Dry/Wet Conditions Monitoring Based on TRMM Rainfall Data and Its Reliability Validation over Poyang Lake Basin, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Data
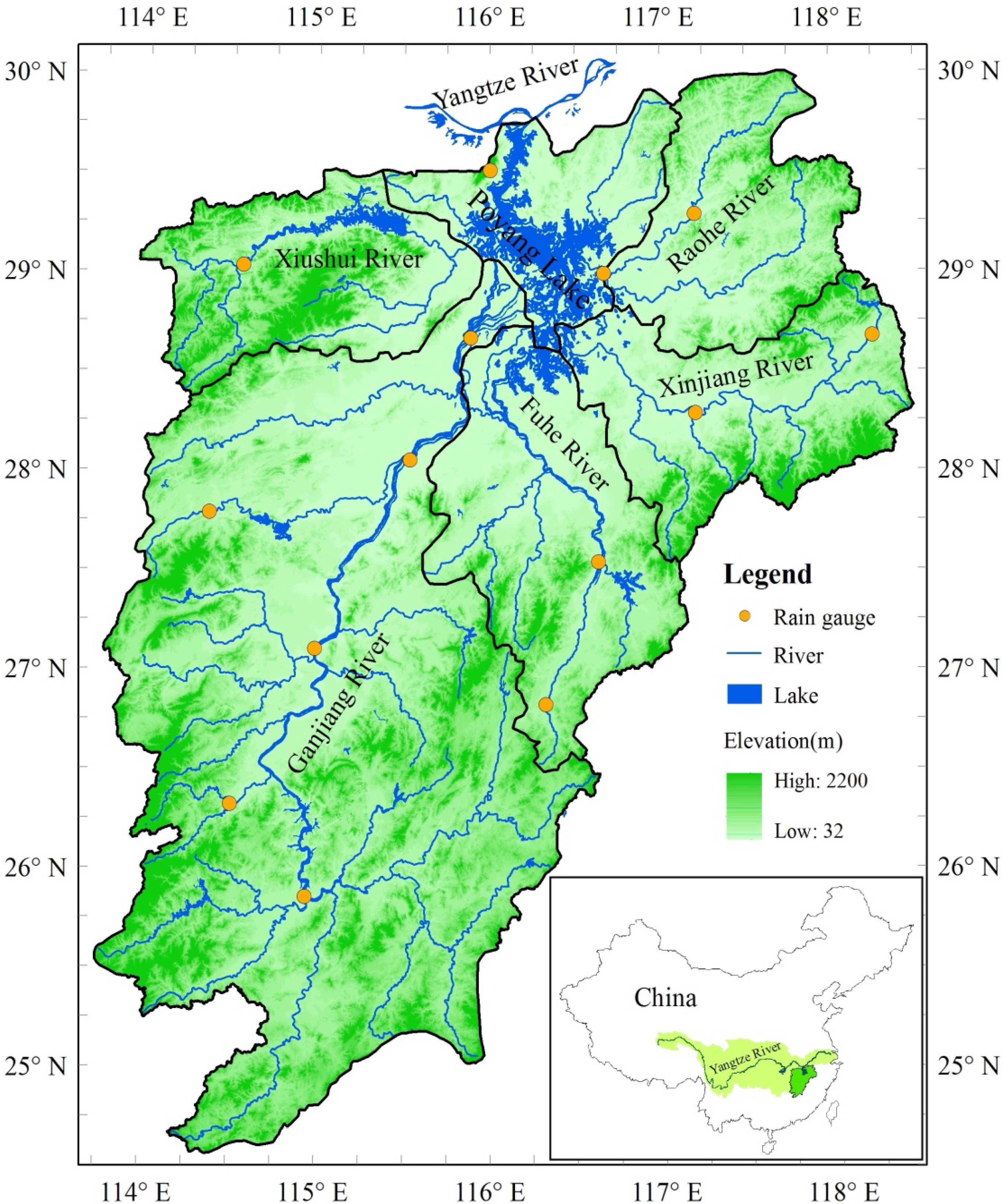
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Z index Method
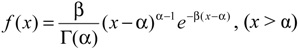
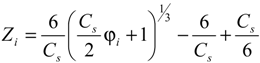
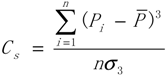
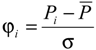
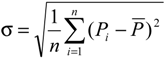
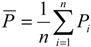
| Class | Type | Z value | SPI value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Severely wet | Z > 1.96 | SPI > 2.0 |
| 2 | Moderately wet | 1.44 < Z ≤ 1.96 | 1.5 < SPI ≤ 2.0 |
| 3 | Abnormally wet | 0.84 < Z ≤ 1.44 | 1.0 < SPI ≤ 1.5 |
