Modulation of Human Serotonin Transporter Expression by 5-HTTLPR in Colon Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. 5-HTTLPR Different Sequence and Transcription Factor Binding Sites
2.2. Expression of 5-HTT, GRα and ERα in Human Colon Carcinoma Cells
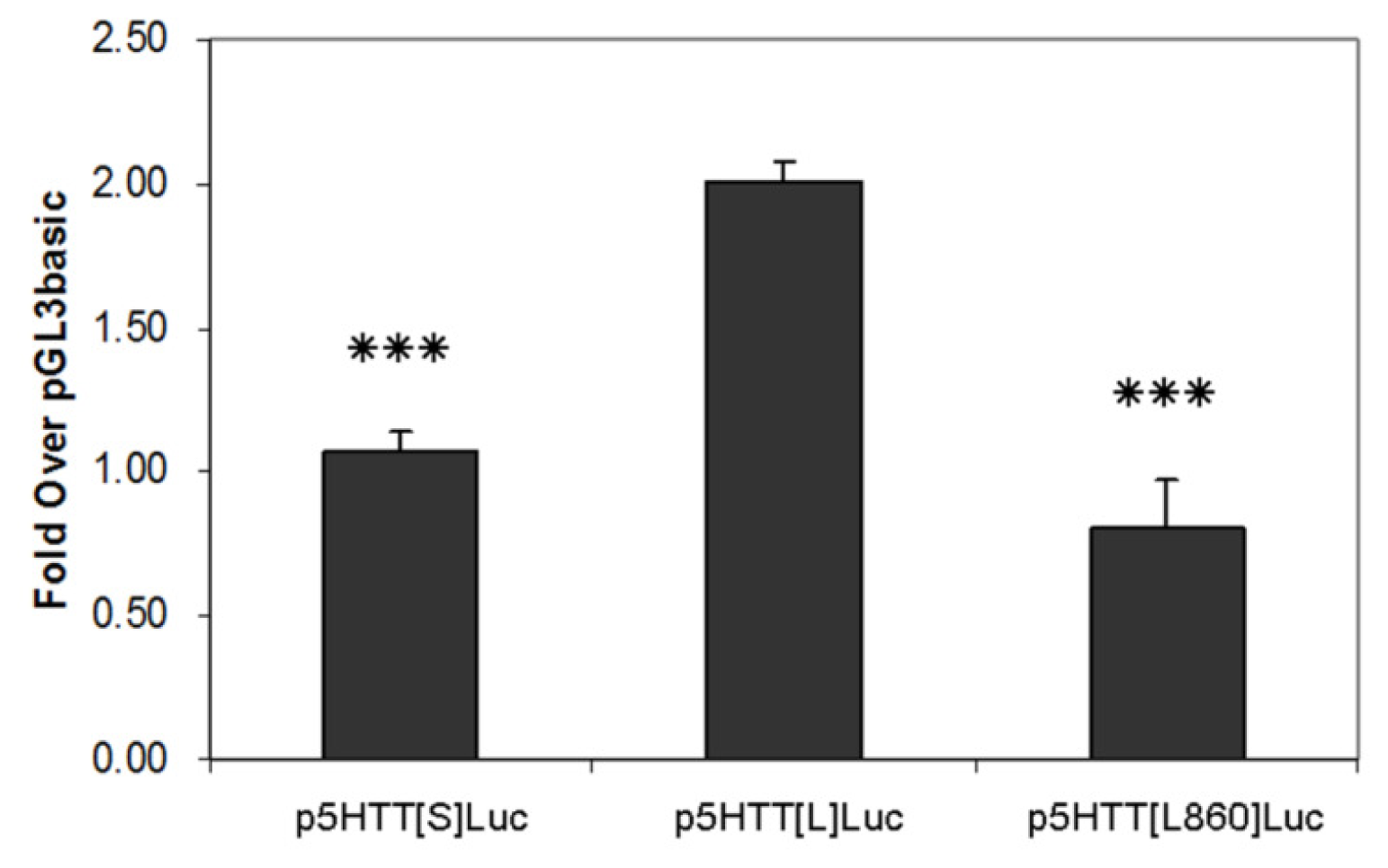
2.3. Allelic-Specific Transcriptional Activity in Human Colon Carcinoma Cells
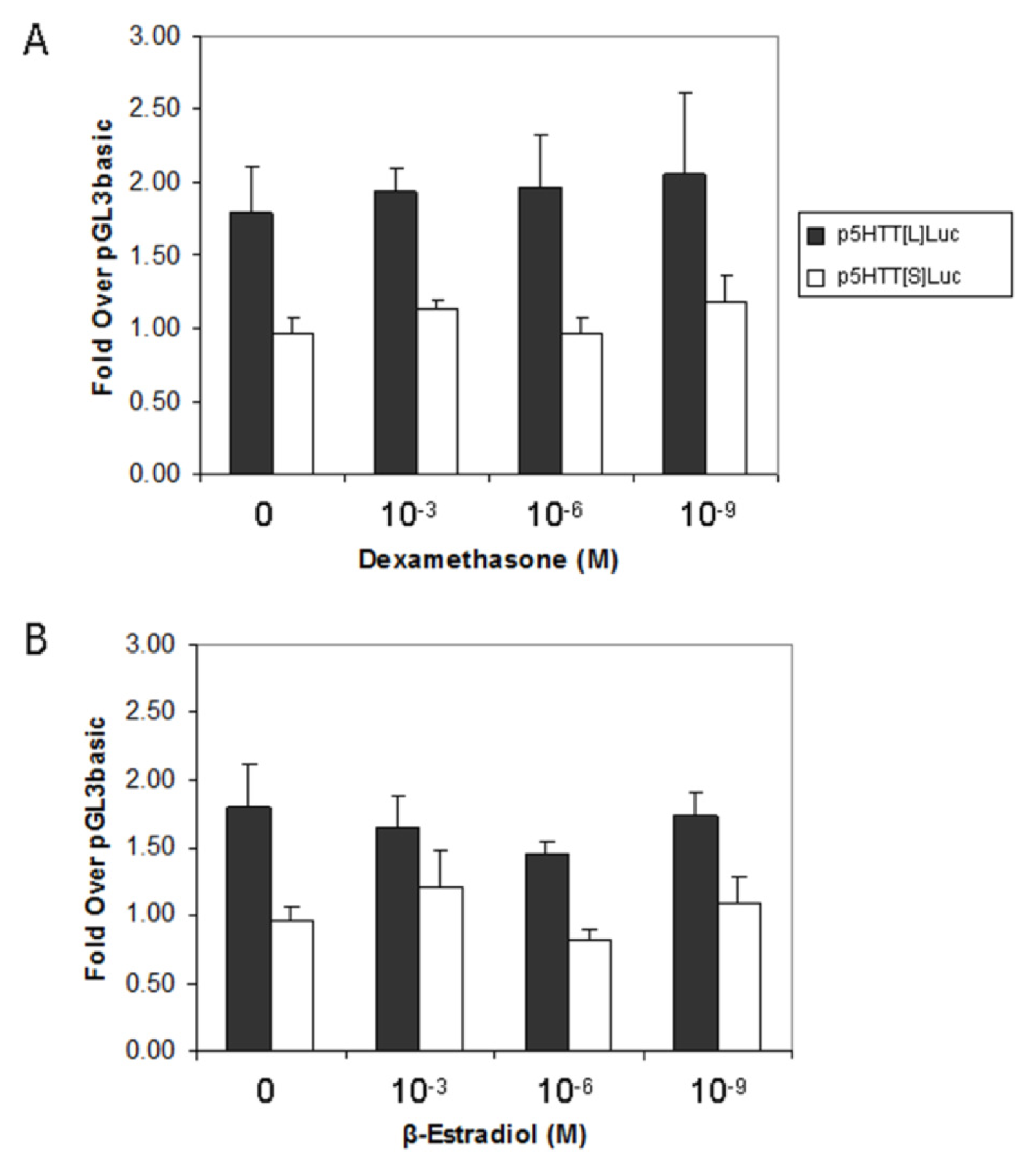
2.4. Effect of Steroids on 5-HTT Promoter Activity
2.5. Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. PCR Analysis of the 5-HTT Gene-Linked Polymorphic Region
3.2. DNA Sequencing
3.3. Transcription Factor Binding Site Analysis
3.4. Plasmid Constructions
3.5. Cell Culture
3.6. Total RNA Extraction and RT-PCR Reaction
3.7. Transient Transfection and Luciferase Reporter Gene Assay
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Gershon, MD. Review article: Roles played by 5-hydroxytryptamine in the physiology of the bowel. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther 1999, 13, 15–30. [Google Scholar]
- Gershon, MD. Plasticity in serotonin control mechanisms in the gut. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol 2003, 3, 600–607. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, DK; Lim, SW; Lee, S; Sohn, SE; Kim, S; Hahn, CG; Carroll, BJ. Serotonin transporter gene polymorphism and antidepressant response. Neuroreport 2000, 11, 215–219. [Google Scholar]
- Ormsbee, HS, III; Fondacaro, JD. Action of serotonin on the gastrointestinal tract. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med 1985, 178, 333–338. [Google Scholar]
- Camilleri, M. Serotonergic modulation of visceral sensation: Lower gut. Gut 2002, 51, i81–i86. [Google Scholar]
- Tack, J; Sarnelli, G. Serotonergic modulation of visceral sensation: Upper gastrointestinal tract. Gut 2002, 51, i77–i80. [Google Scholar]
- Martel, F. Recent advances on the importance of the serotonin transporter SERT in the rat intestine. Pharmacol. Res 2006, 54, 73–76. [Google Scholar]
- Gershon, MD. Serotonin receptors and transporters—roles in normal and abnormal gastrointestinal motility. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther 2004, 20, 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, DL; Lerner, A; Rudnick, G; Lesch, KP. Serotonin transporter: Gene, genetic disorders, and pharmacogenetics. Mol. Interv 2004, 4, 109–123. [Google Scholar]
