Adrenergic Metabolic and Hemodynamic Effects of Octopamine in the Liver
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
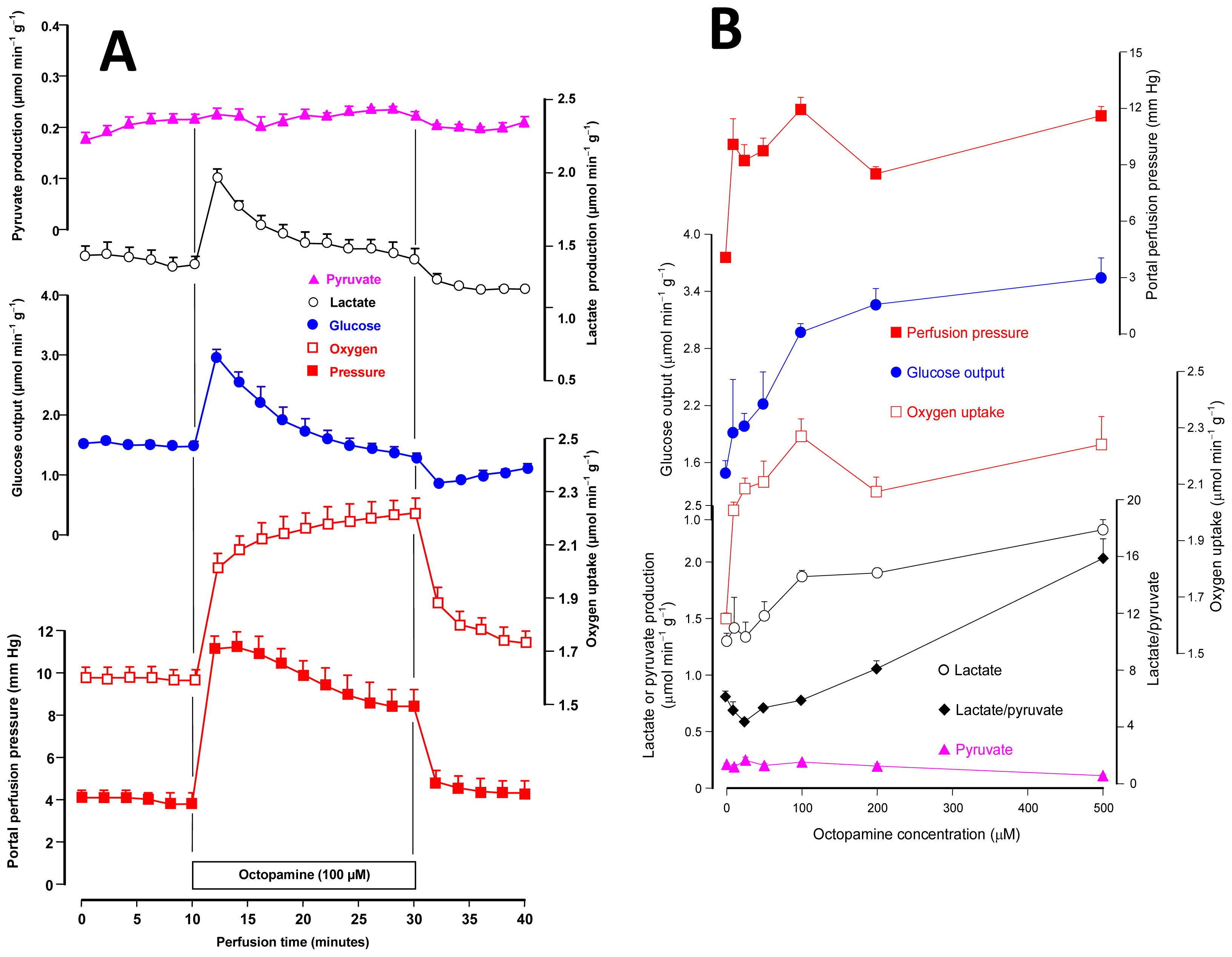
2.1. Effects of Octopamine on Glycogen Catabolism, Oxygen Uptake and Hemodynamics
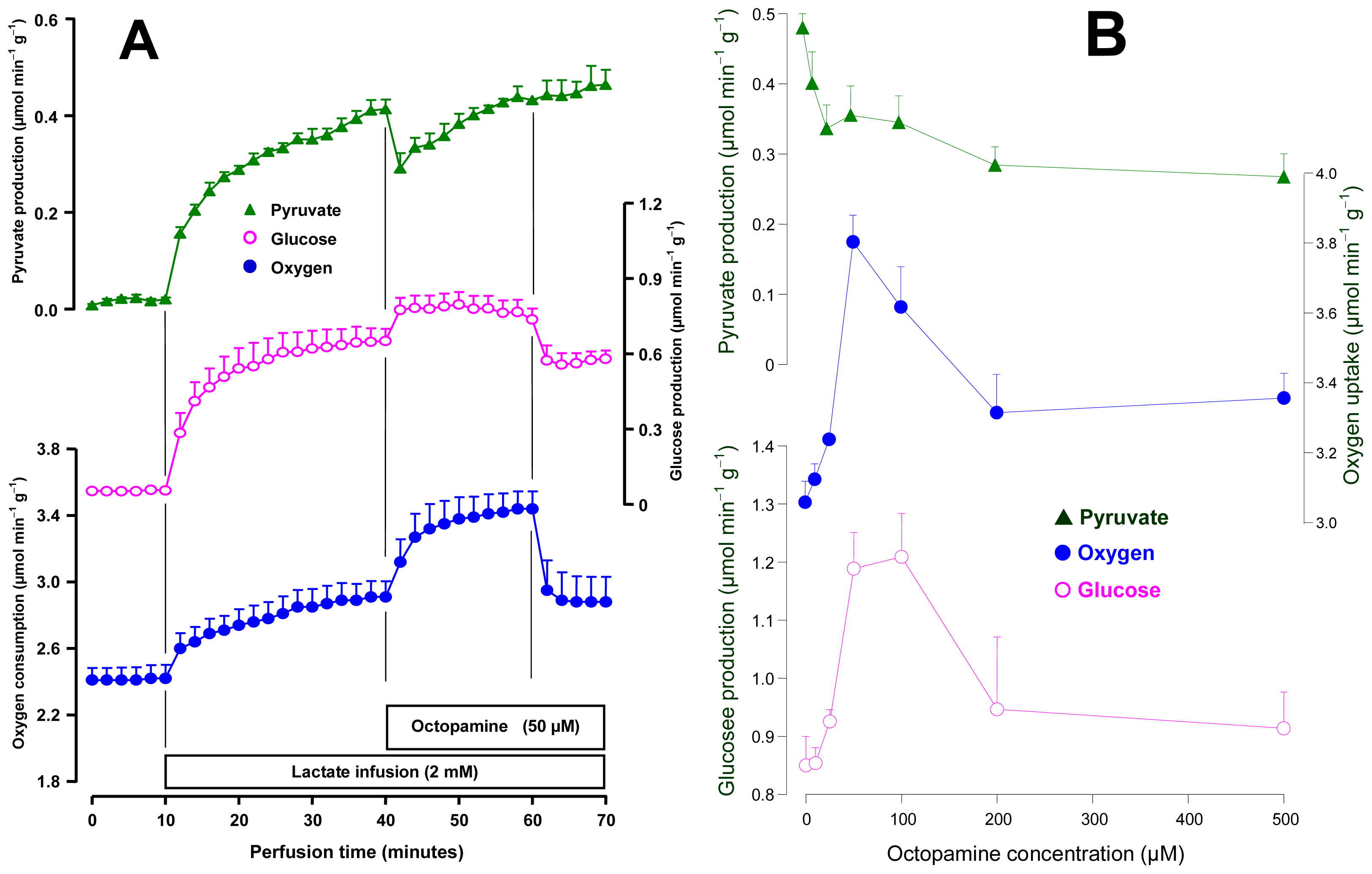
2.2. Effects of Octopamine on Gluconeogenesis and the Associated Oxygen Uptake
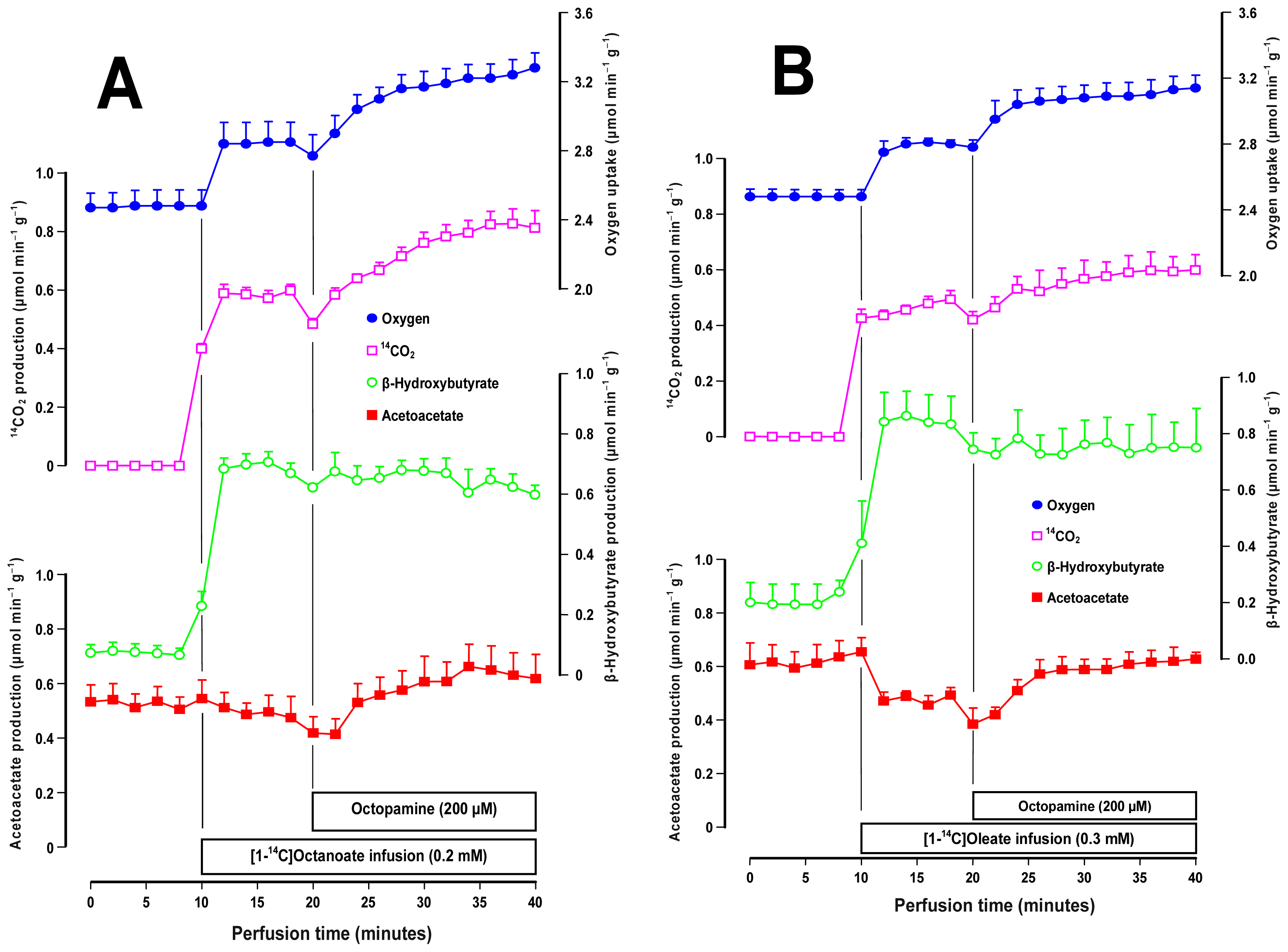
2.3. Effects of Octopamine on Fatty Acid Metabolism
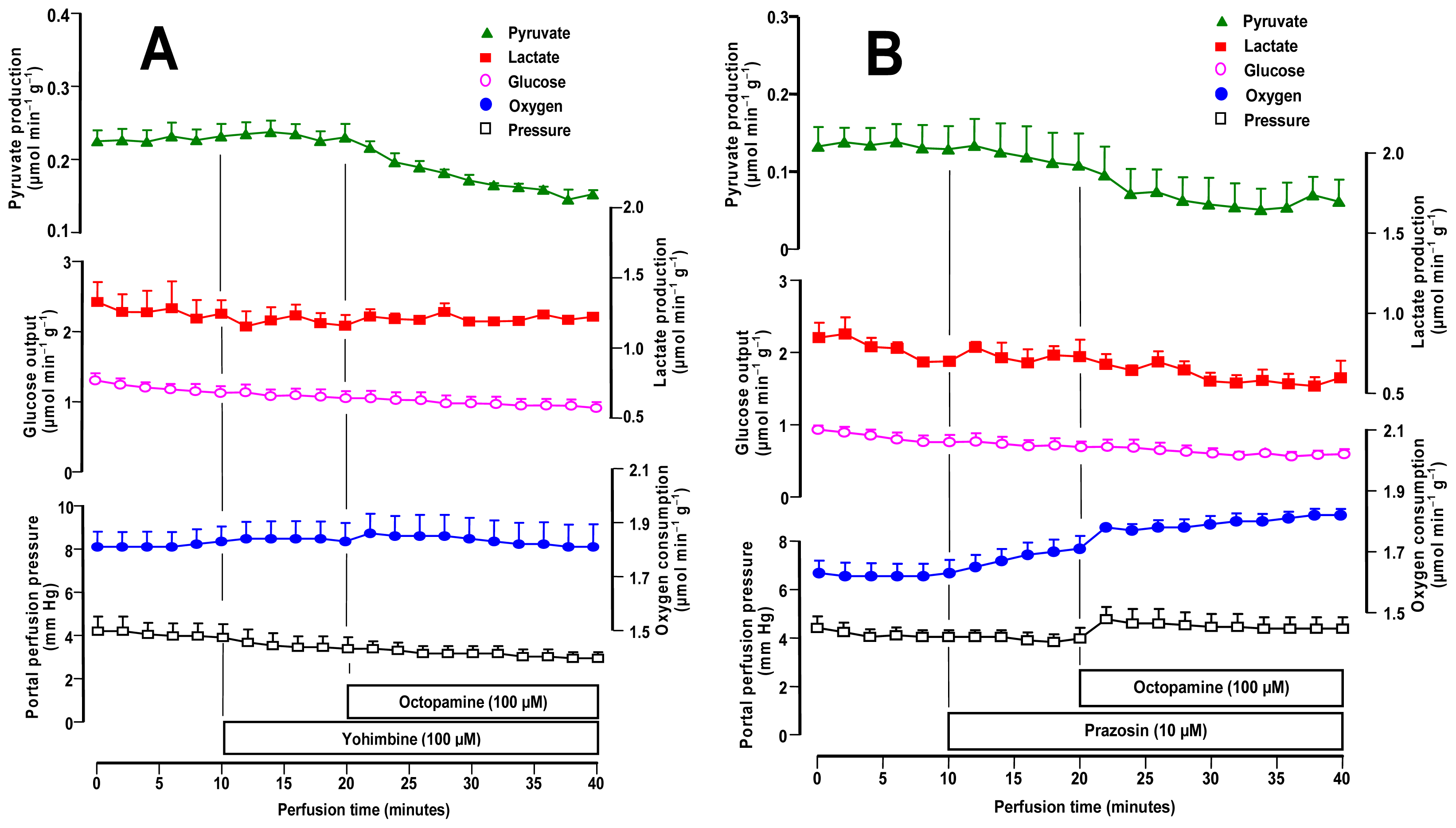
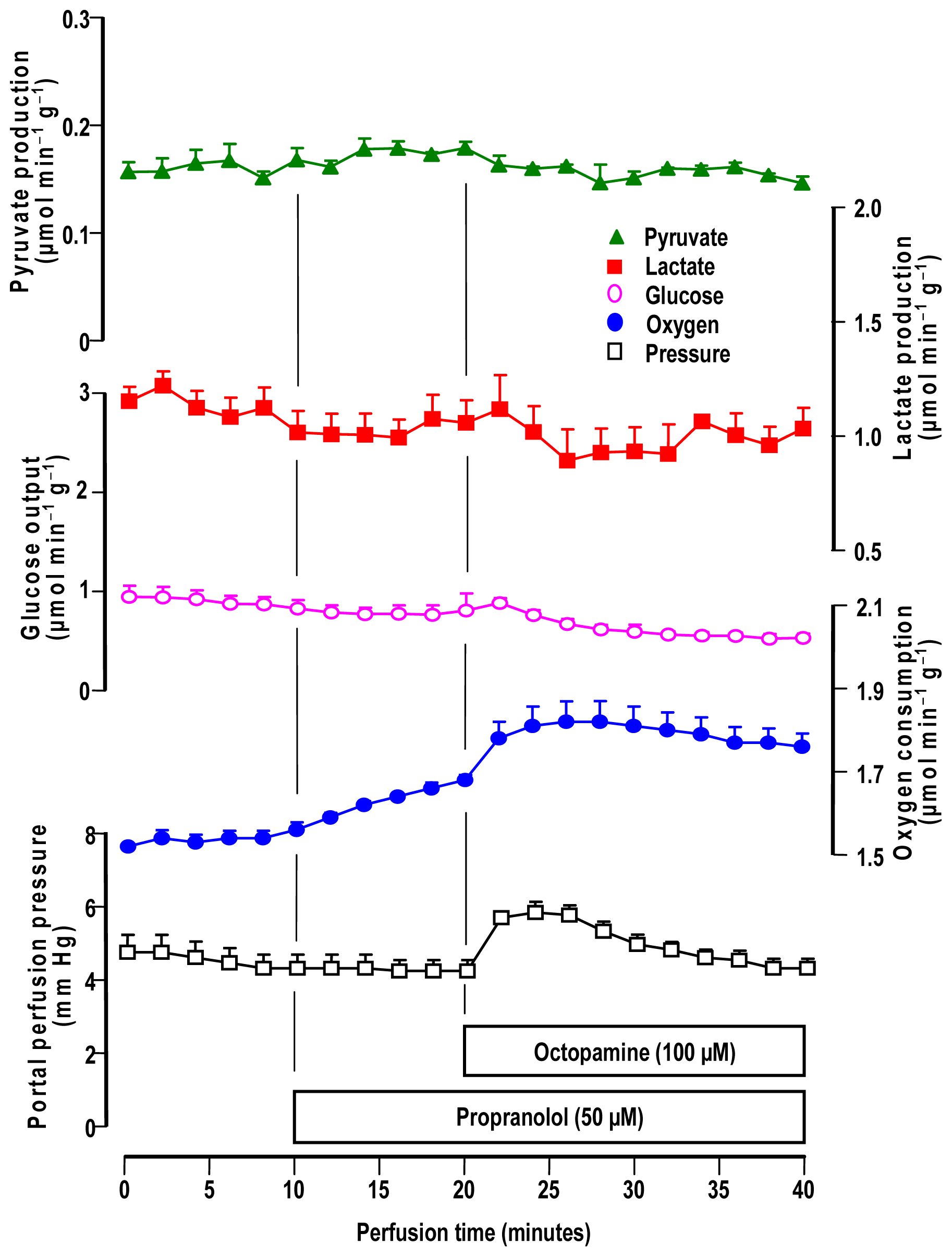
2.4. Influence of Adrenergic Antagonists on the Effects of Octopamine
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials and Animals
3.2. Liver Perfusion
3.3. Analytics
3.4. Statistics
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- David, J.C.; Coulon, J.F. Octopamine in invertebrates and vertebrates. A review. Prog. Neurobiol 1985, 24, 141–185. [Google Scholar]
- Esparmer, V. Adrenaline-like action of extracts of posterior salivary glands of Octopus vulgaris irradiated with ultraviolet light. Arch. Sci. Biol 1940, 26, 443–468. [Google Scholar]
- Thevis, M.; Koch, A.; Sigmund, G.; Thomas, A.; Schänzer, W. Analysis of octopamine in human doping control samples. Biomed. Chromatogr 2012, 26, 610–615. [Google Scholar]
