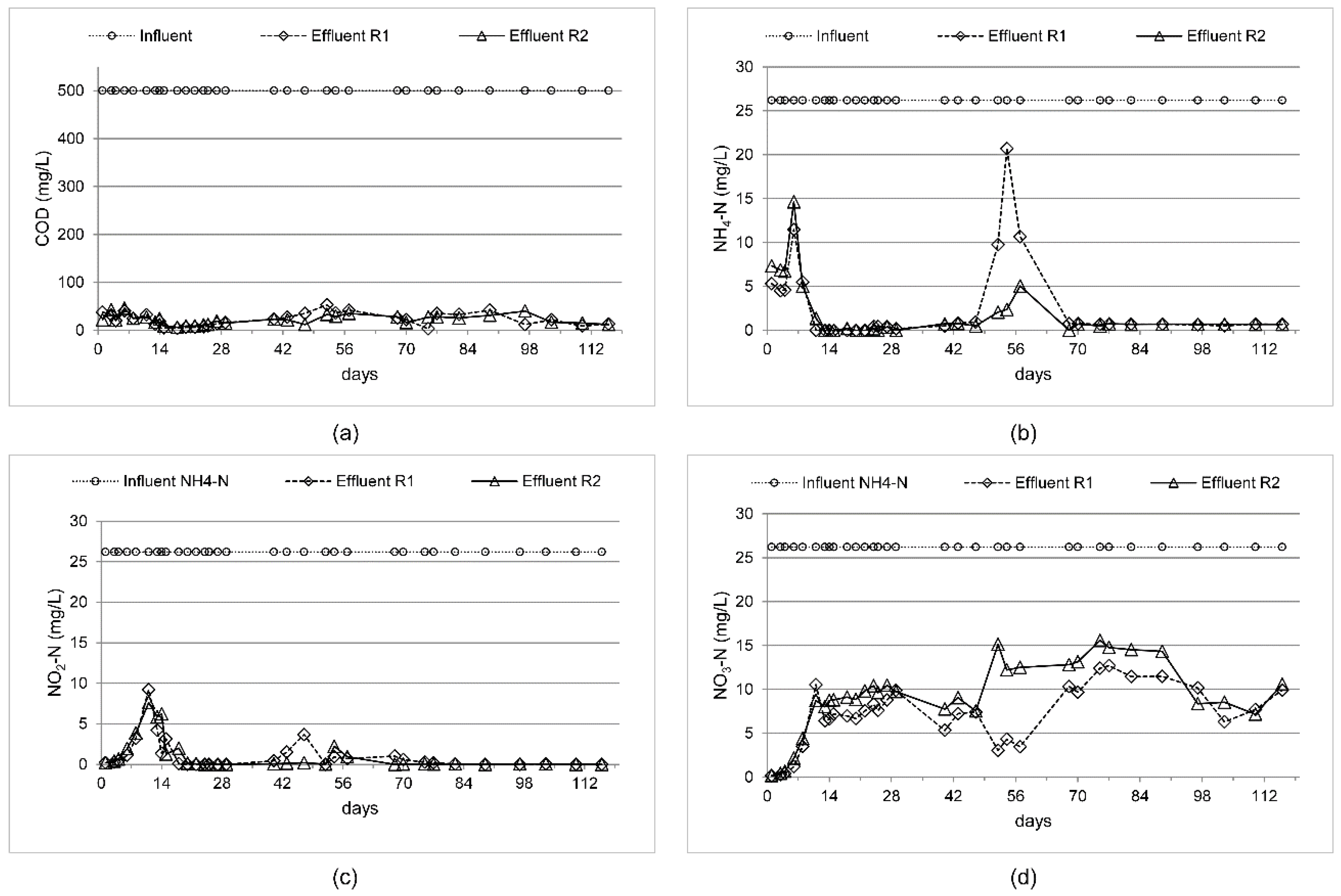
3.2. Process Performance
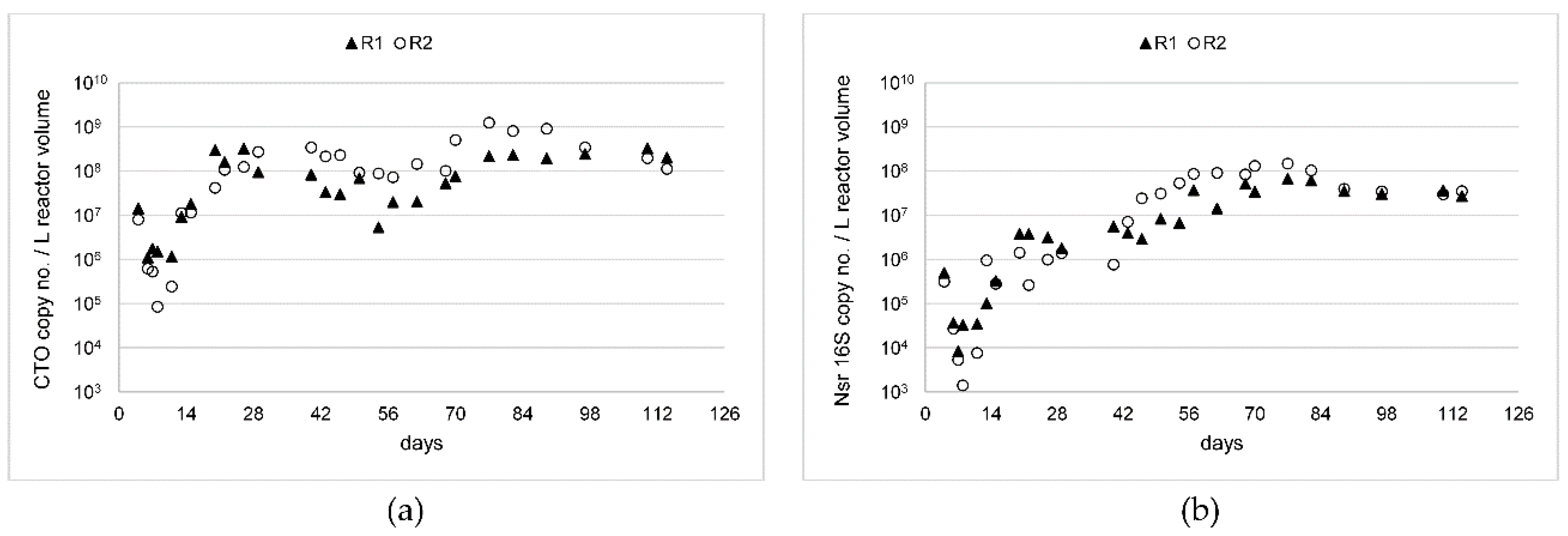
3.3. Abundance of AOB and NOB
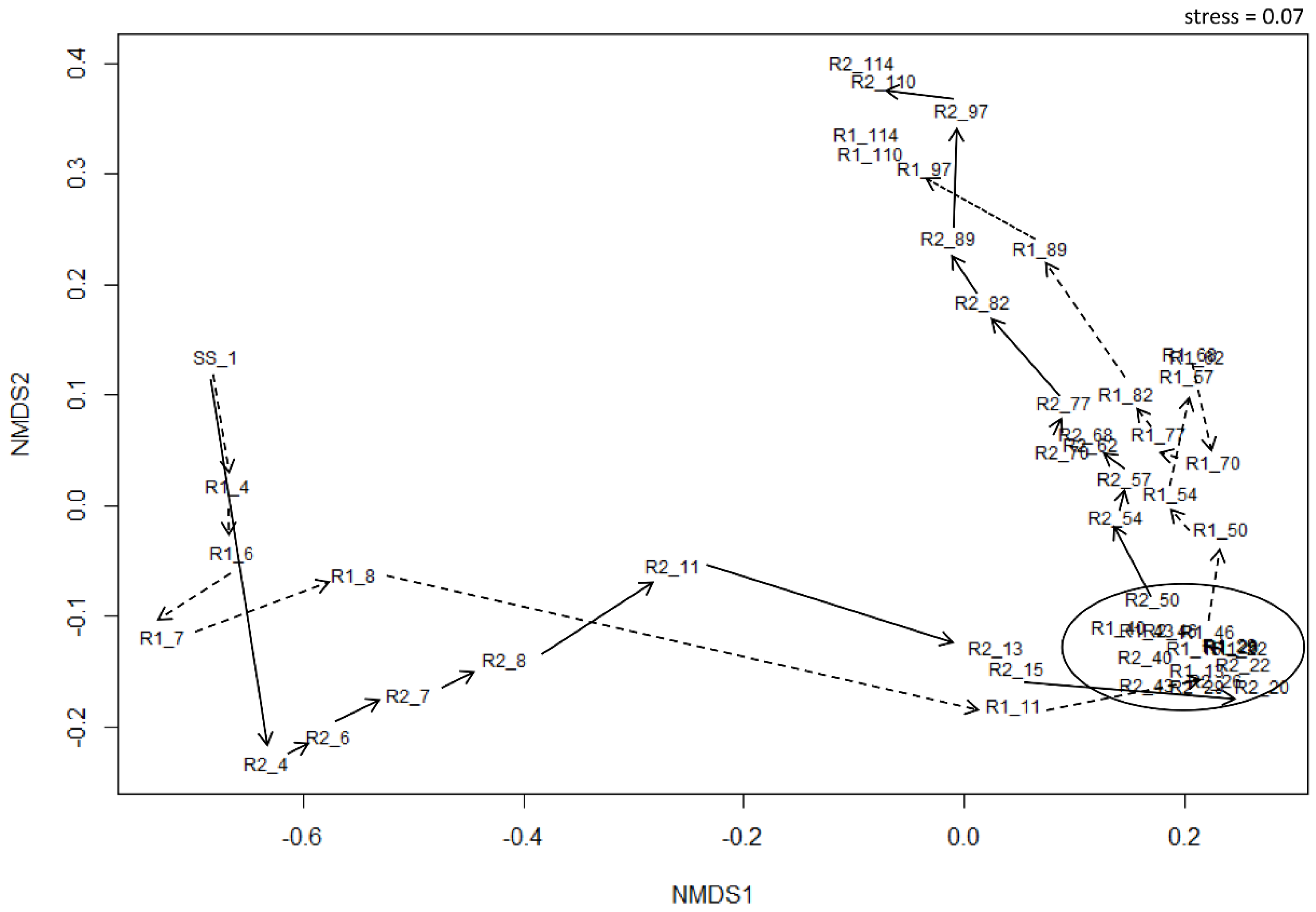
3.4. Bacterial Community Structure
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AOB | ammonium oxidizing bacteria |
| COD | chemical oxygen demand |
| MLSS | mixed liquid suspended solids |
| MLVSS | mixed liquid volatile suspended solids |
| NMDS | non-metric multidimensional scaling |
| NOB | nitrite oxidizing bacteria |
| OLR | organic loading rate |
| qPCR | quantitative polymerase chain reaction |
| SRT | sludge retention time |
| TN | total nitrogen |
| TRF | terminal restriction fragment |
| T-RFLP | terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism |
| TSS | total suspended solids |
References
- Mishima, K.; Nakamura, M. Self-Immobilization of aerobic activated sludge-a pilot study of the aerobic upflow municipal sewage treatment. Water Sci. Technol. 1991, 23, 981–990. [Google Scholar]
- Morgenroth, E.; Sherden, T.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Heijnen, J.J.; Wilderer, P.A. Aerobic granular sludge in a sequencing batch reactor. Water Res. 1997, 31, 3191–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Show, K.-Y.; Lee, D.-J.; Tay, J.-H. Aerobic granulation: Advances and challenges. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 167, 1622–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.Z.; Mondal, P.K.; Sabir, S. Aerobic granulation for wastewater bioremediation: A review. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2013, 91, 1045–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindhu, B.K.; Madhu, G. Selection pressure theory for aerobic granulation-an overview. Int. J. Environ. Waste Manag. 2014, 13, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Dai, X.; Lv, M.; Xu, X. Correlation analysis of major control factors for the formation and stabilization of aerobic granule. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2013, 20, 3165–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adav, S.S.; Lee, D.-J.; Lai, J.-Y. Aerobic granulation in sequencing batch reactors at different settling times. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 5359–5361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Liu, Y.; Tay, J.H. Effect of settling time on aerobic granulation in sequencing batch reactor. Biochem. Eng. J. 2004, 21, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadrzadeh, F.; Dulekgurgen, E. Improving the settling properties of activated sludge by gradually decreasing the settling time. Desalin. Water Treat. 2014, 52, 2465–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, K.Z.; Wang, C.; Fang, H. Cultivation of Aerobic Granular Sludge under Selective Pressure in a Sequencing Batch Reactor. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 255, 3037–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tay, J.-H. The essential role of hydrodynamic shear force in the formation of biofilm and granular sludge. Water Res. 2002, 36, 1653–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, S.M.S.; Irvine, R.L. Dissolved oxygen as a key parameter to aerobic granule formation. Water Sci. Technol. 2008, 58, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, J.H.; Liu, Q.S.; Liu, Y. The effect of upflow air velocity on the structure of aerobic granules cultivated in a sequencing batch reactor. Water Sci. Technol. 2004, 49, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.-Q.; Tay, J.-H. Cultivation of aerobic granules in a bubble column and an airlift reactor with divided draft tubes at low aeration rate. Biochem. Eng. J. 2007, 34, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McSwain, B.S.; Irvine, R.L.; Wilderer, P.A. The influence of settling time on the formation of aerobic granules. Water Sci. Technol. 