- Ramamoorthy, S; Bauman, AL; Moore, KR; Han, H; Yang-Feng, T; Chang, AS; Ganapathy, V; Blakely, RD. Antidepressant- and cocaine-sensitive human serotonin transporter: Molecular cloning, expression, and chromosomal localization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 2542–2546. [Google Scholar]
- Heils, A; Teufel, A; Petri, S; Stober, G; Riederer, P; Bengel, D; Lesch, KP. Allelic variation of human serotonin transporter gene expression. J. Neurochem 1996, 66, 2621–2624. [Google Scholar]
- Lesch, KP; Bengel, D; Heils, A; Sabol, SZ; Greenberg, BD; Petri, S; Benjamin, J; Muller, CR; Hamer, DH; Murphy, DL. Association of anxiety-related traits with a polymorphism in the serotonin transporter gene regulatory region. Science 1996, 274, 1527–1531. [Google Scholar]
- Mortensen, OV; Thomassen, M; Larsen, MB; Whittemore, SR; Wiborg, O. Functional analysis of a novel human serotonin transporter gene promoter in immortalized raphe cells. Mol. Brain Res 1999, 68, 141–148. [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg, BD; Tolliver, TJ; Huang, SJ; Li, Q; Bengel, D; Murphy, DL. Genetic variation in the serotonin transporter promoter region affects serotonin uptake in human blood platelets. Am. J. Med. Genet 1999, 88, 83–87. [Google Scholar]
- Mossner, R; Schmitt, A; Syagailo, Y; Gerlach, M; Riederer, P; Lesch, KP. The serotonin transporter in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. J. Neural. Transm. Suppl 2000, 60, 345–350. [Google Scholar]
- Mossner, R; Henneberg, A; Schmitt, A; Syagailo, YV; Grassle, M; Hennig, T; Simantov, R; Gerlach, M; Riederer, P; Lesch, KP. Allelic variation of serotonin transporter expression is associated with depression in Parkinson’s disease. Mol. Psychiatry 2001, 6, 350–352. [Google Scholar]
- Gonda, X; Juhasz, G; Laszik, A; Rihmer, Z; Bagdy, G. Subthreshold depression is linked to the functional polymorphism of the 5HT transporter gene. J. Affect. Disord 2005, 87, 291–297. [Google Scholar]
- Cervilla, JA; Rivera, M; Molina, E; Torres-Gonzalez, F; Bellon, JA; Moreno, B; de Dios Luna, J; Lorente, JA; de Diego-Otero, Y; King, M; et al. The 5-HTTLPR s/s genotype at the serotonin transporter gene (SLC6A4) increases the risk for depression in a large cohort of primary care attendees: The PREDICT-gene study. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet 2006, 141, 912–917. [Google Scholar]