| 4 | Normal | −0.84 ≤ Z ≤ 0.84 | −1.0 ≤ SPI ≤ 1.0 |
| 5 | Abnormally dry | −1.44 ≤ Z < −0.84 | −1.5 ≤ SPI < −1.0 |
| 6 | Moderately dry | −1.96 ≤ Z < −1.44 | −2.0 ≤ SPI < −1.5 |
| 7 | Severely dry | Z < −1.96 | SPI < −2.0 |
2.2.2. SPI Method
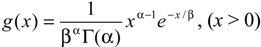
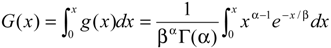
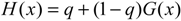
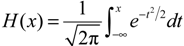


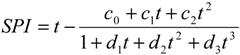
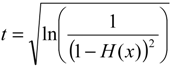
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Validation of TRMM Rainfall with Rain Gauges Data
| Sub-basin | Areal average (mm/day) | Max. daily rainfall (mm/day) | Max. 5-day rainfall (mm/5day) | Annual rainfall (mm/year) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gauge | TRMM | Gauge | TRMM | Gauge | TRMM | Gauge | TRMM | |
| Xiushui | 8.75 | 7.55 | 157.2 | 152.9 | 289.2 | 280.5 | 1642 | 1762 |
| Ganjiang | 6.14 | 5.04 | 68.8 | 92.9 | 155.2 | 171.4 | 1631 | 1642 |
| Fuhe | 8.43 | 6.67 | 99.5 | 113.4 | 300.5 | 268.7 | 1793 | 1770 |
| Xinjiang | 8.99 | 7.67 | 145.1 | 157.5 | 453.7 | 320.8 | 1901 | 1880 |
| Raohe | 10.03 | 8.72 | 134.1 | 143.1 | 371.6 | 320.7 | 1747 | 1894 |
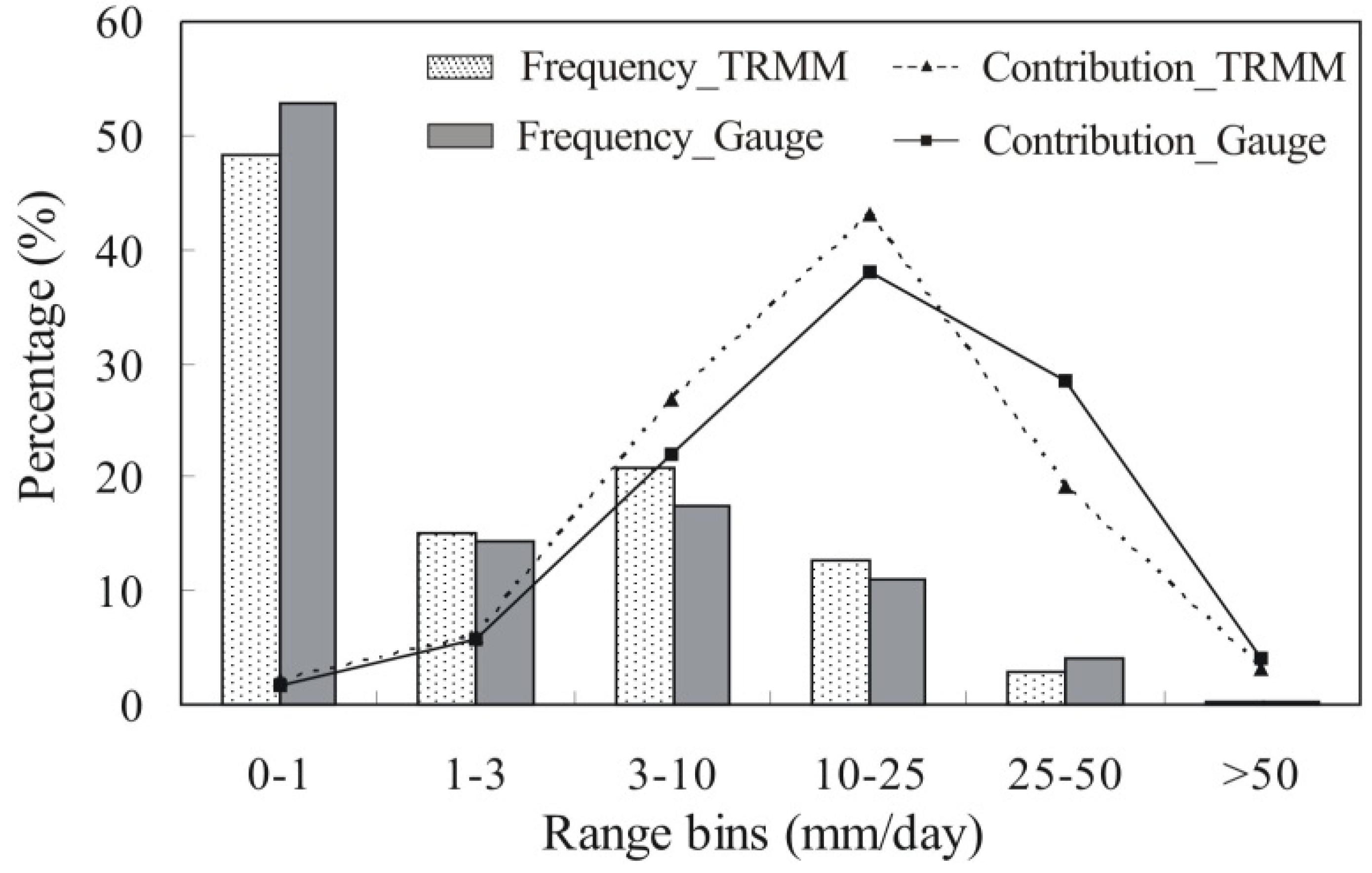
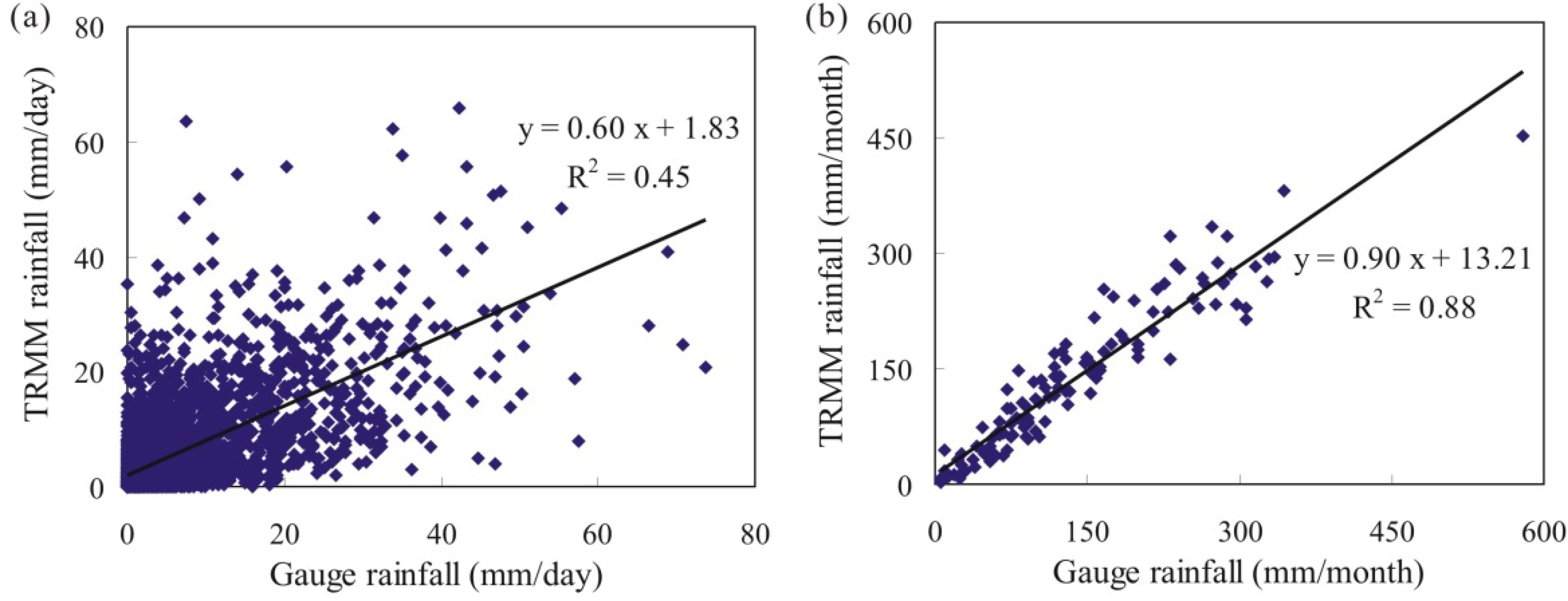
3.2. Temporal Variation of Dry/wet Conditions Based on TRMM Rainfall


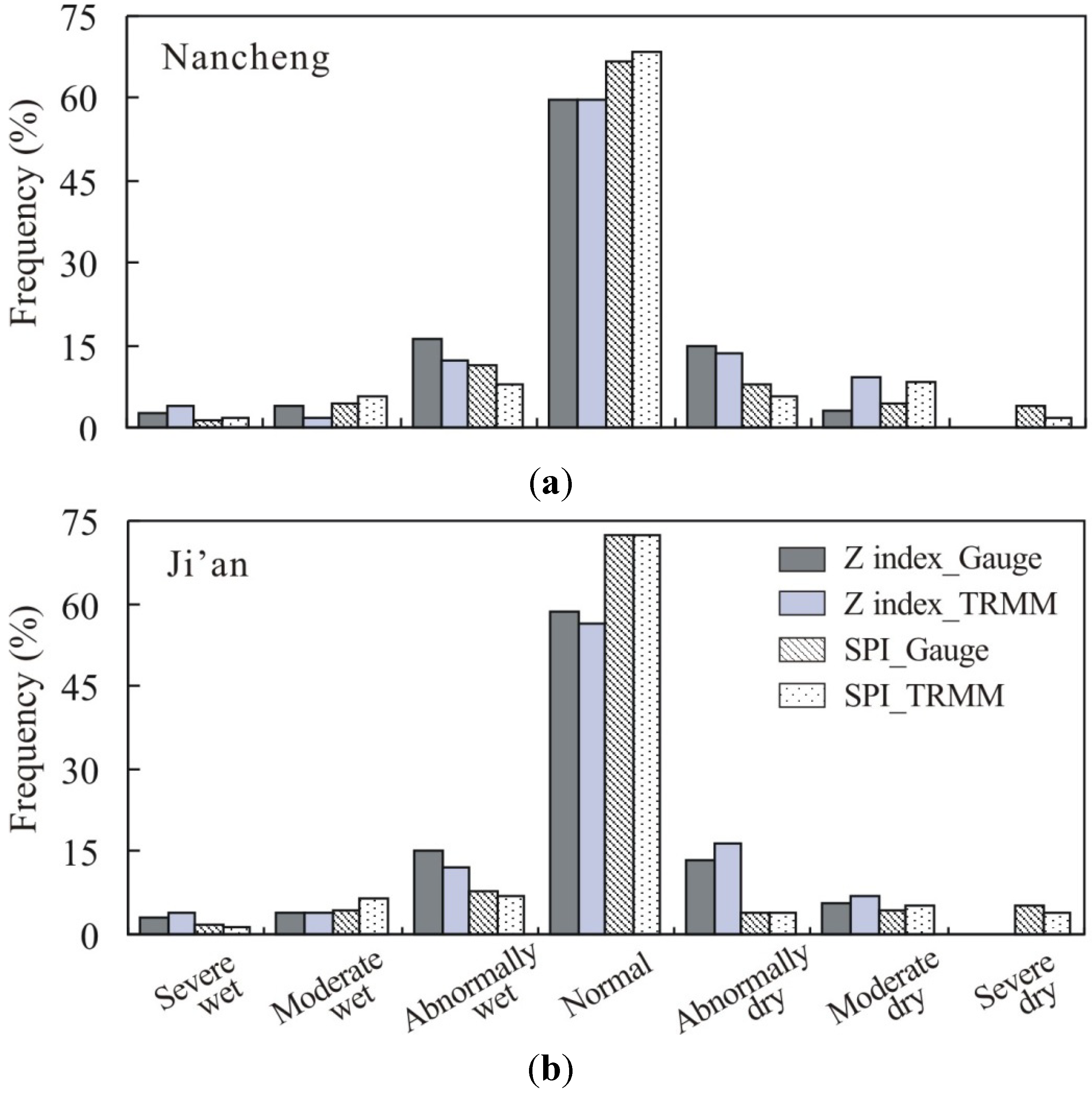
3.3. Spatial Distribution of Dry/wet Conditions Based on TRMM Rainfall
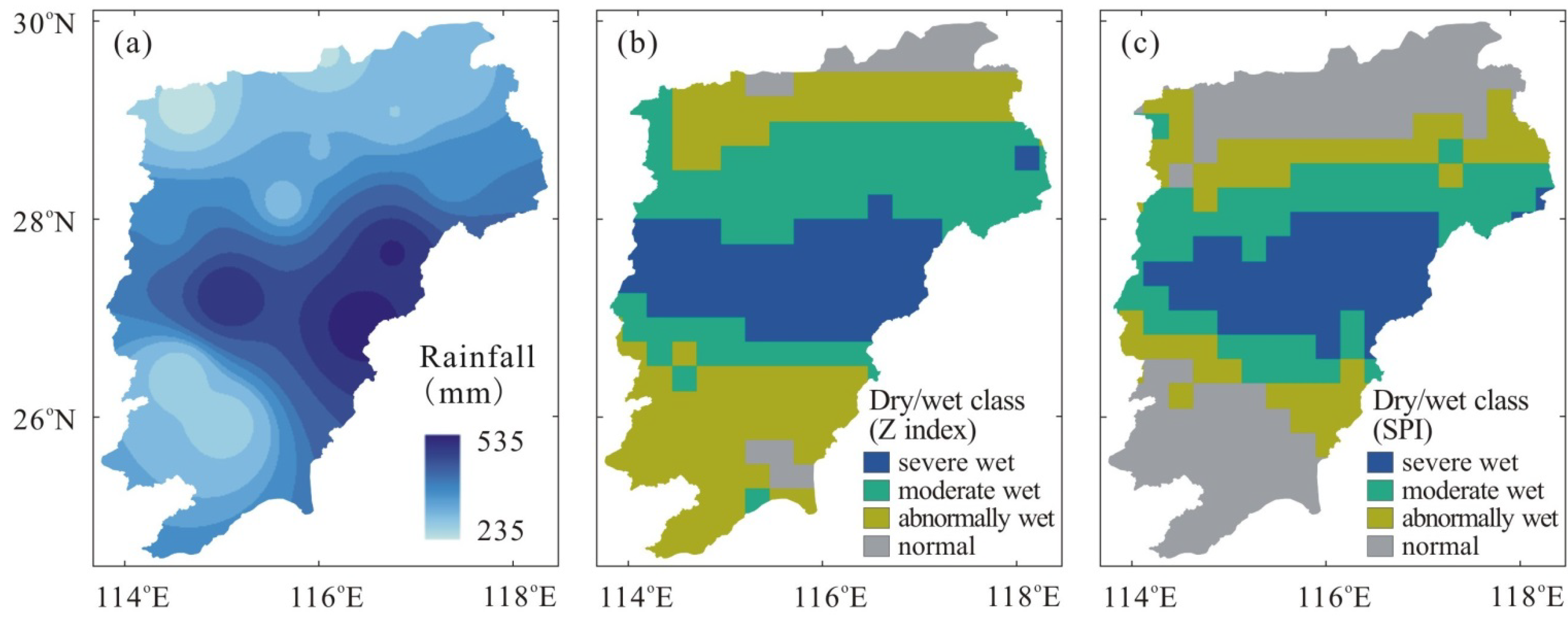
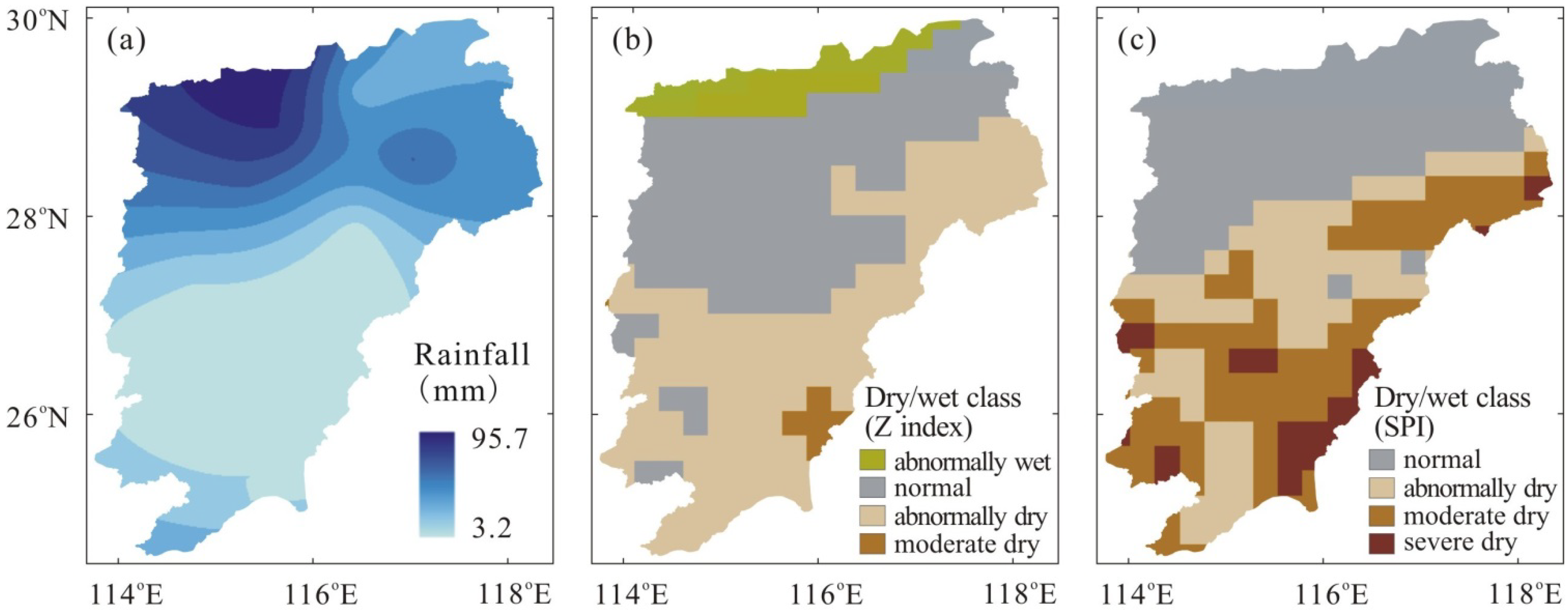
