Identification of Sumoylated Proteins in the Silkworm Bombyx mori
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Results
2.1.1. Subcellular Localization of Small Ubiquitin-Like Modifier of Bombyx mori (BmSUMO)
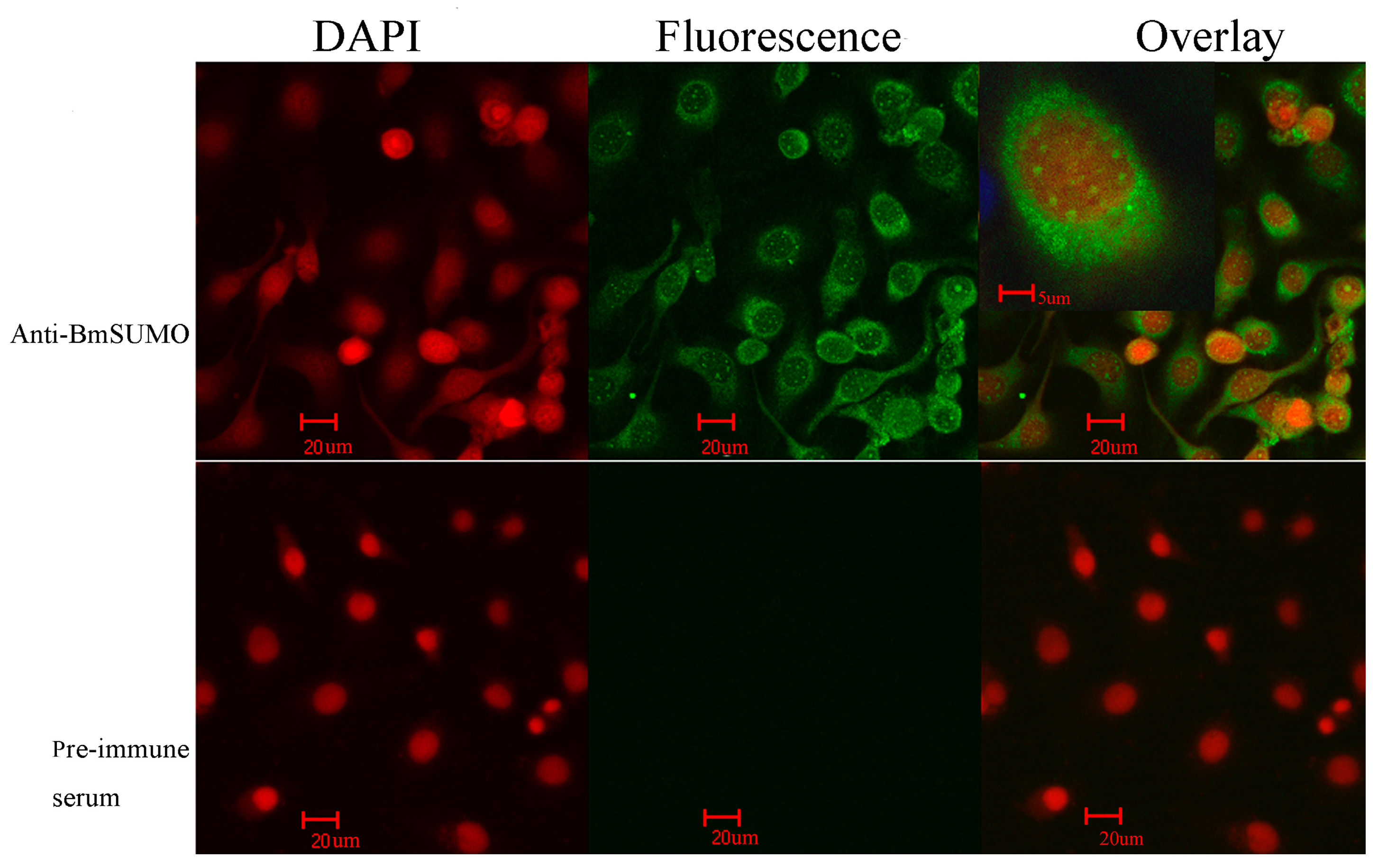
2.1.2. Isolation of SUMOylated Proteins

2.1.3. Identification of Sumoylated Proteins by LC–ESI-MS/MS
| Protein ID | Description | Number of Peptides |
|---|---|---|
| BGIBMGA000115-PA | BUD13 homolog | 2 |
| BGIBMGA000511-PA | 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase | 5 |
| BGIBMGA000828-PA | low quality protein: DNA replication licensing factor Mcm6-like | 2 |
| BGIBMGA001206-PA | chaperonin containing t-complex polypeptide 1 beta subunit | 2 |
| BGIBMGA001241-PA | heat shock protein 75 kDa, mitochondrial-like | 3 |
| BGIBMGA001549-PA | predicted: polyubiquitin-C-like isoform X1 | 3 |
| BGIBMGA001627-PA | hypothetical protein KGM_01391 | 2 |
| BGIBMGA002186-PA | thiol peroxiredoxin | 2 |
| BGIBMGA002620-PA | predicted: sequestosome-1-like isoform X2 | 3 |
| BGIBMGA002755-PA | SUMO-1 activating enzyme | 13 |
| BGIBMGA003351-PA | minichromosome maintenance complex component 7 | 2 |
| BGIBMGA003361-PA | predicted: low quality protein: importin-5-like | 2 |
| BGIBMGA003901-PA | predicted: ATP synthase subunit beta, mitochondrial-like | 6 |
| BGIBMGA004023-PA | predicted: cyclin-related protein FAM58A-like | 12 |
| BGIBMGA004614-PA | predicted: heat shock protein 70 A2-like | 6 |
| BGIBMGA004741-PA | predicted: HIV Tat-specific factor 1 homolog | 4 |
| BGIBMGA005315-PA | predicted: 26S proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit 2-like | 2 |
| BGIBMGA005425-PA | ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 | 23 |
| BGIBMGA005684-PA | 60S ribosomal protein L38 | 4 |
| BGIBMGA005928-PA | ribosomal protein L35 | 3 |
| BGIBMGA006462-PA | eIF2B-alpha protein | 2 |
| BGIBMGA006751-PA | GTP-binding nuclear protein Ran | 5 |
| BGIBMGA006980-PA | predicted: nucleolar protein 12-like | 3 |
| BGIBMGA007311-PA | 40S ribosomal protein SA | 3 |
| BGIBMGA007460-PA | predicted: serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 2A catalytic subunit beta isoform-like | 3 |
| BGIBMGA007477-PA | receptor for activated protein kinase C RACK 1 isoform 1 | 4 |
| BGIBMGA007502-PA | predicted: NAD(P) transhydrogenase, mitochondrial-like isoform X1 | 3 |
| BGIBMGA007720-PA | serine protease inhibitor 2 | 4 |
| BGIBMGA008295-PA | vacuolar ATP synthase catalytic subunit A | 2 |
| BGIBMGA008555-PA | AMP dependent coa ligase | 2 |
| BGIBMGA009250-PA | predicted: cAMP-responsive element-binding protein-like 2-like | 3 |
| BGIBMGA009816-PA | low quality protein: pre-mRNA-processing-splicing factor 8-like | 2 |
| BGIBMGA010005-PA | predicted: transcription initiation factor TFIID subunit 3-like | 2 |
| BGIBMGA010361-PA | muscle glycogen phosphorylase | 2 |
| BGIBMGA012102-PA | predicted: mediator of RNA polymerase II transcription subunit 10-like isoform X1 | 5 |
| BGIBMGA012116-PA | predicted: SUMO-activating enzyme subunit 2-like | 17 |