- Dubertret, C; Hanoun, N; Ades, J; Hamon, M; Gorwood, P. Family-based association study of the 5-HT transporter gene and schizophrenia. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol 2005, 8, 87–92. [Google Scholar]
- You, JS; Hu, SY; Chen, B; Zhang, HG. Serotonin transporter and tryptophan hydroxylase gene polymorphisms in Chinese patients with generalized anxiety disorder. Psychiatr. Genet 2005, 15, 7–11. [Google Scholar]
- Campi-Azevedo, AC; Boson, W; De Marco, L; Romano-Silva, MA; Correa, H. Association of the serotonin transporter promoter polymorphism with suicidal behavior. Mol. Psychiatry 2003, 8, 899–900. [Google Scholar]
- Gaysina, D; Zainullina, A; Gabdulhakov, R; Khusnutdinova, E. The serotonin transporter gene: Polymorphism and haplotype analysis in Russian suicide attempters. Neuropsychobiology 2006, 54, 70–74. [Google Scholar]
- Brune, CW; Kim, SJ; Salt, J; Leventhal, BL; Lord, C; Cook, EH, Jr. 5-HTTLPR genotype-specific phenotype in children and adolescents with autism. Am. J Psychiatry 2006, 163, 2148–2156. [Google Scholar]
- Pata, C; Erdal, ME; Derici, E; Yazar, A; Kanik, A; Ulu, O. Serotonin transporter gene polymorphism in irritable bowel syndrome. Am. J. Gastroenterol 2002, 97, 1780–1784. [Google Scholar]
- Park, JM; Choi, MG; Park, JA; Oh, JH; Cho, YK; Lee, IS; Kim, SW; Choi, KY; Chung, IS. Serotonin transporter gene polymorphism and irritable bowel syndrome. Neurogastroenterol. Motil 2006, 18, 995–1000. [Google Scholar]
- Tack, J; Broekaert, D; Fischler, B; Van Oudenhove, L; Gevers, AM; Janssens, J. A controlled crossover study of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor citalopram in irritable bowel syndrome. Gut 2006, 55, 1095–103. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, M; Murakami, M. Treatment for irritable bowel syndrome—psychotropic drugs, antidepressants and so on. Nihon Rinsho 2006, 64, 1495–1500. [Google Scholar]
- Glatz, K; Mossner, R; Heils, A; Lesch, KP. Glucocorticoid-regulated human serotonin transporter (5-HTT) expression is modulated by the 5-HTT gene-promotor-linked polymorphic region. J. Neurochem 2003, 86, 1072–1078. [Google Scholar]