2004, 50, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Weissbrodt, D.G.; Lochmatter, S.; Ebrahimi, S.; Rossi, P.; Maillard, J.; Holliger, C. Bacterial Selection during the Formation of Early-Stage Aerobic Granules in Wastewater Treatment Systems Operated Under Wash-Out Dynamics. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.Q.; Kong, Y.H.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, X.; Wong, F.S.; Tay, J.H.; Zhu, J.R.; Jiang, W.J.; Liu, W.T. Microbial population dynamics of granular aerobic sequencing batch reactors during start-up and steady state periods. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 62, 1281–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Yang, S.; Li, X.; Gu, J. Microbial population dynamics during aerobic sludge granulation at different organic loading rates. Water Res. 2008, 42, 3552–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Chen, Z.; Qiu, Z.G.; Jin, M.; Chen, Z.Q.; Chen, Z.L.; Li, J.W.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.F. Dynamic and distribution of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria communities during sludge granulation in an anaerobic-aerobic sequencing batch reactor. Water Res. 2011, 45, 6207–6216. [Google Scholar]
- Su, K.-Z.; Ni, B.-J.; Yu, H.-Q. Modeling and optimization of granulation process of activated sludge in sequencing batch reactors. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2013, 110, 1312–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tay, J.H.; Liu, Q.S.; Liu, Y. Microscopic observation of aerobic granulation in sequential aerobic sludge blanket reactor. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 91, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1995.