| BGIBMGA012126-PA | predicted: eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 subunit L | 2 |
| BGIBMGA012558-PA | predicted: protein timeless homolog | 2 |
| BGIBMGA012935-PA | clathrin heavy chain | 12 |
| BGIBMGA012976-PA | predicted: serine/threonine-protein kinase TAO3-like | 3 |
| BGIBMGA013021-PA | fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolase | 22 |
| BGIBMGA013063-PA | predicted: malate dehydrogenase, mitochondrial-like | 8 |
| BGIBMGA013133-PA | predicted: asparagine—tRNA ligase, cytoplasmic-like | 5 |
| BGIBMGA013536-PA | DnaJ-5 | 3 |
| BGIBMGA013792-PA | 40S ribosomal protein S11 | 5 |
| BGIBMGA014087-PA | peroxiredoxin | 3 |
| BGIBMGA014177-PA | predicted: 26S protease regulatory subunit 8-like | 3 |
| BGIBMGA014589-PA | phosphate transport protein | 2 |
| Bm_nscaf2511_205 | predicted: UPF0396 protein CG6066-like | 2 |
| Bm_nscaf2681_31 | predicted: long-chain-fatty-acid—CoA ligase 4-like isoform X1 | 3 |
| Bm_nscaf2810_03 | hypothetical protein KGM_10301 | 3 |
| Bm_nscaf2825_24 | predicted: la-related protein 7-like | 3 |
| Bm_nscaf2829_166 | predicted: low quality protein: myosin heavy chain, non-muscle-like | 3 |
| Bm_nscaf2839_32 | predicted: U4/U6.U5 tri-snRNP-associated protein 1 | 2 |
| Bm_nscaf2847_240 | acinus | 2 |
| Bm_nscaf2887_111 | predicted: ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX3X isoform X1 | 10 |
| Bm_nscaf2888_123 | heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 | 2 |
| Bm_nscaf2916_07 | predicted: putative U5 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein 200 kDa helicase-like | 4 |
| Bm_nscaf2930_118 | predicted: ADP-ribosylation factor 2-like | 2 |
| Bm_nscaf2970_069 | mitochondrial matrix protein p32 | 2 |
| Bm_nscaf2970_070 | predicted: zinc finger CCHC domain-containing protein 4-like isoform X1 | 6 |
| Bm_nscaf2993_193 | predicted: striatin-3-like isoform X1 | 2 |
| Bm_nscaf3015_085 | CAAX prenyl protease 1 homolog | 3 |
| Bm_nscaf3027_031 | asparagine synthetase | 2 |
| Bm_nscaf3031_268 | DNA topoisomerase 2 | 6 |
| Bm_nscaf481_60 | protein LTV1 homolog | 2 |
| BGIBMGA010396-PA | arginine/serine-rich splicing factor 7 | 2 |
| BGIBMGA010668-PA | predicted: barrier-to-autointegration factor B-like | 3 |
2.1.4. Confirmation of SUMOylated Proteins by Co-Immunoprecipitation (co-IP)

2.1.5. Functional Annotation of sumoylated Proteins
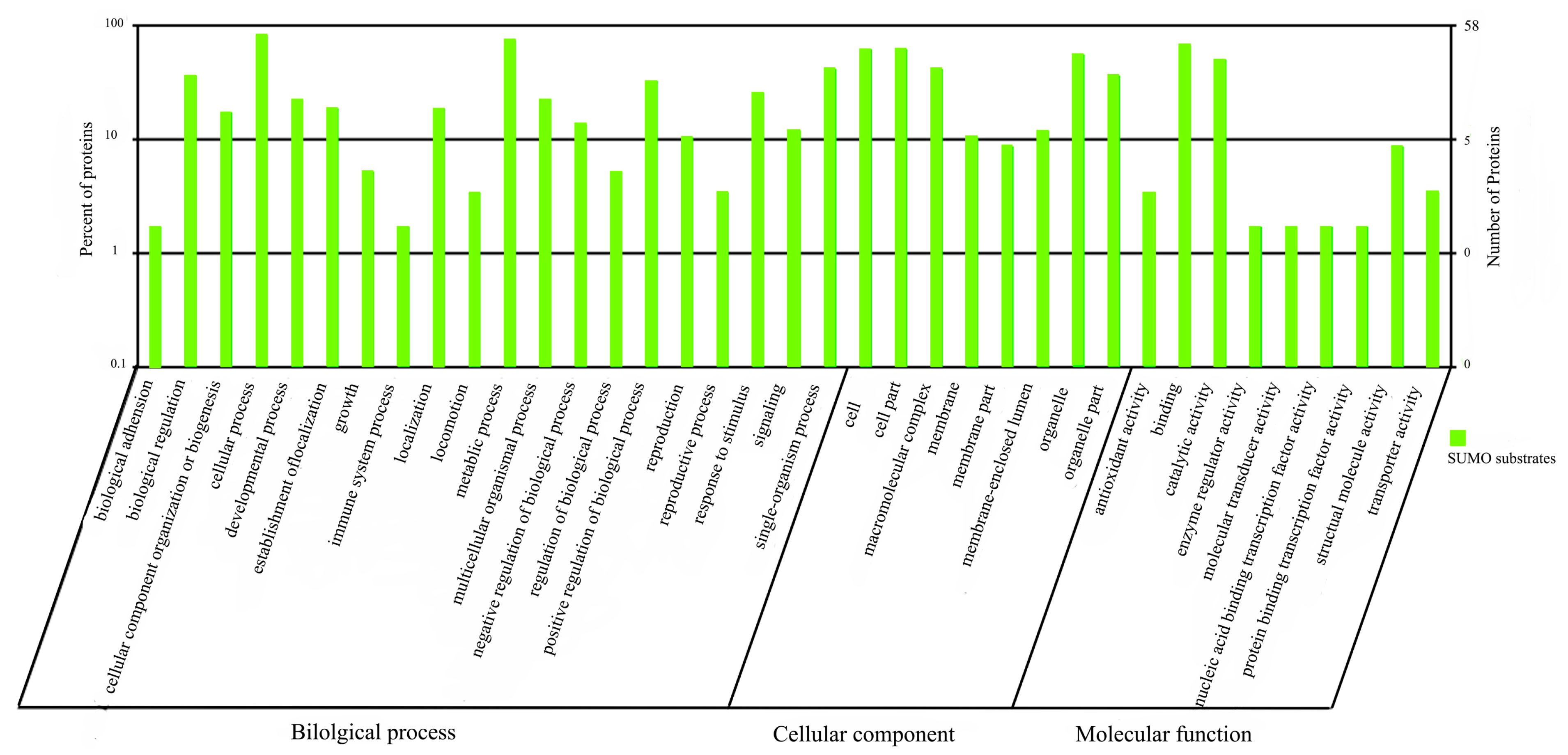
2.2. Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Plasmid Construction and Cell Transfection
3.2. Protein Extraction and Immunoprecipitation
3.3. Western Blotting
3.4. Antibody Preparation and Confocal Laser-Scanning Microscopy
3.5. LC–ESI-MS/MS Analysis
3.6. Confirmation of SUMOylated Proteins in S2 Cells