- Pecins-Thompson, M; Brown, NA; Bethea, CL. Regulation of serotonin re-uptake transporter mRNA expression by ovarian steroids in rhesus macaques. Mol. Brain Res 1998, 53, 120–129. [Google Scholar]
- Bethea, CL; Gundlah, C; Mirkes, SJ. Ovarian steroid action in the serotonin neural system of macaques. Novartis Found Symp 2000, 230, 112–133. [Google Scholar]
- Koldzic-Zivanovic, N; Seitz, PK; Watson, CS; Cunningham, KA; Thomas, ML. Intracellular signaling involved in estrogen regulation of serotonin reuptake. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol 2004, 226, 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Messeguer, X; Escudero, R; Farre, D; Nunez, O; Martinez, J; Alba, MM. PROMO: detection of known transcription regulatory elements using species-tailored searches. Bioinformatics 2002, 18, 333–334. [Google Scholar]
- Farre, D; Roset, R; Huerta, M; Adsuara, JE; Rosello, L; Alba, MM; Messeguer, X. Identification of patterns in biological sequences at the ALGGEN server: PROMO and MALGEN. Nucleic Acids Res 2003, 31, 3651–3653. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, JJ; Li, Z; Pan, H; Murphy, DL; Tamir, H; Koepsell, H; Gershon, MD. Maintenance of serotonin in the intestinal mucosa and ganglia of mice that lack the high-affinity serotonin transporter: Abnormal intestinal motility and the expression of cation transporters. J. Neurosci 2001, 21, 6348–6361. [Google Scholar]
- Coates, MD; Mahoney, CR; Linden, DR; Sampson, JE; Chen, J; Blaszyk, H; Crowell, MD; Sharkey, KA; Gershon, MD; Mawe, GM; et al. Molecular defects in mucosal serotonin content and decreased serotonin reuptake transporter in ulcerative colitis and irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 2004, 126, 1657–1664. [Google Scholar]
- Houghton, LA; Atkinson, W; Whitaker, RP; Whorwell, PJ; Rimmer, MJ. Increased platelet depleted plasma 5-hydroxytryptamine concentration following meal ingestion in symptomatic female subjects with diarrhoea predominant irritable bowel syndrome. Gut 2003, 52, 663–670. [Google Scholar]
