Topical Formulation Comprising Fatty Acid Extract from Cod Liver Oil: Development, Evaluation and Stability Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. In Vitro Evaluation of Antibacterial Activity of Fatty Acid Extract
2.2. Evaluation of Ointments
2.2.1. Spreadability Measurements
2.2.2. Extrudability Measurements
2.2.3. Determination of pH
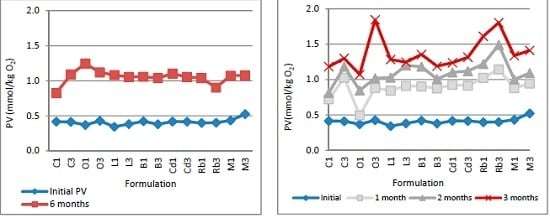
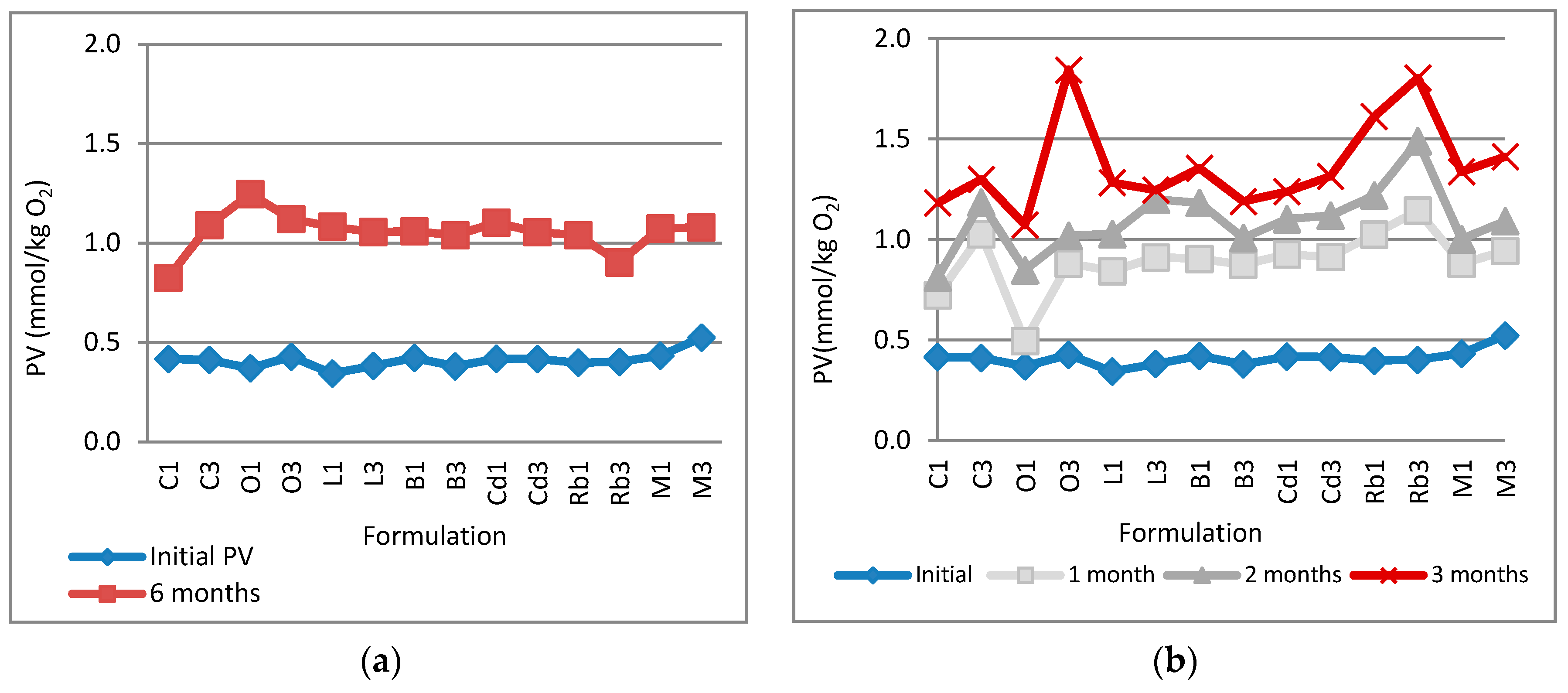
2.2.4. Determination of Lipid Oxidation
2.2.5. Sensory Evaluation
3. Discussion
3.1. Antibacterial Activity of the Fatty Acid Extract
3.2. Ointment Design and Evaluation
3.3. Stability Studies
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Antibacterial Assay
4.2. Ointment Preparation
4.3. Evaluation of Ointments
4.3.1. Spreadability
4.3.2. Extrudability
4.3.3. pH Determination
4.3.4. Sensory Evaluation
- (1)
- Excellent: smooth and homogeneous texture, light brown color, distinctive fishy odor.