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, Y. Thinking on the flood disaster in the middle reaches of the Yangtze river. Earth Sci. Front. 2000, 7, 87–93. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, S.M.; Du, Y.; Huang, J.L.; Wu, S.J.; Xue, H.P. Causes of flooding andwater logging in middle reaches of The Yangtze River and construction of decision-making support system for monitoring and evaluation of flooding and water logging hazards. Earth Sci. 2001, 26, 643–647. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama, T.; Watanabe, M. Role of flood storage ability of lakes in the Changjiang River catchment. Glob. Planet Chang. 2008, 63, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.N.; Shao, Q.X.; Chen, X.H.; Li, Y.; Wang, D.G. Flood changes during the past 50 years in Wujiang River, South China. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 26, 3561–3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Hu, Q.; Jiang, T. Annual and seasonal streamflow responses to climate and land-cover changes in the Poyang Lake basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2008, 355, 106–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Feng, S.; Guo, H.; Chen, G.; Jiang, T. Interactions of the Yangtze river flow and hydrologic processes of the Poyang Lake, China. J. Hydrol. 2007, 347, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Fang, J.; Xu, W.; Shi, P.J. Analysis of dry/wet conditions using the standardized precipitation index and its potential usefulness for drought/flood monitoring in Hunan Province, China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2013, 27, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, C.J.; Li, H.R.; Yang, L.S.; Wu, S.H.; Liu, Y.; Liao, Y.F. Spatial and temporal changes in flooding and the affecting factors in China. Nat. Hazards 2012, 61, 425–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, W.C. Keeping track of crop moisture conditions, nationwide: The new crop moisture index. Weatherwise 1968, 21, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, T.B.; Doesken, N.J.; Kleist, J. The Relationship of Drought Frequency and Duration of Time Scales. In Proceedings of the Eighth Conference on Applied Climatology, Boston, MA, USA, 17–23 January 1993.