- Yeo, A; Boyd, P; Lumsden, S; Saunders, T; Handley, A; Stubbins, M; Knaggs, A; Asquith, S; Taylor, I; Bahari, B; et al. Association between a functional polymorphism in the serotonin transporter gene and diarrhoea predominant irritable bowel syndrome in women. Gut 2004, 53, 1452–1458. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, JE; Papp, A; Pinsonneault, J; Sadee, W; Saffen, D. Allelic expression of serotonin transporter (SERT) mRNA in human pons: lack of correlation with the polymorphism SERTLPR. Mol. Psychiatry 2006, 11, 649–662. [Google Scholar]
- Philibert, R; Madan, A; Andersen, A; Cadoret, R; Packer, H; Sandhu, H. Serotonin transporter mRNA levels are associated with the methylation of an upstream CpG island. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet 2007, 144B, 101–105. [Google Scholar]
- Flattem, NL; Blakely, RD. Modified structure of the human serotonin transporter promoter. Mol. Psychiatry 2000, 5, 110–115. [Google Scholar]
- Linden, DR; White, SL; Brooks, EM; Mawe, GM. Novel promoter and alternate transcription start site of the human serotonin reuptake transporter in intestinal mucosa. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2009, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Gill, RK; Anbazhagan, AN; Esmaili, A; Kumar, A; Nazir, S; Malakooti, J; Alrefai, WA; Saksena, S. Epidermal growth factor upregulates serotonin transporter in human intestinal epithelial cells via transcriptional mechanisms. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol 2011, 300, G627–G636. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y; Ehli, EA; Hudziak, JJ; Davies, GE. Berberine and evodiamine influence serotonin transporter (5-HTT) expression via the 5-HTT-linked polymorphic region. Pharmacogenomics J 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, Z; Canli, T; Epperson, CN. Effect of estrogen-serotonin interactions on mood and cognition. Behav. Cogn. Neurosci. Rev 2005, 4, 43–58. [Google Scholar]
- Gundlah, C; Lu, NZ; Mirkes, SJ; Bethea, CL. Estrogen receptor beta (ERbeta) mRNA and protein in serotonin neurons of macaques. Mol. Brain Res 2001, 91, 14–22. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H; Ozawa, H; Nishi, M; Ito, T; Kawata, M. Serotonergic neurones in the dorsal raphe nucleus that project into the medial preoptic area contain oestrogen receptor beta. J. Neuroendocrinol 2001, 13, 839–845. [Google Scholar]
- Alves, SE; Weiland, NG; Hayashi, S; McEwen, BS. Immunocytochemical localization of nuclear estrogen receptors and progestin receptors within the rat dorsal raphe nucleus. J. Comp. Neurol 1998, 391, 322–334. [Google Scholar]