- Verlinde, H.; Vleugels, R.; Marchal, E.; Badisco, L.; Pflüger, H.J.; Blenau, W.; Broeck, J.V. The role of octopamine in locusts and other arthropods. J. Insect Physiol 2010, 56, 854–867. [Google Scholar]
- Even, N.; Devaud, J.M.; Barron, A.B. General stress responses in the honey bee. Insects 2012, 3, 1271–1298. [Google Scholar]
- Roeder, T. Octopamine in invertebrates. Progr. Neurobiol 1999, 59, 533–561. [Google Scholar]
- Arrese, E.L.; Soulages, J.L. Insect fat body: Energy, metabolism, and regulation. Annu. Rev. Entomol 2010, 55, 207–225. [Google Scholar]
- Pellati, F.; Benvenuti, S.; Melegari, M.; Firenzuoli, F. Determination of adrenergic agonists from extracts and herbal products of Citrus aurantium L. var. amara by LC. J. Pharmac. Biomed. Anal 2002, 29, 1113–1119. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, F.; Tao, L.; Luo, X.; Ding, L.; Guo, M.; Nie, L.; Yao, S. Determination of octopamine, synephrine and tyramine in Citrus herbs by ionic liquid improved ‘green’ chromatography. J. Chromatogr 2006, 1125, 182–188. [Google Scholar]
- He, D.; Shan, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liu, G.; Chen, B.; Yao, S. Simultaneous determination of flavanones, hydroxycinnamic acids and alkaloids in citrus fruits by HPLC-DAD–ESI/MS. Food Chem 2011, 127, 880–885. [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer, J.T.; Allison, D.B.; Coates, P.M. Dietary supplements in weight reduction. J. Am. Diet Assoc 2005, 105, 80–86. [Google Scholar]