3.7. Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burnett, G.; Kennedy, E.P. The enzymatic phosphorylation of proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1954, 211, 969–980. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grewal, S.I.; Rice, J.C. Regulation of heterochromatin by histone methylation and small RNAs. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2004, 16, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glozak, M.A.; Sengupta, N.; Zhang, X.; Seto, E. Acetylation and deacetylation of non-histone proteins. Gene 2005, 363, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiro, R.G. Protein glycosylation: Nature, distribution, enzymatic formation, and disease implications of glycopeptide bonds. Glycobiology 2002, 12, 43R–56R. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waby, J.S.; Bingle, C.D.; Corfe, B.M. Post-translational control of sp-family transcription factors. Curr. Genomics 2008, 9, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orford, K.; Crockett, C.; Jensen, J.P.; Weissman, A.M.; Byers, S.W. Serine phosphorylation-regulated ubiquitination and degradation of β-catenin. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 24735–24738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayer, P.; Arndt, A.; Metzger, S.; Mahajan, R.; Melchior, F.; Jaenicke, R.; Becker, J. Structure determination of the small ubiquitin-related modifier SUMO-1. J. Mol. Biol. 1998, 280, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hershko, A.; Ciechanover, A. The ubiquitin pathway for the degradation of intracellular proteins. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 1986, 33, 19–56. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Muller, S.; Hoege, C.; Pyrowolakis, G.; Jentsch, S. SUMO, ubiquitinʼs mysterious cousin. Nat. Rev. 2001, 2, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, E.S. Protein modification by SUMO. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2004, 73, 355–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.J.; Hochstrasser, M. A new protease required for cell-cycle progression in yeast. Nature 1999, 398, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.J.; Hochstrasser, M. The yeast ULP2 (SMT4) gene encodes a novel protease specific for the ubiquitin-like Smt3 protein. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 2367–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desterro, J.M.; Rodriguez, M.S.; Kemp, G.D.; Hay, R.T. Identification of the enzyme required for activation of the small ubiquitin-like protein SUMO-1. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 10618–10624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, J.; Zuo, D.; Park, M. Pc2-mediated sumoylation of Smad-interacting protein 1 attenuates transcriptional repression of E-cadherin. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 35477–35489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotaja, N.; Karvonen, U.; Janne, O.A.; Palvimo, J.J. PIAS proteins modulate transcription factors by functioning as SUMO-1 ligases. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 22, 5222–5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwienhorst, I.; Johnson, E.S.; Dohmen, R.J. SUMO conjugation and deconjugation. Mol. Gen. Genet. 2000, 263, 771–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, M.S.; Dargemont, C.; Hay, R.T. SUMO-1 conjugation in vivo requires both a consensus modification motif and nuclear targeting. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 12654–12659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.; Crowe, E.; Stevens, T.A.; Candido, E.P. Functional and phylogenetic analysis of the ubiquitylation system in Caenorhabditis elegans: Ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes, ubiquitin-activating enzymes, and ubiquitin-like proteins. Genome Biol. 2002, 3, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Nishida, T.; Yasuda, H. PIAS1 and PIASxalpha function as SUMO-E3 ligases toward androgen receptor and repress androgen receptor-dependent transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 41311–41317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.P.; Hao, W.; He, D.; Xu, Y.S. Smt3 is required for the immune response of silkworm, Bombyx mori. Biochimie 2010, 92, 1306–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, H.L.; Li, S.S. Molecular features of human ubiquitin-like SUMO genes and their encoded proteins. Gene 2002, 296, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeler, J.S.; Dejean, A. Nuclear and unclear functions of SUMO. Nat. Rev. 2003, 4, 690–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashiyama, K.; Shigenobu, S.; Kobayashi, S. Expression of genes involved in sumoylation in the Drosophila germline. Gene Expr. Patterns 2009, 9, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.; Bhaskar, V.; Fernandez, J.; Courey, A.J. Drosophila Ulp1, a nuclear pore-associated SUMO protease, prevents accumulation of cytoplasmic SUMO conjugates. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 43805–43814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denison, C.; Rudner, A.D.; Gerber, S.A.; Bakalarski, C.E.; Moazed, D.; Gygi, S.P. A proteomic strategy for gaining insights into protein sumoylation in yeast. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2005, 4, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.T.; Kim, K.K.; Matunis, M.J.; Ahn, J.H. Enhanced SUMOylation of proteins containing a SUMO-interacting motif by SUMO-Ubc9 fusion. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 388, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barysch, S.V.; Dittner, C.; Flotho, A.; Becker, J.; Melchior, F. Identification and analysis of endogenous SUMO1 and SUMO2/3 targets in mammalian cells and tissues using monoclonal antibodies. Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 896–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, J.; Barysch, S.V.; Karaca, S.; Dittner, C.; Hsiao, H.H.; Berriel Diaz, M.; Herzig, S.; Urlaub, H.; Melchior, F. Detecting endogenous SUMO targets in mammalian cells and tissues. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2013, 20, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leach, M.D.; Stead, D.A.; Argo, E.; Brown, A.J. Identification of sumoylation targets, combined with inactivation of SMT3, reveals the impact of sumoylation upon growth, morphology, and stress resistance in the pathogen Candida albicans. Mol. Biol. Cell 2010, 22, 687–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.C.; Choi, W.; Park, H.J.; Cheong, M.S.; Koo, Y.D.; Shin, G.; Chung, W.S.; Kim, W.Y.; Kim, M.G.; Bressan, R.A.; et al. Identification and molecular properties of SUMO-binding proteins in Arabidopsis. Mol. Cells 2011, 32, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, Y.; Lee, D.; Kalichamy, K.; Hong, S.E.; Michalak, M.; Ahnn, J.; Kim do, H.; Lee, S.K. Sumoylation regulates ER stress response by modulating calreticulin gene expression in XBP-1-dependent mode in Caenorhabditis elegans. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2014, 53, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyer-Guittaut, M.; Birsoy, K.; Potel, C.; Elliott, G.; Jaffray, E.; Desterro, J.M.; Hay, R.T.; Oelgeschlager, T. SUMO-1 modification of human transcription factor (TF) IID complex subunits: Inhibition of TFIID promoter-binding activity through SUMO-1 modification of hsTAF5. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 9937–9945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, T.J.; Powers, L.S.; Boudreau, R.L.; Brink, B.; Reisetter, A.; Goel, K.; Gerke, A.K.; Hassan, I.H.; Monick, M.M. A microRNA processing defect in smokersʼ macrophages is linked to SUMOylation of the endonuclease DICER. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 12823–12834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigodner, M.; Shrivastava, V.; Gutstein, L.E.; Schneider, J.; Nieves, E.; Goldstein, M.; Feliciano, M.; Callaway, M. Localization and identification of sumoylated proteins in human sperm: Excessive sumoylation is a marker of defective spermatozoa. Hum. Reprod. 2013, 28, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, C.Y.; Shin, H.S.; Kim, H.D.; Kim, J.W.; Choi, S.Y.; Kim, J. Ribosomal protein S3 is stabilized by sumoylation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 414, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahner, A.; Gong, X.; Schmidt, B.Z.; Peters, K.W.; Rabeh, W.M.; Thibodeau, P.H.; Lukacs, G.L.; Frizzell, R.A. Small heat shock proteins target mutant cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator for degradation via a small ubiquitin-like modifier-dependent pathway. Mol. Biol. Cell 2012, 24, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunet Simioni, M.; de Thonel, A.; Hammann, A.; Joly, A.L.; Bossis, G.; Fourmaux, E.; Bouchot, A.; Landry, J.; Piechaczyk, M.; Garrido, C. Heat shock protein 27 is involved in SUMO-2/3 modification of heat shock factor 1 and thereby modulates the transcription factor activity. Oncogene 2009, 28, 3332–3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finkbeiner, E.; Haindl, M.; Muller, S. The SUMO system controls nucleolar partitioning of a novel mammalian ribosome biogenesis complex. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 1067–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panse, V.G.; Kressler, D.; Pauli, A.; Petfalski, E.; Gnadig, M.; Tollervey, D.; Hurt, E. Formation and nuclear export of preribosomes are functionally linked to the small-ubiquitin-related modifier pathway. Traffic 2006, 7, 1311–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, V.G. Sumoylation at the host-pathogen interface. Biomolecules 2012, 2, 203–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimmer, P.; Schreiner, S.; Dobner, T. Human pathogens and the host cell SUMOylation system. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 642–654. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boggio, R.; Colombo, R.; Hay, R.T.; Draetta, G.F.; Chiocca, S. A mechanism for inhibiting the SUMO pathway. Mol. Cell 2004, 16, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boggio, R.; Passafaro, A.; Chiocca, S. Targeting SUMO E1 to ubiquitin ligases: A viral strategy to counteract sumoylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 15376–15382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, T.H.; Kubota, T.; Matsuoka, M.; Jones, S.; Bradfute, S.B.; Bray, M.; Ozato, K. Ebola Zaire virus blocks type I interferon production by exploiting the host SUMO modification machinery. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heaton, P.R.; Deyrieux, A.F.; Bian, X.L.; Wilson, V.G. HPV E6 proteins target Ubc9, the SUMO conjugating enzyme. Virus Res. 2011, 158, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bentz, G.L.; Whitehurst, C.B.; Pagano, J.S. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) C-terminal-activating region 3 contributes to LMP1-mediated cellular migration via its interaction with Ubc9. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 10144–10153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherer, M.; Reuter, N.; Wagenknecht, N.; Otto, V.; Sticht, H.; Stamminger, T. Small ubiquitin-related modifier (SUMO) pathway-mediated enhancement of human cytomegalovirus replication correlates with a recruitment of SUMO-1/3 proteins to viral replication compartments. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 1373–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangasamy, D.; Woytek, K.; Khan, S.A.; Wilson, V.G. SUMO-1 modification of bovine papillomavirus E1 protein is required for intranuclear accumulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 37999–38004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohl, C.R.; Abrahamyan, L.G.; Wood, C. Human Ubc9 is involved in intracellular HIV-1 Env stability after trafficking out of the trans-Golgi network in a Gag dependent manner. PLoS One 2013, 8, e69359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gravel, A.; Dion, V.; Cloutier, N.; Gosselin, J.; Flamand, L. Characterization of human herpesvirus 6 variant B immediate-early 1 protein modifications by small ubiquitin-related modifiers. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, P.C.; Izumiya, Y.; Wu, C.Y.; Fitzgerald, L.D.; Campbell, M.; Ellison, T.J.; Lam, K.S.; Luciw, P.A.; Kung, H.J. Kaposiʼs sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) encodes a SUMO E3 ligase that is SIM-dependent and SUMO-2/3-specific. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 5266–5273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennella, M.A.; Liu, Y.; Woo, J.L.; Kim, C.A.; Berk, A.J. Adenovirus E1B 55-kilodalton protein is a p53-SUMO1 E3 ligase that represses p53 and stimulates its nuclear export through interactions with promyelocytic leukemia nuclear bodies. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 12210–12225. [Google Scholar]