- Shukla, S.; Wood, A.W. Use of a standardized runoff index for characterizing hydrologic drought. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; AghaKouchak, A. Multivariate standardized drought index: Aparametric multi-index model. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 57, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Begueria, S.; López-Moreno, J.I. A multiscalar drought index sensitive to global warming: The standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 1696–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttman, N.B. Comparing the palmer drought index and the standardized precipitation index. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1998, 34, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyantash, J.; Dracup, J.A. The quantification of drought: an evaluation of drought indices. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2002, 83, 1167–1180. [Google Scholar]
- Quiring, S.M. Monitoring drought: An evaluation of meteorological drought indices. Geogr. Compass 2009, 3, 64–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttman, N.B. Accepting the standardized precipitation index: A calculation algorithm. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1999, 35, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, M.; Svoboda, M.; Wall, N.; Widhalm, M. The Lincoln declaration on drought indices: Universal meteorological drought index recommended. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 92, 485–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Climate Research Programme (WCRP), Drought Predictability and Prediction in A Changing Climate: Assessing Current Predictive Knowledge and Capabilities, User Requirements and Research Priorities; Technical Report; WCRP: Barcelona, Spain, 2010.
- AghaKouchak, A.; Nakhjiri, N. A near real-time satellite-based global drought climate data record. Environ. Res. Lett. 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.F.; Pulido-Calvo, I.; Portela, M.M. Spatial and temporal variability of droughts in Portugal. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, J.; Valdes, J.B. New drought frequency index: definition and comparative performance analysis. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrangi, A.; Khakbaz, B.; Jaw, T.C.; AghaKouchak, A.; Hsu, K.; Sorooshian, S. Hydrologic evaluation of satellite precipitation products over a mid-size basin. J. Hydrol. 2011, 397, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghile, Y.; Schulze, R.; Brown, C. Evaluating the performance of ground-based and remotely sensed near real-time rainfall fields from a hydrological perspective. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2010, 55, 497–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taesombat, W.; Sriwongsitanon, N. Areal rainfall estimation using spatial interpolation techniques. Sci. ASIA 2009, 35, 268–275. [Google Scholar]
- Sawunyama, T.; Hughes, D.A. Application of satellite-derived rainfall estimates to extend water resource simulation modelling in South Africa. Water SA 2008, 34, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, S.; Srinivasan, G.; Nemani, R. Evaluation of multi-satellite TRMM derived rainfall estimates over a western state of India. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2009, 87, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, E.; Buytaert, W.; Peaver, L.; Wheater, H. Evaluation of precipitation products over complex mountainous terrain: A water resources perspective. Adv. Water Resour. 2011, 34, 1222–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, C.Y. Suitability of the TRMM satellite rainfalls in driving a distributed hydrological model for water balance computations in Xinjiang catchment, Poyang lake basin. J. Hydrol. 2012, 426–427, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, M.S.; Shah, S.; Kishtawal, C.M.; Sathiyamoorthy, V.; Rajeevan, M.; Kriplani, R.H. Validation of TRMM Merge Daily Rainfall withIMD Raingauge Analysis over Indian Land Mass; Technical Report; Space Applications Centre: Ahmedabad, India, 2005.