- Haaz, S.; Fontaine, K.R.; Cutter, G.; Limdi, N.; Perumean-Chaney, S.; Allison, D.B. Citrus aurantium and synephrine alkaloids in the treatment of overweight and obesity: An update. Obesity Rev 2006, 7, 79–88. [Google Scholar]
- Berman-Fugh, A.; Myers, A. Citrus aurantium, an ingredient of dietary supplements marketed for weight loss: Current status of clinical and basic research. Exp. Biol. Med 2004, 229, 698–704. [Google Scholar]
- Carpéné, C.; Galitzky, J.; Fontana, E.; Atgié, C.; Lafontan, N.; Berlan, M. Selective activation of β3-adrenoreceptors by octopamine: Comparative studies in mammalian fat cells. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol 1999, 359, 310–321. [Google Scholar]
- Mercader, J.; Wanecq, E.; Chen, J.; Carpéné, C. Isopropylnorsynephrine is a stronger lipolytic agent in human adipocytes than synephrine and other amines present inCitrus aurantium. J. Physiol. Biochem 2011, 67, 443–452. [Google Scholar]
- Peixoto, J.S.; Comar, J.F.; Moreira, C.T.; Soares, A.A.; Oliveira, A.L.; Bracht, A.; Peralta, R.M. Effects of Citrus aurantium (bitter orange) fruit extracts and p-synephrine on metabolic fluxes in the rat liver. Molecules 2012, 17, 5854–5869. [Google Scholar]