- Mitra, SW; Hoskin, E; Yudkovitz, J; Pear, L; Wilkinson, HA; Hayashi, S; Pfaff, DW; Ogawa, S; Rohrer, SP; Schaeffer, JM; et al. Immunolocalization of estrogen receptor beta in the mouse brain: comparison with estrogen receptor alpha. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 2055–2067. [Google Scholar]
- Arai, N; Strom, A; Rafter, JJ; Gustafsson, JA. Estrogen receptor beta mRNA in colon cancer cells: growth effects of estrogen and genistein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 2000, 270, 425–431. [Google Scholar]
- Pfaffl, MW; Lange, IG; Meyer, HH. The gastrointestinal tract as target of steroid hormone action: quantification of steroid receptor mRNA expression (AR, ERalpha, ERbeta and PR) in 10 bovine gastrointestinal tract compartments by kinetic RT-PCR. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol 2003, 84, 159–166. [Google Scholar]
- Di Paolo, T; Diagle, M; Picard, V; Barden, N. Effect of acute and chronic 17 beta-estradiol treatment on serotonin and 5-hydroxyindole acetic acid content of discrete brain nuclei of ovariectomized rat. Exp. Brain Res 1983, 51, 73–76. [Google Scholar]
- Morissette, M; Levesque, D; Belanger, A; Di Paolo, T. A physiological dose of estradiol with progesterone affects striatum biogenic amines. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol 1990, 68, 1520–1526. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, NZ; Eshleman, AJ; Janowsky, A; Bethea, CL. Ovarian steroid regulation of serotonin reuptake transporter (SERT) binding, distribution, and function in female macaques. Mol. Psychiatry 2003, 8, 353–360. [Google Scholar]
- Krajnak, K; Rosewell, KL; Duncan, MJ; Wise, PM. Aging, estradiol and time of day differentially affect serotonin transporter binding in the central nervous system of female rats. Brain Res 2003, 990, 87–94. [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand, PP; Paranavitane, UT; Chavez, C; Gogos, A; Jones, M; van den Buuse, M. The effect of low estrogen state on serotonin transporter function in mouse hippocampus: A behavioral and electrochemical study. Brain Res 2005, 1064, 10–20. [Google Scholar]
- Gundlah, C; Lu, NZ; Bethea, CL. Ovarian steroid regulation of monoamine oxidase-A and -B mRNAs in the macaque dorsal raphe and hypothalamic nuclei. Psychopharmacology 2002, 160, 271–282. [Google Scholar]