- (2)
- Satisfactory: smooth texture, non-consistency, light brown color, distinctive fishy odor.
- (3)
- Unsatisfactory: rough texture, visible solid particles, non- consistency, dark brown color, rancid fishy odor.
4.3.5. Determination of Peroxide Value
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FAs | Fatty acids |
| PUFAs | Polyunsaturated fatty acid |
| PV | Fatty acids |
| MIC | Minimum inhibitory concentration |
References
- Siriwardhana, N.; Kalupahana, N.S.; Moustaid-Moussa, N. Health benefits of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids: Eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2012, 65, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jump, D.B.; Depner, C.M.; Tripathy, S. Omega-3 fatty acid supplementation and cardiovascular disease. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 53, 2525–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahidi, F. Nutraceutical and Specialty Lipids and Their Co-Products; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; pp. 231–232. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.Q.; O’Connor, C.J.; Roberton, A.M. Antibacterial actions of fatty acids and monoglycerides against Helicobacter pylori. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2003, 36, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilika, F.; Bremner, P.D.; Meyer, M.J.J. Antibacterial activity of linoleic and oleic acids isolated from Helichrysum pedunculatum: A plant used during circumcision rites. Fitoterapia 2000, 71, 450–452. [Google Scholar]
- Thormar, H.; Issacs, C.E.; Brown, H.R.; Marc, R.; Barshatzky, M.R.; Pessolono, T. Inactivation of Enveloped Viruses and Killing of Cells by Fatty Acids and Monoglycerides. Antimcrob. Agents Chemother. 1987, 31, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibane, V.S.; Kock, J.L.; Ells, R.; Wyk, P.W.; Pohl, C.H. Effect of marine polyunsaturated fatty acids on biofilm formation of Candida albicans and Candida dubliniensis. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2597–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walters, D.; Raynor, L.; Mitchell, A.; Walker, R.; Walker, K. Antifungal activities of four fatty acids against plant pathogenic fungi. Mycopathologia 2004, 157, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kabara, J.J.; Swieczkowski, D.M.; Conley, A.J.; Truant, T.J.P. Fatty Acids and Derivatives as Antimicrobial Agents. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1972, 2, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftsson, T.; Thormar, H.; Hjalmarsdottir, M. Antibacterial activities of fatty acids extracts from cod liver oil. 1997; unpublsihed work. [Google Scholar]
- Loftsson, T.; Ilievska, B.; Asgrimsdottir, G.M.; Ormarsson, O.T.; Stefansson, E. Fatty acids from marine lipids: Biological activity, formulation and stability. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftsson, T.; Thormar, H.; Ólafsson, J.H.; Gunarsdottir, T.M.; Hjaltason, B.; Gudmundsson, G. Fatty Acid Extract From Cod-liver Oil: Activity Against Herpes Simplex Virus and Enhancement of Transdermal Delivery of Acyclovir In-vitro. Pharm. Pharmacol. Commun. 1998, 4, 287–291. [Google Scholar]
- Loftsson, T.; Gudmundsdóttir, T.K.; Fridriksdóttir, H.; Sigurdardóttir, A.M.; Thorkelsson, J.; Gudmundsson, G.; Hjaltason, B. Fatty acids from cod-liver oil as skin penetration enhancers. Pharmazie 1995, 50, 188–190. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thormar, H. Lipids and Essential Oils as Antimicrobial Agents; John Wiley&Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2011; pp. 53–57. [Google Scholar]
- Desbois, A.P.; Smith, V.J. Antibacterial free fatty acids: Activities, mechanisms of action and biotechnological potential. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 85, 1629–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ueda, C.T.; Shah, V.P.; Derdzinski, K.; Ewing, G.; Flynn, G.; Maibach, H.; Marques, M.; Rytting, H.; Shaw, S.; Thakker, K.; et al. Topical and Transdermal Drug Products. Pharmacop. Forum 2009, 35, 750–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, L.; Ansel, C.H. Ansel’s Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms and Drug Delivery Systems, 9th ed.; Lippincott Williams&Williams: Philadelhpia, PA, USA, 2013; pp. 272–293. [Google Scholar]