- Blau, C.; Wegener, G.; Candy, D.J. The effect of octopamine on the glycolytic activator fructose 2,6-bisphosphate in perfused locust flight muscle. Insect Biochem. Molec. Biol 1994, 24, 677–683. [Google Scholar]
- Broetto-Biazon, A.B.; Bracht, A.; Ishii-Iwamoto, E.L.; Moraes Silva, V.; Kelmer-Bracht, A.M. The action of extracellular NAD+ on Ca2+ efflux, hemodynamics and some metabolic parameters in the isolated perfused rat liver. Eur. J. Pharmacol 2004, 484, 291–301. [Google Scholar]
- Bracht, A.; Kouyoumdjian, M.; Ishii-Iwamoto, E.L.; Borges, D.R. Indicator injections and pressure monitoring as complementary tools for investigating microcirculatory changes in the liver. Trends Comp. Biochem. Physiol 2002, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Scholz, R.; Bücher, T. Hemoglobin-free Perfusion of Rat Liver. In Control of Energy Metabolism, 1st ed; Chance, B., Estabrook, R.W., Williamson, J.R., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1965; pp. 393–414. [Google Scholar]
- Sies, H. Nicotinamide Nucleotide Compartmentation. In Metabolic Compartmentation, 1st ed; Sies, H., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1982; pp. 205–231. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.H.; Keeley, L.L. The effect of biogenic amines and their analogs on carbohydrate metabolism in the fat body of the cockroach Blaberus discoidalis. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol 1998, 110, 88–95. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, N.S.; Ishii-Iwamoto, E.L.; Bracht, A. Activation of glycogenolysis by methotrexate. Influence of calcium and inhibitors of hormone action. Biochem. Pharmacol 1992, 44, 781–787. [Google Scholar]
- Soboll, S.; Scholz, R. Control of energy metabolism by glucagon and adrenaline in perfused rat liver. FEBS Lett 1986, 205, 109–112. [Google Scholar]
- Bazotte, R.B.; Constantin, J.; Curi, R.; Kemmelmeier, F.S.; Hell, N.S.; Bracht, A. The sensitivity of glycogenolysis to glucagon, epinephrine and cyanide in livers from rats in different metabolic conditions. Res. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol 1989, 64, 193–203. [Google Scholar]
- Marques da Silva, A.C.; D’Avila, R.B.; Ferrari, A.G.; Kelmer-Bracht, A.M.; Constantin, J.; Yamamoto, N.S.; Bracht, A. Ca2+-dependence of gluconeogenesis stimulation by glucagon at different cytosolic NAD(+)-NADH redox potentials. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res 1997, 30, 827–836. [Google Scholar]
- Menahan, L.A.; Wieland, O. The role of endogenous lipid in gluconeogenesis and ketogenesis of perfused rat liver. Eur. J. Biochem 1969, 9, 182–188. [Google Scholar]