- Langereis, M.A.; Rosas-Acosta, G.; Mulder, K.; Wilson, V.G. Production of sumoylated proteins using a baculovirus expression system. J. Virol. Methods 2007, 139, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Xie, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Jiang, S.; Liu, W.; Mu, W.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Xue, Y.; Ren, J. GPS-SUMO: A tool for the prediction of sumoylation sites and SUMO-interaction motifs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W325–W330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GPS-SUMO. Available online: http://sumosp.biocuckoo.org/ (accessed on 17 September 2014).
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S.; Sato, Y.; Furumichi, M.; Tanabe, M. Kegg for integration and interpretation of large-scale molecular data sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D109–D114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- KEGG. Available online: http://www.genome.jp/kegg/ (accessed on 4 June 2014).
- Kristensen, D.M.; Kannan, L.; Coleman, M.K.; Wolf, Y.I.; Sorokin, A.; Koonin, E.V.; Mushegian, A. A low-polynomial algorithm for assembling clusters of orthologous groups from intergenomic symmetric best matches. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1481–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- COGs. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/COG/ (accessed on 13 November 2014).
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, X.; Fu, X.; Hao, B.; Zhu, F.; Xiao, S.; Xu, L.; Shen, Z. Identification of Sumoylated Proteins in the Silkworm Bombyx mori. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 22011-22027. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151222011
Tang X, Fu X, Hao B, Zhu F, Xiao S, Xu L, Shen Z. Identification of Sumoylated Proteins in the Silkworm Bombyx mori. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2014; 15(12):22011-22027. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151222011
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Xudong, Xuliang Fu, Bifang Hao, Feng Zhu, Shengyan Xiao, Li Xu, and Zhongyuan Shen. 2014. "Identification of Sumoylated Proteins in the Silkworm Bombyx mori" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 15, no. 12: 22011-22027. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151222011
APA StyleTang, X., Fu, X., Hao, B., Zhu, F., Xiao, S., Xu, L., & Shen, Z. (2014). Identification of Sumoylated Proteins in the Silkworm Bombyx mori. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 15(12), 22011-22027. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151222011