- Lane, D.J. 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In Nucleic Acid Techniques in Bacterial Systematics; Stackebrandt, E., Goodfellow, E., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd: Chichester, UK, 1991; pp. 115–175. [Google Scholar]
- Fredriksson, N.J.; Hermansson, M.; Wilén, B. Tools for T-RFLP data analysis using Excel. BMC Bioinform. 2014, 15, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. Available online: http://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 21 April 2016).
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Peter, S.M.; Henry, H.S.; Helene, W. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R package version 2.0–10. Available online: http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 21 April 2016).
- Clarke, K.R.; Warwick, R.M. Change in Marine Communities : An Approach to Statistical Analysis and Interpretation; PRIMER-E Ltd.: Plymouth, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.-W.; Qin, L.; Liu, Y.-Q.; Tay, J.-H. Selection pressure-driven aerobic granulation in a sequencing batch reactor. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2005, 67, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhao, H.; Yang, H. Microbial community and N removal of aerobic granular sludge at high COD and N loading rates. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 143, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimi, S.; Gabus, S.; Rohrbach-Brandt, E.; Hosseini, M.; Rossi, P.; Maillard, J.; Holliger, C. Performance and microbial community composition dynamics of aerobic granular sludge from sequencing batch bubble column reactors operated at 20 °C, 30 °C, and 35 °C. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 87, 1555–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Val del Río, Á.; Morales, N.; Figueroa, M.; Mosquera-Corral, A.; Campos, J.L.; Méndez, R. Effect of coagulant-flocculant reagents on aerobic granular biomass. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2012, 87, 908–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, D.W.; Knapp, C.W.; Van Vleck, E.S.; Bloor, K.; Lane, T.B.; Graham, C.E. Experimental demonstration of chaotic instability in biological nitrification. ISME J. 2007, 1, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkler, M.K.H.; Kleerebezem, R.; de Bruin, L.M.M.; Verheijen, P.J.T.; Abbas, B.; Habermacher, J.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Microbial diversity differences within aerobic granular sludge and activated sludge flocs. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 7447–7458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szabó, E.; Hermansson, M.; Modin, O.; Persson, F.; Wilén, B.-M. Effects of Wash-Out Dynamics on Nitrifying Bacteria in Aerobic Granular Sludge During Start-Up at Gradually Decreased Settling Time. Water 2016, 8, 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8050172
Szabó E, Hermansson M, Modin O, Persson F, Wilén B-M. Effects of Wash-Out Dynamics on Nitrifying Bacteria in Aerobic Granular Sludge During Start-Up at Gradually Decreased Settling Time. Water. 2016; 8(5):172. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8050172
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzabó, Enikö, Malte Hermansson, Oskar Modin, Frank Persson, and Britt-Marie Wilén. 2016. "Effects of Wash-Out Dynamics on Nitrifying Bacteria in Aerobic Granular Sludge During Start-Up at Gradually Decreased Settling Time" Water 8, no. 5: 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8050172
APA StyleSzabó, E., Hermansson, M., Modin, O., Persson, F., & Wilén, B.-M. (2016). Effects of Wash-Out Dynamics on Nitrifying Bacteria in Aerobic Granular Sludge During Start-Up at Gradually Decreased Settling Time. Water, 8(5), 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8050172