- Reinhart, P.H.; Taylor, W.M.; Bygrave, F.L. Studies on α-adrenergic-induced respiration and glycogenolysis in perfused rat liver. J. Biol. Chem 1982, 257, 1906–1912. [Google Scholar]
- Haga, N.; Aikawa, K.; Shishido, K.; Yanagida, T.; Kushida, N.; Takahashi, N.; Yazaki, J.; Yamaguchi, O. Effect of long-term prazosin and yohimbine administration on c-Fos expression in spinal neurons: Inhibitory effect of α-1 and α-2 adrenoceptors on afferents from the lower urinary tract. Urol. Inter 2011, 87, 230–237. [Google Scholar]
- Landau, A.M.; Doudet, D.J.; Jakobsen, S. Amphetamine challenge decreases yohimbine binding to α2 adrenoceptors in Landrace pig brain. Psychopharmacology 2012, 222, 155–163. [Google Scholar]
- Machackova, J.; Sanganalmath, S.K.; Elimban, V.; Dhalla, N.S. β-Adrenergic blockade attenuates cardiac dysfunction and myofibrillar remodelling in congestive heart failure. J. Cell. Mol. Med 2011, 15, 545–554. [Google Scholar]
- Saitoh, Y.; Ui, M. Stimulation of glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis by epinephrine independent of its β-adrenergic function in perfused rat liver. Biochem. Pharmacol 1976, 25, 841–845. [Google Scholar]
- Bygrave, F.L.; Benedetti, A. Calcium: Its modulation in liver by cross-talk between the actions of glucagon and calcium-mobilizing agonists. Biochem. J 1993, 296, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Docherty, J.R. Pharmacology of stimulants prohibited by the world anti-doping agency (WADA). Br. J. Pharmacol 2008, 154, 606–622. [Google Scholar]
