Activated Persulfate Oxidation of Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) in Groundwater under Acidic Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical Reagents
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.3. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
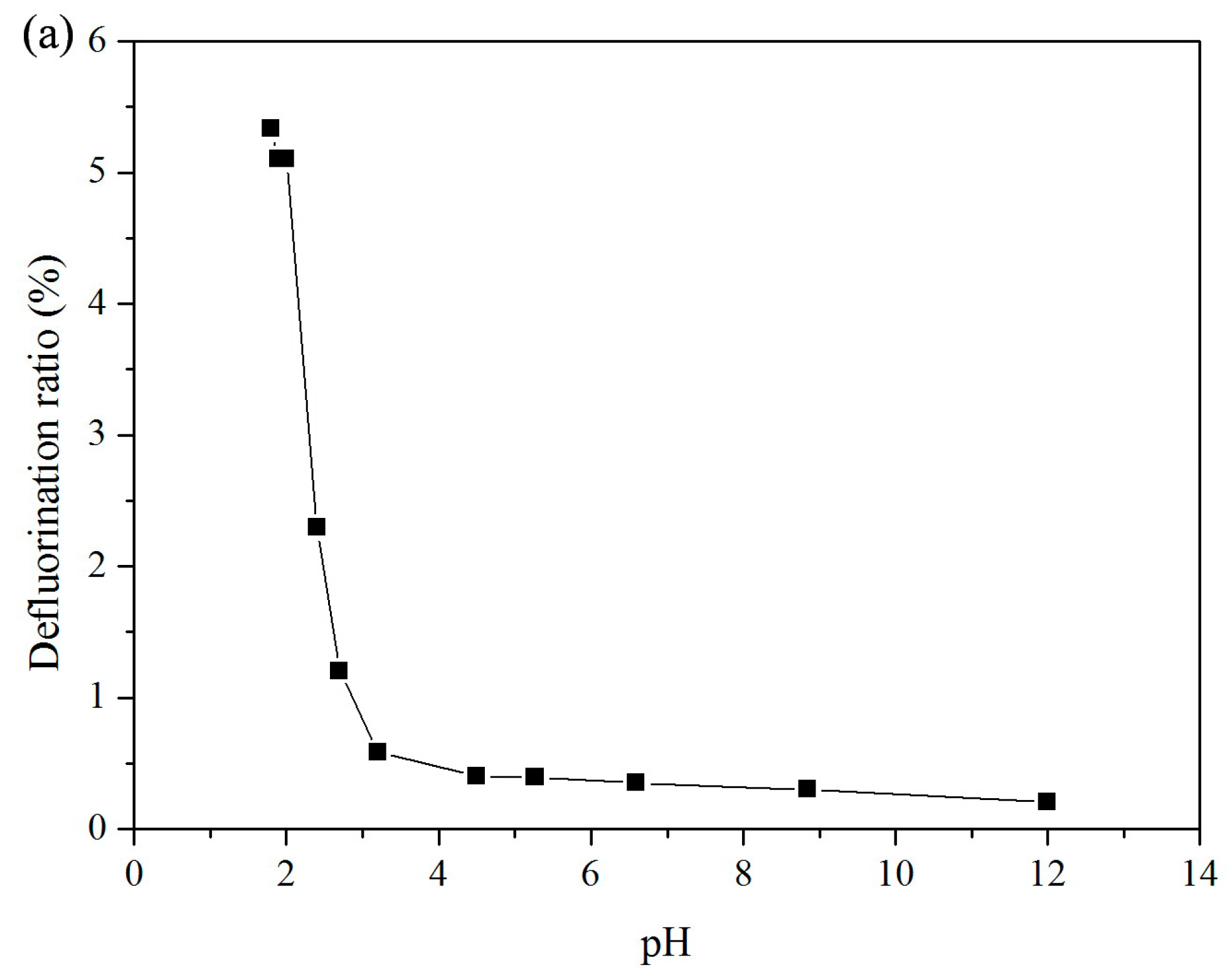
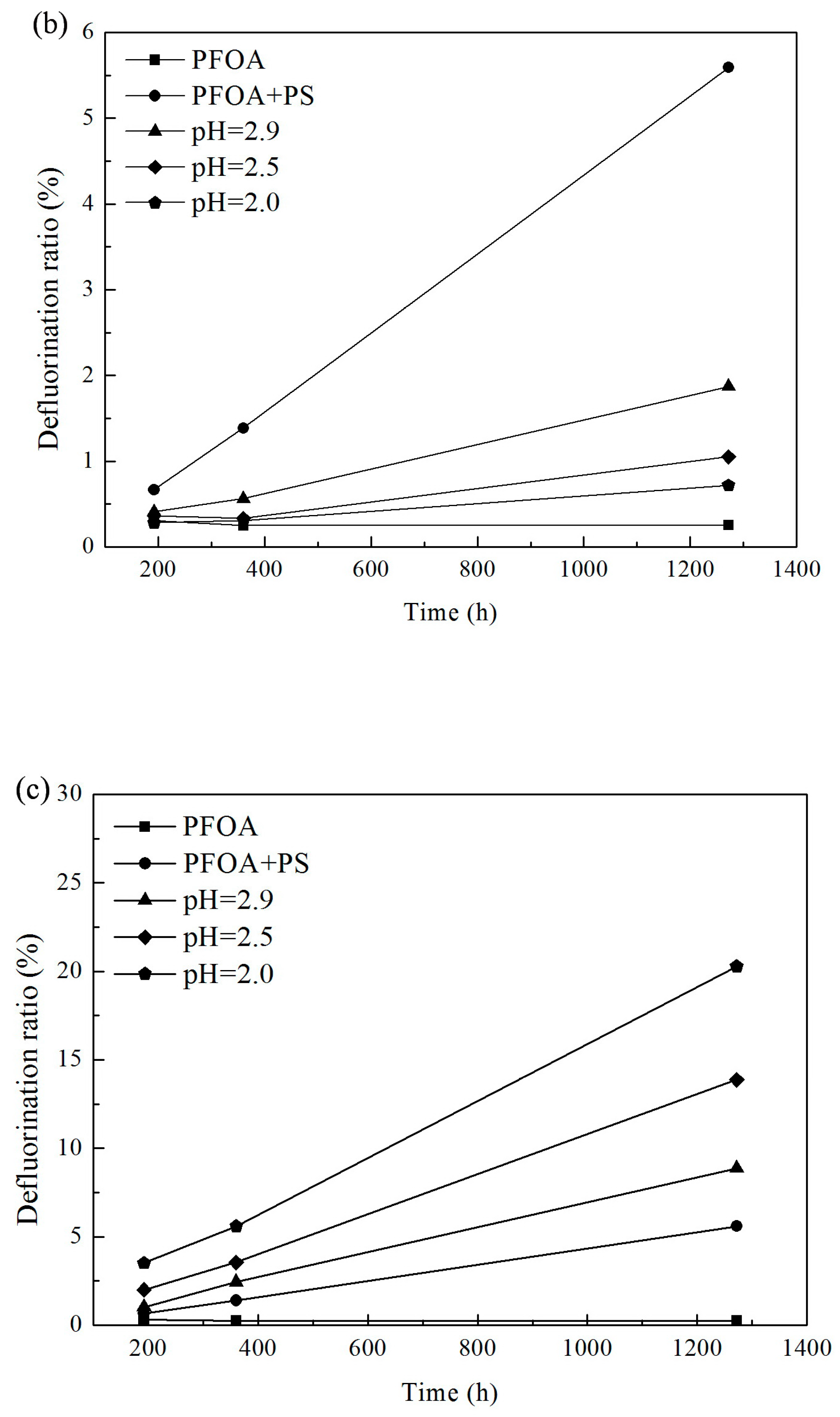
3.1. Effect of pH
3.2. Effect of Persulfate Dosage
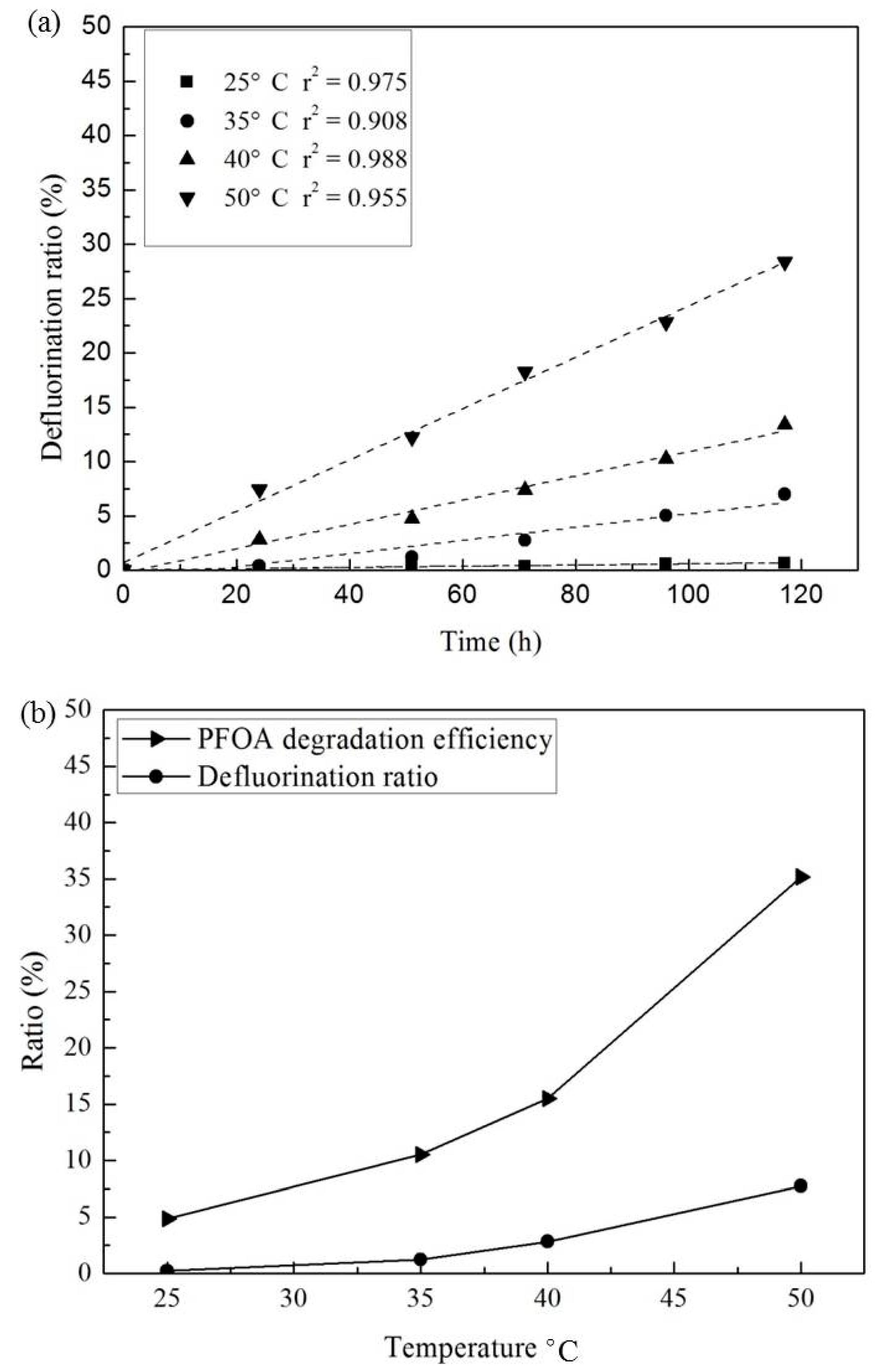
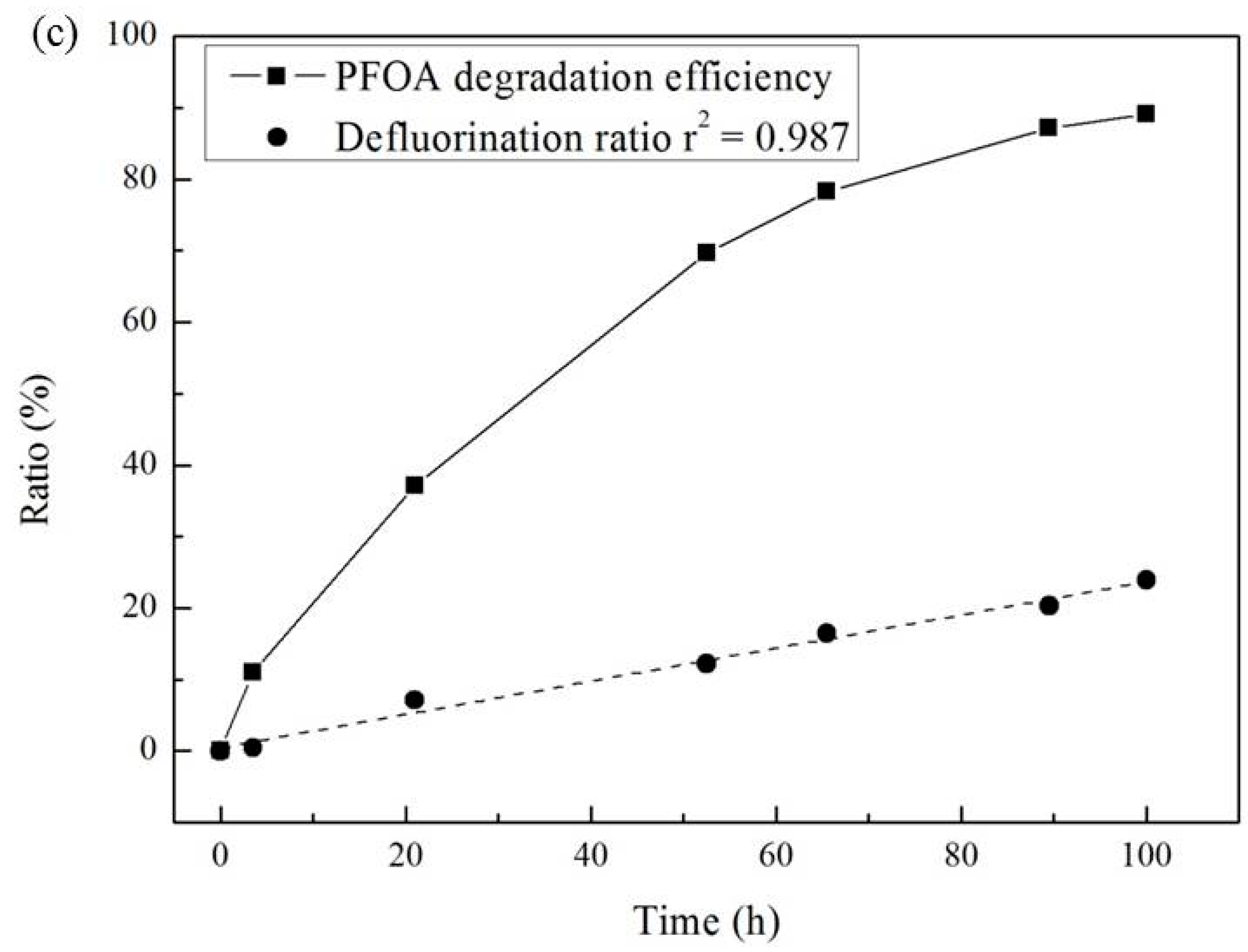
3.3. Effect of Temperature and Reaction Time
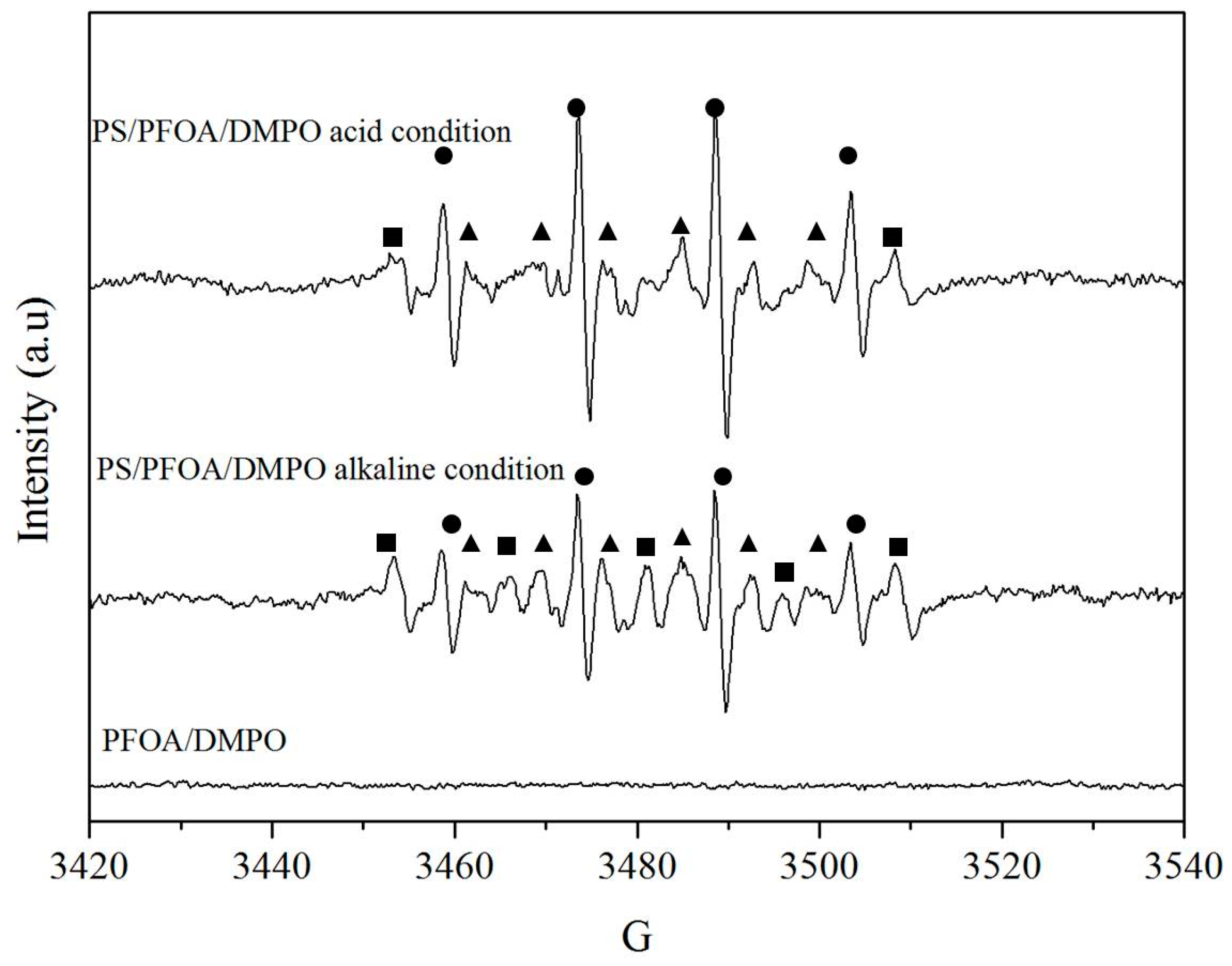
3.4. Reaction Mechanisms
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arias, E.V.A.; Mallavarapu, M.; Naidu, R. Identification of the source of PFOS and PFOA contamination at a military air base site. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espanaa, V.A.A.; Mallavarapua, M.; Naidu, R. Treatment technologies for aqueous perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoate (PFOA): A critical review with an emphasis on field testing. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2015, 4, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, E.T.; Adami, H.O.; Boffetta, P.; Cole, P.; Starr, T.B.; Mandel, J.S. A critical review of perfluorooctanoate and perfluorooctanesulfonate exposure and cancer risk in humans. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2014, 44, 1–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moody, C.A.; Martin, J.W.; Kwan, W.C.; Muir, D.C.G.; Mabury, S.C. Monitoring perfluorinated surfactants in biota and surface water samples following an accidental release of fire-fighting foam into etobicoke creek. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliaei, F.; Kriens, D.; Kessler, K. Investigation of Perfluorochemical (PFC) Contamination in Minnesotasphase One. Available online: http://www.nikwax.com/cmsdata/Downloads/pr/7-investigation_PFC_minnesota.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2016).
- Hoffman, K.; Webster, T.F.; Bartell, S.M.; Weisskopf, M.G.; Fletcher, T.; Vieira, V.M. Private drinking water wells as a source of exposure to perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) in communities surrounding a fluoropolymer production facility. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US-EPA. Provisional Health Advisories for Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) and Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS); US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2009.
- UBA. Vorl€aufige Bewertung von Perfluorierten Tensiden (PFT) im Trinkwasser am Beispiel Ihrer Leitsubstanzen Perfluoroctans€aure (PFOA) und Perfluoroctansulfons€aure (PFOS); Stellungnahme der Trinkwasserkommission des Bundesministeriums f€ur Gesundheit (bmg) bei Umweltbundesamt vom 21.06.06, €uberarbeitet am 13.07.06; Federal Environmental Agency (UBA): Dessau, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair, E.; Kannan, K. Mass loading and fate of perfluoroalkyl surfactants in wastewater treatment plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 1408–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, M.M.; Higgins, C.P.; Huset, C.A.; Luthy, R.G.; Barofsky, D.F.; Field, J.A. Fluorochemical mass flows in a municipal wastewater treatment facility. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 7350–7357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollingsworth, J.; Sierra-Alvarez, R.; Zhou, M.; Ogden, K.L.; Field, J.A. Anaerobic biodegradability and methanogenic toxicity of key constituents in copper chemical mechanical planarization effluents of the semiconductor industry. Chemosphere 2005, 59, 1219–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Key, B.D.; Howell, R.D.; Criddle, C.S. Defluorination of organofluorine sulfur compounds by Pseudomonas sp. Strain D2. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 2283–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, H.; Hayakawa, E.; Einaga, H.; Kutsuna, S.; Koike, K.; Ibusuki, T.; Kiatagawa, H.; Arakawa, R. Decomposition of environmentally persistent perfluorooctanoic acid in water by photochemical approaches. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 6118–6124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, P. Photodegradation of perfluorooctanoic acid in water under irradiation of 254 nm and 185 nm light by use of persulfate. Water Sci. Technol. 2006, 54, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, P.Y.; Zhang, L. Photocatalytic decomposition of environmentally persistent perfluorooctanoic acid. Chem. Lett. 2006, 35, 230–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, H.; Yamamoto, A.; Kutsuna, S. Efficient photochemical decomposition of long-chain perfluorocarboxylic acids by means of an aqueous/liquid CO2 biphasic system. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 7692–7697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hori, H.; Yamamoto, A.; Hayakawa, E.; Taniyasu, S.; Yamashita, N.; Kutsuna, S. Efficient decomposition of environmentally persistent perfluorocarboxylic acids by use of persulfate as a photochemical oxidant. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 2383–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutsuna, S.; Hori, H. Rate constants for aqueous-phase reactions of SO4− with C2F5C(O)O− and C3F7C(O)O− at 298 k. Int. J. Chem. Kinet. 