- Harwood, J.L.; Gurr, M.I. Lipid Biochemistry: An Introduction, 4th ed.; Chapmen& Hall: London, UK, 1991; pp. 157–158. [Google Scholar]
- Budai, L.; Antal, I.; Klebovich, I.; Budai, M. Natural oils and waxes. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2012, 63, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Darvell, B.W. Materials Science for Dentistry, 9th ed.; Woodhead Ltd.: Cambridge, UK, 2009; pp. 390–400. [Google Scholar]
- Nasopoulou, C.; Karantonis, H.C.; Andriotis, M.; Demopoulos, C.A.; Zabetakis, I. Antibacterial and anti-PAF activity of lipid extracts from sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) and gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata). Food Chem. 2008, 111, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGaw, L.J.; Jager, A.K.; Van Staden, J.; Houghton, P.J. Antibacterial effects of fatty acids and related compounds from plants. South Afr. Bot. 2002, 68, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, S.P.; Patil, P.S. Pharmaceutical Excipients: A review. Int. J. Adv. Pharm. Biol. Chem. 2012, 1, 21–34. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, R.K.; Raw, A.; Lionberger, R.; Yu, L. Generic development of topical dermatologic products: Formulation development, process development, and testing of topical dermatologic products. AAPS J. 2013, 15, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kryscio, D.R.; Sathe, P.M.; Lionberger, R.; Yu, L.; Bell, M.A.; Jay, M.; Hilt, J.Z. Spreadability measurements to assess structural equivalence (Q3) of topical formulations—A technical note. AAPS PharmSciTech 2008, 9, 84–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivens, U.I.; Steinkjer, B.; Serup, J.; Tetens, V. Ointment is evenly spread on the skin, in contrast to creams and solutions. Br. J. Dermatol. 2001, 145, 264–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noren, B. A method to evaluate the tubesqueezing properties of toothpaste. J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem. 1976, 27, 47–61. [Google Scholar]
- Shellhammer, T.H.; Rumsey, T.R.; Krochta, J.M. Viscoelastic properties of edible lipids. J. Food Eng. 1997, 33, 305–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanicky, J.R.; Shah, D.O. Effect of Degree, Type, and Position of Unsaturation on the pKa of Long-Chain Fatty Acids. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 256, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paudel, S.K.; Milewski, M.; Swadley, L.C.; Brogden, K.N.; Ghosh, P.; Stinchcomb, A.L. Challenges and opportunities in dermal/transdermal delivery. Ther. Deliv. 2010, 1, 109–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nangia, A.; Andersen, P.H.; Berner, B.; Maibach, H.I. High dissociation constants (pKa) of basic permeants are associated with in vivo skin irritation in man. Contact Dermat. 1996, 34, 237–242. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, S.M.; Yosipovitch, G. Skin pH: From basic science to basic skin care. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2013, 93, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, I.F.; Gaio, A.R.; Bahia, M.F. Hedonic and descriptive skin feel analysis of two oleogels: Comparison with other topical formulations. J. Sens. Stud. 2008, 23, 92–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hootman, R.C. Manual on Descriptive Analysis Testing for Sensory Evaluation; ASTM: Baltimor, MD, USA, 1992; pp. 15–51. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA Panel on Biological Hazards (BIOHAZ). Scientific Opinion on Fish Oil for Human Consumption. Food Hygiene, including Rancidity. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1874. [Google Scholar]
- Loyd, V.A. Remington: An Introduction to Pharmacy; Pharmaceutical Press: London, UK, 2013; p. 157. [Google Scholar]
- Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically; Approved Standard—Eighth Edition; CLSI document M07-A8; Clinical Laboratory Standards Instiute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2009.
- Gad, C.S. Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Handbook: Production and Processes; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 267–288. [Google Scholar]