- Zucci, R.; Chiellini, G.; Scanlan, T.S.; Grandy, D.K. Trace amine-associated receptors and their ligands. Br. J. Pharmacol 2006, 149, 967–978. [Google Scholar]
- Broadly, K.J.; Fehler, M.; Ford, W.R.; Kidd, E.J. Functional evaluation of the receptors mediating vasoconstriction of rat aorta by trace amines and amphetamines. Eur. J. Pharmacol 2013, 715, 370–380. [Google Scholar]
- Roeder, T. High-affinity antagonists of the locust neuronal octopamine receptor. Eur. J. Pharmacol 1990, 191, 221–224. [Google Scholar]
- Bracht, A.; Ishii-Iwamoto, E.L.; Kelmer-Bracht, A.M. O Estudo do Metabolismo no Fígado em Perfusão. In Métodos de Laboratório em Bioquímica, (in Portuguese), 1st ed; Bracht, A., Ishii-Iwamoto, E.L., Eds.; Editora Manole: São Paulo, Brazil, 2003; pp. 275–289. [Google Scholar]
- Bergmeyer, H.U. Methods of Enzymatic Analysis; Verlag Chemie-Academic Press: Weinheim-London, Germany-UK, 1974; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Comar, J.F.; Suzuki-Kemmelmeier, F.; Bracht, A. The action of oxybutynin on haemodynamics and metabolism in the perfused rat liver. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol 2003, 93, 147–152. [Google Scholar]