2007, 39, 276–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Noma, Y.; Sakai, S.-I.; Shibata, Y. Photodegradation of perfluorooctane sulfonate by UV irradiation in water and alkaline 2-propanol. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 5660–5665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hori, H.; Hayakawa, E.; Koike, K.; Einaga, H.; Ibusuki, T. Decomposition of nonafluoropentanoic acid by heteropolyacid photocatalyst H3PW12O40 in aqueous solution. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2004, 211, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutsuna, S.; Nagaoka, Y.; Takeuchi, K.; Hori, H. TiO2-induced heterogeneous photodegradation of a fluorotelomer alcohol in air. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 6824–6829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Q.Z.; Ravikrishna, R.; Valsaraj, K.T. Reusable adsorbents for dilute solution separation. 5. Photodegradation of organic compounds on surfactant-modified titania. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2001, 24, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroder, H.F.; Meesters, R.J.W. Stability of fluorinated surfactants in advanced oxidation processes—A follow up of degradation products using flow injection-mass spectrometry, liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry and liquid chromatography-multiple stage mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1082, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriwaki, H.; Takagi, Y.; Tanaka, M. Sonochemical decomposition of perfluorooctane sulfonate and perfluorooctanoic acid. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 3388–3392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hori, H.; Murayama, M.; Inoue, N.; Ishida, K.; Kutsuna, S. Efficient mineralization of hydroperfluorocarboxylic acids with persulfate in hot water. Catal. Today 2010, 151, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, T.K.; Chu, W.; Graham, N.J.D. The aqueous degradation of butylated hydroxyanisole by UV/S2O82−: Study of reaction mechanisms via dimerization and mineralization. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couttenye, R.A.; Huang, K.-C.; Hoag, G.E.; Suib, S.L. Evidence of sulfate free radical (SO4−•) formation under heat-assisted persulfate oxidation of mtbe. In Proceedings of the 19th Petroleum Hydrocarbons and Organic Chemicals in Ground Water: Prevention, Assessment, and Remediation, Conference and Exposition, Atlanta, GA, USA, 5–8 November 2002.