- Luine, VN; Khylchevskaya, RI; McEwen, BS. Effect of gonadal steroids on activities of monoamine oxidase and choline acetylase in rat brain. Brain Res 1975, 86, 293–306. [Google Scholar]
- Summer, BE; Fink, G. Estrogen increases the density of 5-hydroxytryptamine(2A) receptors in cerebral cortex and nucleus accumbens in the female rat. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol 1995, 54, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Cyr, M; Bosse, R; Di Paolo, T. Gonadal hormones modulate 5-hydroxytryptamine2A receptors: emphasis on the rat frontal cortex. Neuroscience 1998, 83, 829–836. [Google Scholar]
- Tencomnao, T; Yu, RK; Kapitonov, D. Characterization of the human UDP-galactose:ceramide galactosyltransferase gene promoter. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2001, 1517, 416–423. [Google Scholar]
- Tencomnao, T; Kapitonov, D; Bieberich, E; Yu, RK. Transcriptional regulation of the human UDP-galactose:ceramide galactosyltransferase (hCGT) gene expression: functional role of GC-box and CRE. Glycoconj. J 2004, 20, 339–351. [Google Scholar]
- Kubota, N; Kiuchi, Y; Nemoto, M; Oyamada, H; Ohno, M; Funahashi, H; Shioda, S; Oguchi, K. Regulation of serotonin transporter gene expression in human glial cells by growth factors. Eur. J. Pharmacol 2001, 417, 69–76. [Google Scholar]
- Torrego, A; Pujols, L; Roca-Ferrer, J; Mullol, J; Xaubet, A; Picado, C. Glucocorticoid receptor isoforms alpha and beta in in vitro cytokine-induced glucocorticoid insensitivity. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med 2004, 170, 420–425. [Google Scholar]
- You, HJ; Kim, JY; Jeong, HG. 17 beta-estradiol increases inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in macrophages. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 2003, 303, 1129–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, LH; Chen, FH; Li, YR; Wang, L. Real-time determination of human telomerase reverse transcriptase mRNA in gastric cancer. World J. Gastroenterol 2004, 10, 3514–3517. [Google Scholar]
- Fisker, S; Hansen, B; Fuglsang, J; Kristensen, K; Ovesen, P; Orskov, H; Jorgensen, JO. Gene expression of the GH receptor in subcutaneous and intraabdominal fat in healthy females: Relationship to GH-binding protein. Eur. J. Endocrinol 2004, 150, 773–777. [Google Scholar]