- Frayn, K.N.; Arner, P.; Yki-Järvinen, H. Fatty acid metabolism in adipose tissue, muscle and liver in health and disease. Essays Biochem 2006, 42, 89–103. [Google Scholar]
- Bour, S.; Visentin, V.; Prévot, D.; Carpéné, C. Moderate weight-lowering effect of octopamine treatment in obese Zucher rats. J. Physiol. Biochem 2003, 59, 175–182. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
De Oliveira, A.L.; De Paula, M.N.; Comar, J.F.; Vilela, V.R.; Peralta, R.M.; Bracht, A. Adrenergic Metabolic and Hemodynamic Effects of Octopamine in the Liver. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 21858-21872. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141121858
De Oliveira AL, De Paula MN, Comar JF, Vilela VR, Peralta RM, Bracht A. Adrenergic Metabolic and Hemodynamic Effects of Octopamine in the Liver. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2013; 14(11):21858-21872. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141121858
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Oliveira, Andrea Luiza, Mariana Nascimento De Paula, Jurandir Fernando Comar, Vanessa Rodrigues Vilela, Rosane Marina Peralta, and Adelar Bracht. 2013. "Adrenergic Metabolic and Hemodynamic Effects of Octopamine in the Liver" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 14, no. 11: 21858-21872. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141121858