- Tian, Y.; Peters-Lidard, C.; Eylander, J.; Joyce, R.; Huffman, G.; Adler, R.; Hsu, K.; Turk, F.; Garcia, M.; Zeng, J. Component analysis of errors in satellite-based precipitation estimates. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AghaKouchak, A.; Behrangi, A.; Sorooshian, S.; Hsu, K.; Amitai, E. Evaluation of satellite-retrieved extreme precipitation rates across the central United States. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorooshian, S.; AghaKouchak, A.; Arkin, P. Advanced concepts on remote sensing of precipitation at multiple scales. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 92, 1353–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, S.E.; Some, B.; McCollum, J.; Nelkin, E.; Klotter, D.; Berte, Y.; Diallo, B.M. Validation of TRMM and other rainfall estimates with a high-density gauge dataset for West Africa. Part I: Validation of GPCC rainfall product and Pre-TRMM satellite and blended products. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2003, 42, 1337–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehran, A.; AghaKouchak, A. Capabilities of satellite precipitation datasets to estimate heavy precipitation rates at different temporal accumulations. Hydrol. Process. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, F.; Hong, Y.; Lettenmaier, D. Evaluation of TRMM multi-satellite precipitation analysis (TMPA) and its utility in hydrologic prediction in La Plata Basin. J. Hydrometeorol. 2008, 9, 622–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernimmen, R.R.E.; Hooijer, A.; Mamenun; Aldrian, E.; van Dijk, A.I.J.M. Evaluation and bias correction of satellite rainfall data for drought monitoring in Indonesia. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, L.; Malhi, Y.; Aragao, L.; Saatchi, S. Spatial Patterns of the Canopy Stress during 2005 Drought in Amazonia. In Proceedings of 2007 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Barcelona, Spain, 23–27 July 2008.
- Du, L.T.; Tian, Q.J.; Yu, T. A comprehensive drought monitoring method integrating MODIS and TRMM data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2013, 23, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, J.Y.; Im, J.; Carbone, G.J. Monitoring agricultural drought for arid and humid regions using multi-sensor remote sensing data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2875–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Hu, C.M.; Chen, X.L. Satellites Capture the Drought Severity Around China’s Largest Freshwater Lake. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2012, 5, 1266–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumann, G.; Barbosa, P.; Carrao, H. Monitoring drought conditions and their uncertainties in africa using TRMM data. J. Appl. Meteor. Climatol. 2012, 51, 1867–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Qin, Z. Flood estimation methods for Poyang Lake Area. J. Lake Sci. 1998, 10, 51–56. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.H.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, C.Y. Assessing the performance of satellite-based precipitation products and its dependence on topography over Poyang Lake basin. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisdal, H.; Tallaksen, L.M. Estimation of regional meteorological and hydrological drought characteristics. J. Hydrol. 2003, 281, 230–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.G.; Li, J.R.; Huang, S.F.; Li, X.T. Characteristics of the recent 10-year flood/drought over the Dongting Lake basin based on TRMM precipitation data and regional integrated Z-index. Resour. Sci. 2010, 32, 1103–1110. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Daley, R. Atmospheric Data Analysis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Bonaccorso, B.; Bordi, I.; Cancelliere, A.; Rossi, G.; Sutera, A. Spatial variability of drought: An analysis of SPI in Sicily. Water Resour. Manag. 2003, 17, 273–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheffield, J.; Wood, E.; Roderick, M. Little change in global drought over the past 60 years. Nature 2012, 491, 435–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damberg, L.; AghaKouchak, A. Global trends and patterns of droughts from space. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Ye, X. Dry/Wet Conditions Monitoring Based on TRMM Rainfall Data and Its Reliability Validation over Poyang Lake Basin, China. Water 2013, 5, 1848-1864. https://doi.org/10.3390/w5041848
Li X, Zhang Q, Ye X. Dry/Wet Conditions Monitoring Based on TRMM Rainfall Data and Its Reliability Validation over Poyang Lake Basin, China. Water. 2013; 5(4):1848-1864. https://doi.org/10.3390/w5041848
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xianghu, Qi Zhang, and Xuchun Ye. 2013. "Dry/Wet Conditions Monitoring Based on TRMM Rainfall Data and Its Reliability Validation over Poyang Lake Basin, China" Water 5, no. 4: 1848-1864. https://doi.org/10.3390/w5041848