- Contreras, M.D.; Sanchez, R. Application of a factorial design to the study of the flow behavior, spreadability and transparency of a Carbopol ETD 2020 gel. Part II. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 234, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanad, V.; Aleykutty, N.A.; Jayakar, B.; Zacharia, S.M.; Thomas, L. Development and evaluation of antimicrobial herbal formulations containing the methanolic extract of Samadera indica for skin diseases. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2012, 3, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasupathi, A.; Palanisamy, P.B.; Jaykar, R.; Chandira, M.; Venkateswarlu, B.S. Formualtion, development, evaluation of calcitriol and clobetasol propionate ointment. Indian J. Res. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2009, 2, 630–635. [Google Scholar]
| Fatty Acid | Amount (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Name | Shorthand | |
| Saturated fatty acids | ||
| Myristic acid | 14:0 | 3.6 |
| Palmitic acid | 16:0 | 10.4 |
| Stearic acid | 18:0 | 2.6 |
| Monounsaturated fatty acids | ||
| Palmitoleic acid | 16:1 n-7 | 6.5 |
| cis-Vaccenic acid | 18:1 n-7 | 4.4 |
| Oleic acid | 18:1 n-9 | 16.2 |
| Gondoic acid | 20:1 n-9 | 9.4 |
| Gadoleic acid | 20:1 n-11 | 1.6 |
| Erucic acid | 22:1 n-9 | 0.6 |
| Cetoleic acid | 22:1 n-11 | 7.8 |
| Polyunsaturated fatty acids | ||
| Linoleic acid | 18:2 n-6 | 1.5 |
| Moroctic acid | 18:4 n-3 | 2.4 |
| Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) | 20:5 n-3 | 9.3 |
| Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) | 22:6 n-3 | 11.9 |
| Formulation Code | Compound (% w/w) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fatty Acid Extract | Vaseline | Coconut Butter | Wax | Lavender Oil | Lemon Oil | |
| C1, O1, L1, B1, Cd1, Rb1, M1 | 40 | 43.5 | 14 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 |
| C2, O2, L2, B2, Cd1, Rb2, M2 | 40 | 43.5 | 12 | 3 | 1 | 0.5 |
| C3, O3, L3, B3, Cd3, Rb3, M3 | 40 | 43.5 | 10 | 5 | 1 | 0.5 |
| Strains | Staphylococcus aureus | Streptococcus pyogenes | Streptococcus pneumonia | Enterococcus faecalis | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Escherichia coli |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATCC | ATCC | ATCC | ATCC | ATCC | ATCC | |
| 29213 | 19615 | 49169 | 29212 | 27853 | 25922 | |
| MIC (μg/mL) | 512 | 256 | 128 | 256 | >16.384 | >16.384 |
| Formulation | Spreadability (mm ± SD) | Tube Extrudability (g ± SD) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 21.50 ± 0.87 | 3.23 ± 0.19 | 5.44 ± 0.04 |
| C2 | 14.66 ± 0.20 | 1.84 ± 0.05 | 5.21 ± 0.01 |
| C3 | 13.33 ± 0.57 | 1.67 ± 0.10 | 5.06 ± 0.05 |
| O1 | 19.66 ± 0.57 | 3.23 ± 0.39 | 4.70 ± 0.03 |
| O2 | 15.66 ± 0.2 | 2.84 ± 0.62 | 4.62 ± 0.07 |
| O3 | 12.66 ± 1.5 | 1.69 ± 0.53 | 4.48 ± 0.02 |
| L1 | 25.33 ± 2.51 | 2.50 ± 0.12 | 3.83 ± 0.03 |
| L2 | 22.66 ± 0.57 | 2.15 ± 0.07 | 4.03 ± 0.005 |
| L3 | 19.66 ± 1.52 | 2.04 ± 0.09 | 4.06 ± 0.05 |
| B1 | 30.50 ± 1.32 | 4.84 ± 0.79 | 4.30 ± 0.03 |
| B2 | 30.13 ± 0.28 | 3.95 ± 0.49 | 4.05 ± 0.05 |
| B3 | 27.33 ± 0.57 | 3.32 ± 0.07 | 3.96 ± 0.01 |
| Cd1 | 19.33 ± 1.15 | 3.30 ± 0.26 | 4.28 ± 0.04 |
| Cd2 | 17.33 ± 0.57 | 3.20 ± 0.10 | 3.84 ± 0.02 |
| Cd | 17.66 ± 0.57 | 2.92 ± 0.36 | 3.83 ± 0.02 |
| Rb1 | 22.50 ± 0.50 | 2.97 ± 0.67 | 4.85 ± 0.02 |
| Rb2 | 18.66 ± 0.57 | 1.67 ± 0.34 | 4.54 ± 0.03 |
| Rb3 | 17.33 ± 1.52 | 1.24 ± 0.16 | 4.32 ± 0.02 |
| M1 | 24.66 ± 6.65 | 3.30 ± 0.26 | 4.24 ± 0.02 |
| M2 | 21.66 ± 0.57 | 3.33 ± 0.14 | 4.21 ± 0.01 |
| M3 | 18.66 ± 2.88 | 2.90 ± 0.13 | 4.09 ± 0.02 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ilievska, B.; Loftsson, T.; Hjalmarsdottir, M.A.; Asgrimsdottir, G.M. Topical Formulation Comprising Fatty Acid Extract from Cod Liver Oil: Development, Evaluation and Stability Studies. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14060105
Ilievska B, Loftsson T, Hjalmarsdottir MA, Asgrimsdottir GM. Topical Formulation Comprising Fatty Acid Extract from Cod Liver Oil: Development, Evaluation and Stability Studies. Marine Drugs. 2016; 14(6):105. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14060105
Chicago/Turabian StyleIlievska, Biljana, Thorsteinn Loftsson, Martha Asdis Hjalmarsdottir, and Gudrun Marta Asgrimsdottir. 2016. "Topical Formulation Comprising Fatty Acid Extract from Cod Liver Oil: Development, Evaluation and Stability Studies" Marine Drugs 14, no. 6: 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14060105