- Liang, C.; Su, H.-W. Identification of sulfate and hydroxyl radicals in thermally activated persulfate. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 5558–5562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furman, O.S.; Teel, A.L.; Watts, R.J. Mechanism of base activation of persulfate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 6423–6428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayon, E.; Treinin, A.; Wilf, J. Electronic spectra, photochemistry, and autoxidation mechanism of sulfite-bisulfite-pyrosulfite systems. SO2−, SO3−, SO4−, and SO5− radicals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1972, 94, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buxton, G.V.; Greenstock, C.L.; Helman, W.P.; Ross, A.B. Critical review of rate constants for reactions of hydrated electrons, hydrogen-atoms and hydroxyl radicals(•OH/•O−) in aqueous solution. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1988, 17, 513–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, M.C.; Grahame, D.A.; Samuni, A.; Mitchell, J.B.; Russo, A. Oxoammonium cation intermediate in the nitroxide-catalyzed dismutation of superoxide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 5537–5541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.C.; Lo, S.L.; Chiueh, P.T.; Chang, D.G. Efficient decomposition of perfluorocarboxylic acids in aqueous solution using microwave-induced persulfate. Water Res. 2009, 43, 2811–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.S.; Higgins, C.P.; Wang, F.; Shih, K. Effect of temperature on oxidative transformation of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) by persulfate activation in water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 91, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Rackov, C.K.O.D.; Lawal, W.A.; Nfodzo, P.A.; Vianna, M.M.G.R.; Nascimento, C.A.O.D.; Choi, H. Degradation of PFOA by hydrogen peroxide and persulfate activatedby iron-modified diatomite. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 192, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.C.; Lo, S.L.; Kuo, J.; Lin, Y.L. Persulfate oxidation of perfluorooctanoic acid under the temperatures of 20–40 °C. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 198, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, N.; Shi, W.; Zhang, B.; Su, G.; Feng, J.; Zhang, X.; Wei, S.; Yu, H. Occurrence of perfluoroalkyl acids including perfluorooctane sulfonate isomers in Huai river basin and Taihu Lake in Jiangsu province, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 710–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, C.J.; Lei, J.H. Identification of active radical species in alkaline persulfate oxidation. Water Environ. Res. 2015, 87, 656–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, S.; Quan, X.; Yu, H.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y. Efficient mineralization of perfluorooctanoate by electro-fenton with H2O2 electro-generated on hierarchically porous carbon. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 13528–13533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huie, R.E.; Clifton, C.L. Temperature-dependence of the rate constants for reactions of the sulfate radical, SO4−, with anions. J. Phys. Chem. 1990, 94, 8561–8567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grebel, J.E.; Pignatello, J.J.; Mitch, W.A. Effect of halide ions and carbonates on organic contaminant degradation by hydroxyl radical-based advanced oxidation processes in saline waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2010, 44, 6822–6828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Lo, S.; Kuo, J.; Hsieh, C. Decomposition of perfluorooctanoic acid by microwaveactivated persulfate: Effects of temperature, pH, and chloride ions. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2012, 6, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldemer, R.H.; Tratnyek, P.G.; Johnson, R.L.; Nurmi, J.T. Oxidation of chlorinated ethenes by heat-activated persulfate: Kinetics and products. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 1010–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vecitis, C.D.; Park, H.; Cheng, J.; Mader, B.T.; Hoffmann, M.R. Treatment technologies for aqueous perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoate (PFOA). Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. China 2009, 3, 129–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Teel, A.L.; Furman, O.S.; Reed, J.I.; Watts, R.J. Oxidative and reductive pathways in iron-ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid-activated persulfate systems. J. Environ. Eng. 2012, 138, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Lu, S.; Qiu, Z.; Su, Q.; Banks, C.J.; Imai, T.; Lin, K.; Luo, Q. Photodegradation performance of 1,1,1-trichloroethane in aqueous solution: In the presence and absence of persulfate. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 215, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, Q.; Deng, S.; Yang, B.; Huang, J.; Yu, G. Efficient electrochemical oxidation of perfluorooctanoate using a Ti/SnO2-Sb-Bi anode. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 2973–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hori, H.; Yamamoto, A.; Koike, K.; Kutsuna, S.; Osaka, I.; Arakawa, R. Photochemical decomposition of environmentally persistent short-chain perfluorocarboxylic acids in water mediated by iron(ii)/(iii) redox reactions. Chemosphere 2007, 68, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nohara, K.; Toma, M.; Kutsuna, S.; Takeuchi, K.; Ibusuki, T. Cl atom-initiated oxidation of three homologous methyl perfluoroalkyl ethers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debruyn, W.J.; Shorter, J.A.; Davidovits, P.; Worsnop, D.R.; Zahniser, M.S.; Kolb, C.E. Uptake of haloacetyl and carbonyl halides by water surfaces. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1995, 29, 1179–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

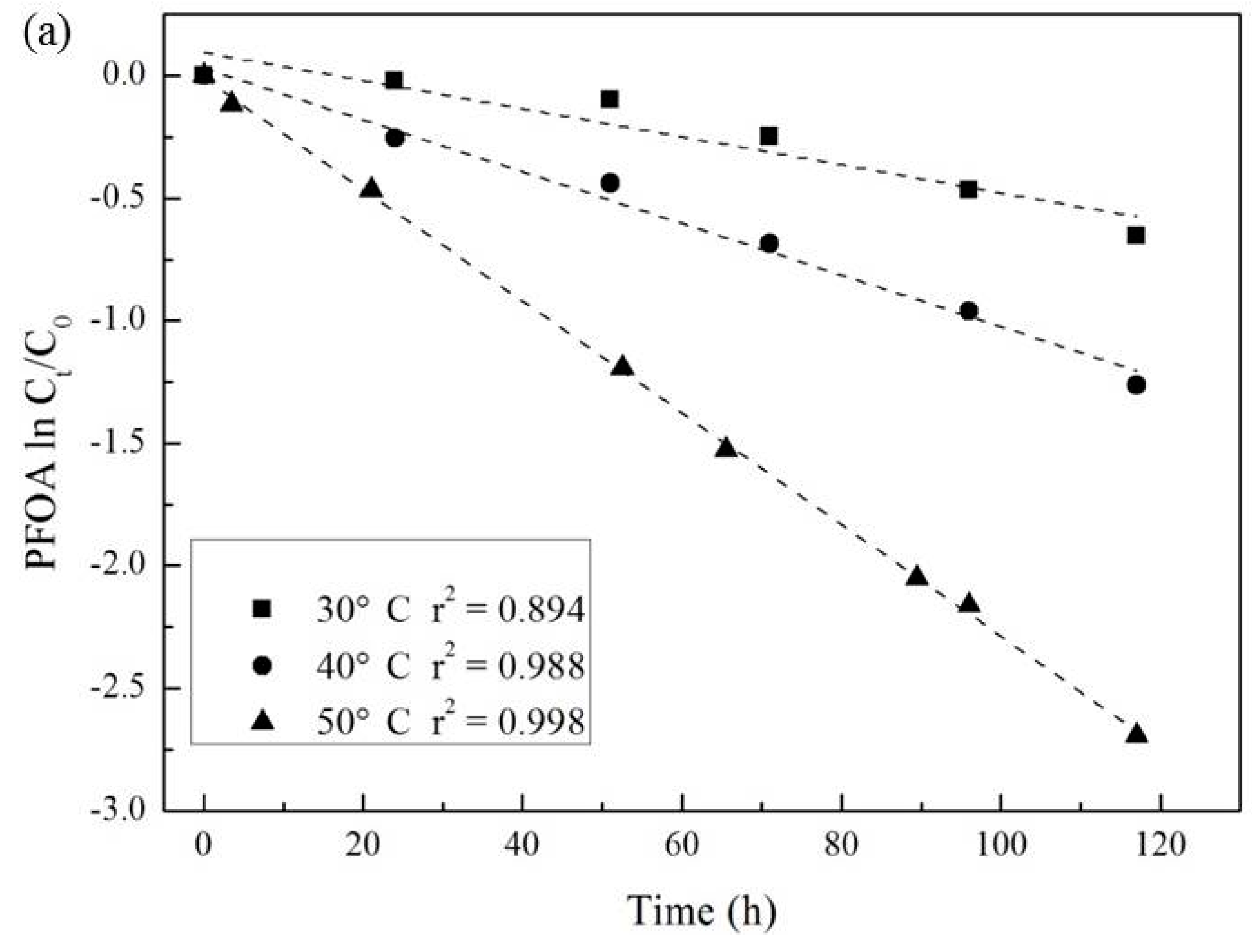


| Temperature (°C) | Pseudo-First-Order Kinetic Constant k (10−2·h−1) | t1/2 (h) | r2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | 0.57 | 138 | 0.894 |
| 40 | 1.06 | 69 | 0.988 |
| 50 | 2.28 | 30 | 0.998 |
| PFCA Intermediates | Concentrations (μmol/L) |
|---|---|
| PFOA, C8 | 1.93 |
| Perfluoroheptanoic acid, PFHpA, C7 | 5.91 |
| Perfluorohexanoic acid, PFHeA, C6 | 3.82 |
| Perfluoropentanoic acid, PFPeA, C5 | 2.07 |
| Perfluorobutyric acid, PFBA, C4 | 3.03 |
| Perfluoropropionic acid, PFPrA, C3 | 2.10 |
| Trifluoroacetic acid, TFA, C2 | 2.13 |
| Total PFCAs | 20.99 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, P.; Hu, Z.; Song, X.; Liu, J.; Lin, N. Activated Persulfate Oxidation of Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) in Groundwater under Acidic Conditions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13060602
Yin P, Hu Z, Song X, Liu J, Lin N. Activated Persulfate Oxidation of Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) in Groundwater under Acidic Conditions. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2016; 13(6):602. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13060602
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Penghua, Zhihao Hu, Xin Song, Jianguo Liu, and Na Lin. 2016. "Activated Persulfate Oxidation of Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA) in Groundwater under Acidic Conditions" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 13, no. 6: 602. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13060602