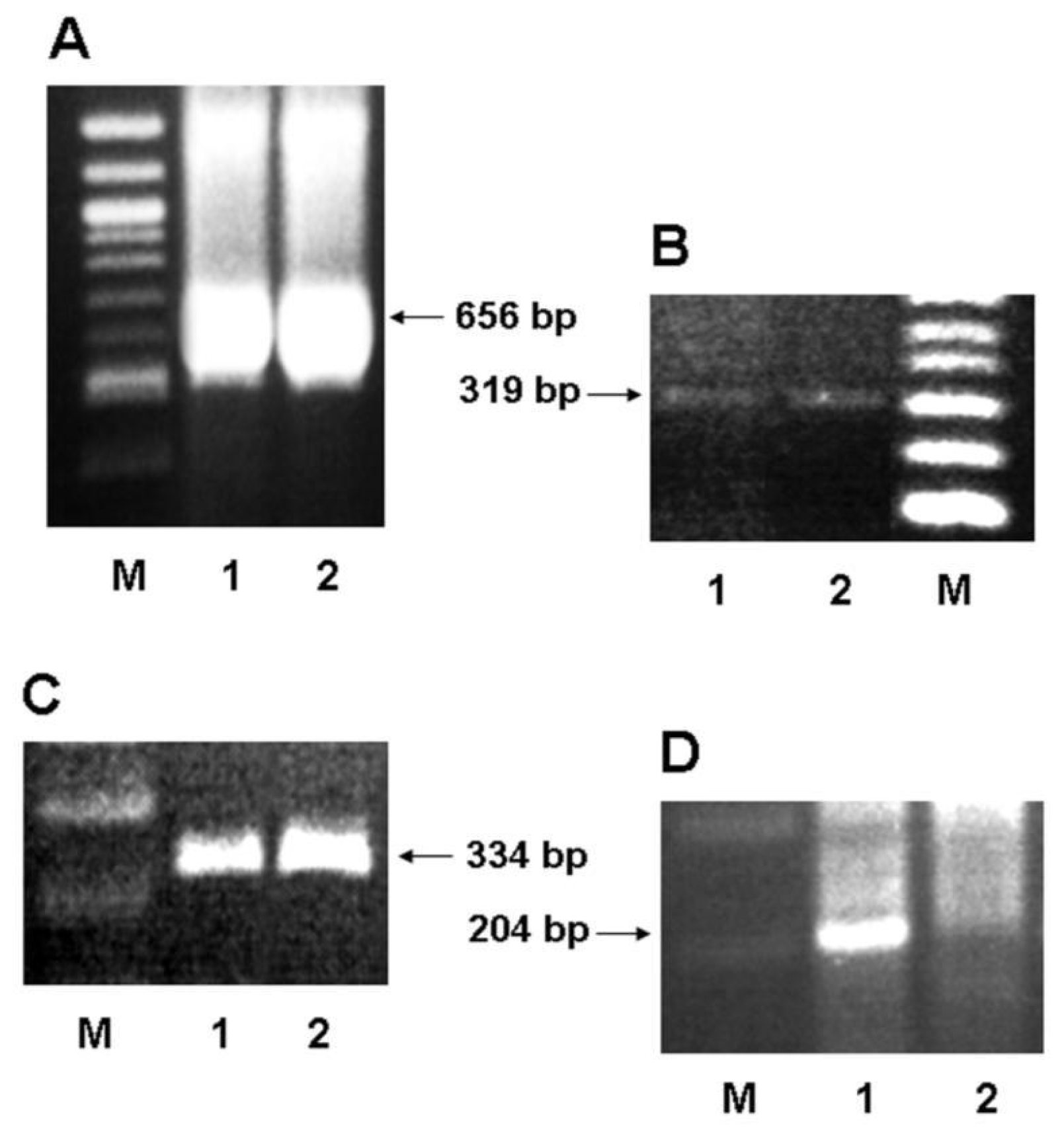

| Name | Oligonucleotide sequence a (5′→3′) | Position b,* | Construct |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5-HTTLPR-F | GGCGTTGCCGCTCTGAATTGC | −1416/−1397 | |
| 5-HTTLPR-R | GAGGGACTGAGCTGGACAACCAC | −910/−889 | |
| −1796F/KpnI | CAAAGGTACCGTTGCCGCTCTGAATGCCAG | −1796/−1767 | ph5HTT[L]Luc |
| ph5HTT[S]Luc | |||
| −736F/KpnI | CAAGGTACCGAATTCCTGGGCTCAAGCAATCCT | −736/−704 | ph5HTT[L860]Luc |
| +124R/HindIII | CCG GAAACGTGGGTTCGAGGCGGAGAG | +124/+156 |
| Name | Oligonucleotide sequence (5′→3′) | Product Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| SERT-sense | CATCTGGAAAGGCGTCAAG | 319 |
| SERT-antisense | CGAAACGAAGCTCGTCATG | |
| GRα-sense | CTTACTGCTTCTCTCTTCAGTTCCT | 204 |
| GRα-antisense | GCAATAGTTAAGGAGATTTTCAACC | |
| ERα-sense | TATGGGGTCTGGTCCTGTGA | 334 |
| ERα-antisense | GGGCGGGGCTATTCTTCTTA | |
| GAPDH-sense | GAAGGTGAAGGTCGGAGTC | 226 |
| GAPDH-antisense | GAAGATGGTGATGGGATTTC | |
| β-actin-sense | ACGGGTCACCCACACTGTGC | 656 |
| β-actin-antisense | CTAGAAGCATTTGCGGTGGACGATG |
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Prasansuklab, A.; Poovorawan, Y.; Tencomnao, T. Modulation of Human Serotonin Transporter Expression by 5-HTTLPR in Colon Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 6619-6634. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12106619
Prasansuklab A, Poovorawan Y, Tencomnao T. Modulation of Human Serotonin Transporter Expression by 5-HTTLPR in Colon Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2011; 12(10):6619-6634. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12106619
Chicago/Turabian StylePrasansuklab, Anchalee, Yong Poovorawan, and Tewin Tencomnao. 2011. "Modulation of Human Serotonin Transporter Expression by 5-HTTLPR in Colon Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 12, no. 10: 6619-6634. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12106619
APA StylePrasansuklab, A., Poovorawan, Y., & Tencomnao, T. (2011). Modulation of Human Serotonin Transporter Expression by 5-HTTLPR in Colon Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 12(10), 6619-6634. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12106619






