Tamaractam, a New Bioactive Lactam from Tamarix ramosissima, Induces Apoptosis in Rheumatoid Arthritis Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Purification of Compounds 1–3
2.2. Structure Elucidation of Compounds 1–3
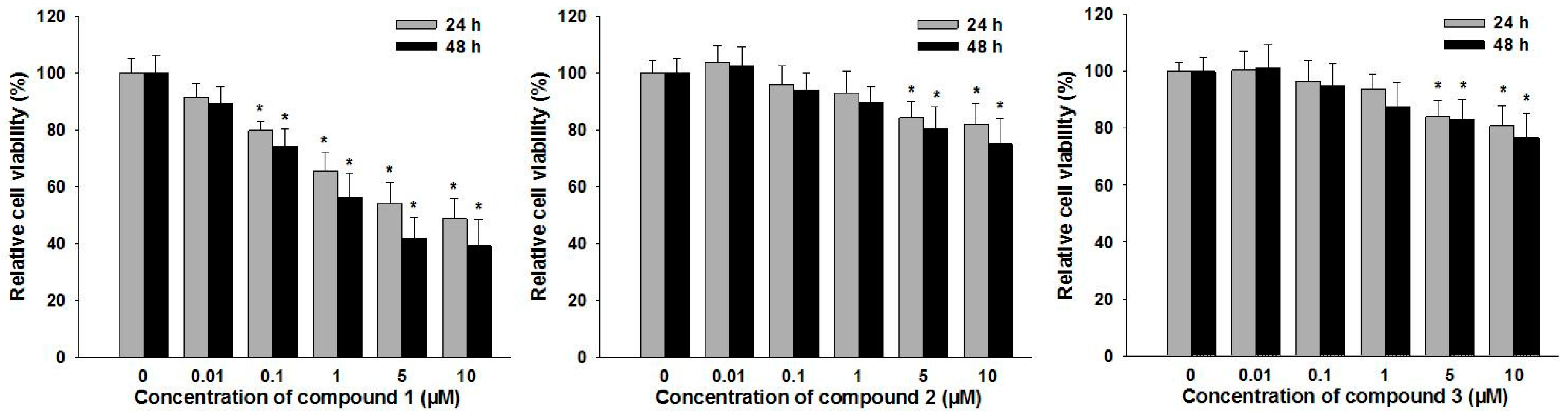
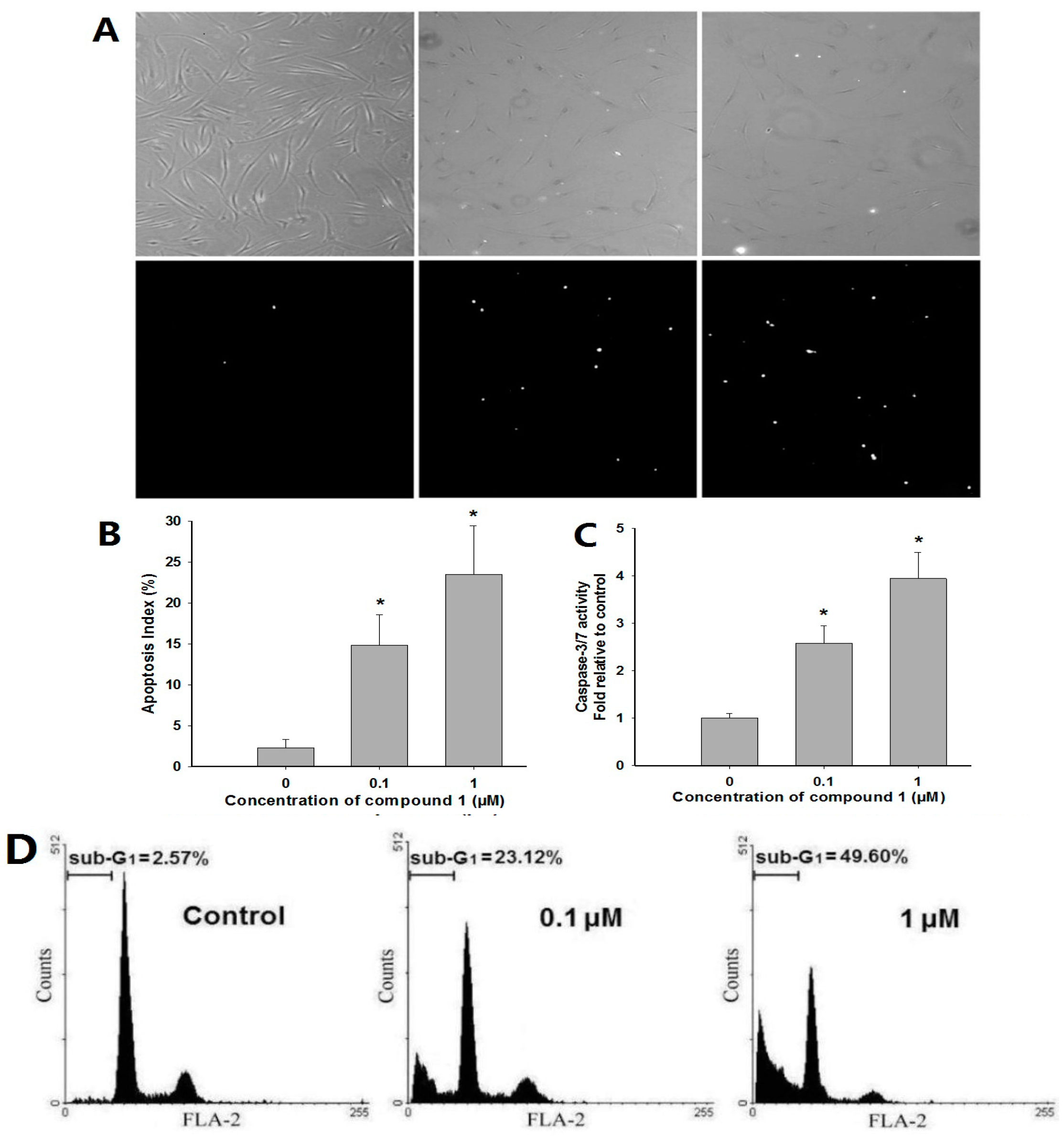
2.3. In Vitro Anti-RA Activity of Compounds 1–3
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Biological Materials
3.3. Isolation and Purification of Compounds 1–3
3.4. Characterization of Compounds 1–3
3.5. Biological Activity Assessment of Compounds 1–3
3.5.1. RA-FLS Cell Culture
3.5.2. Assessment of Cell Viability Using MTT Assay
3.5.3. TUNEL Assay
3.5.4. Measurement of Caspase-3/7 Activity
3.5.5. Assessment of Sub-G1 Fraction
3.6. Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sultanova, N.; Makhmoor, T.; Abilov, Z.A.; Parween, Z.; Omurkamzinova, V.B.; Ur-Rahman, A.; Choudhary, M.I. Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Tamarix ramosissima. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2001, 78, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.K.; Parmar, V.S. Novel constitutes of Tamarix species. J. Sci. Ind. Res. 1998, 57, 873–890. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, J.; Xing, Y.C.; Li, N.; Zhang, J.; Ni, H.; Jia, X.G. Advances in studies on chemical constituents in plants of Tamarix L. and their pharmacological activities. Drugs Clin. 2012, 27, 404–408. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Tu, P.F. Chemical constituents of Tamarix ramosissima. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2006, 37, 1764–1768. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Li, W.Q.; Zheng, P.; Wang, R.; Yu, J.Q.; Yang, J.H.; Yao, Y. Phenolic compounds in branches of Tamarix rasissima. Chin. J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2014, 39, 2047–2050. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, H.; Xie, D.; Yang, R.; Cheng, Y. Synthesis of caffeic acid phenethyl ester derivatives, and their cytoprotective and neuritogenic activities in PC12 cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 5046–5053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navickiene, H.M.; Lopes, L.M. Alkamides and Phenethyl Derivatives from Aristolochia gehrtii. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2001, 12, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, H.A.; Steffensen, S.K.; Christophersen, C. Cinnamoylphenethylamine 1H-NMR Chemical Shifts:A Concise Reference for Ubiquitous Compounds. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2010, 5, 1259–1262. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Heiland, G.; Zhao, Y.; Derer, A.; Braun, T.; Engelke, K.; Neumann, E.; Mueller-Ladner, U.; Liu, Y.; Zwerina, J.; Schett, G. Deletion of the receptor tyrosine kinase Tyro3 inhibits synovial hyperplasia and bone damage in arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 73, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziswiler, H.R.; Aeberli, D.; Villiger, P.M.; Möller, B. High-resolution ultrasound confirms reduced synovial hyperplasia following rituximab treatment in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2009, 48, 939–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartok, B.; Firestein, G.S. Fibroblast-like synoviocytes: Key effector cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol. Rev. 2010, 233, 233–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottini, N.; Firestein, G.S. Duality of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in RA: Passive responders and imprinted aggressors. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2012, 9, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, L.C.; Distler, O.; Tarner, I.; Gay, R.E.; Gay, S.; Pap, T. Synovial fibroblasts: Key players in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2006, 45, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wachsmann, D.; Sibilia, J. Survival in the rheumatoid synovium. Jt. Bone Spine 2011, 78, 435–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefèvre, S.; Knedla, A.; Tennie, C.; Kampmann, A.; Wunrau, C.; Dinser, R.; Korb, A.; Schnäker, E.M.; Tarner, I.H.; Robbins, P.D. Synovial fibroblasts spread rheumatoid arthritis to unaffected joints. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 1414–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakhani, S.A.; Masud, A.; Kuida, K.; Porter, G.A.; Booth, C.J.; Mehal, W.Z.; Inayat, I.; Flavell, R.A. Caspases 3 and 7: Key mediators of mitochondrial events of apoptosis. Science 2006, 311, 847–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byun, H.; Song, J.Y.; Piao, L. Caspase-8 has an essential role in resveratrol-induced apoptosis of rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Rheumatology 2008, 47, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mor, A.; Abramson, S.B.; Pillinger, M.H. The fibroblast-like synovial cell in rheumatoid arthritis: A key player in inflammation and joint destruction. Clin. Immunol. 2005, 115, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baier, A.; Meineckel, I.; Gay, S.; Pap, T. Apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2003, 15, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korb, A.; Pavenstädt, H.; Pap, T. Cell death in rheumatoid arthritis. Apoptosis 2009, 14, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Lao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Qin, J.; Fu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H. Screening active compounds from Garcinia species native to China reveals novel compounds targeting the STAT/JAK signaling pathway. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 910453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, G.Y.; Huang, S.M.; Liu, S.T.; Liu, P.Y.; Chou, W.Y.; Lin, W.S. Caffeine induces tumor cytotoxicity via the regulation of alternative splicing in subsets of cancer-associated genes. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2014, 47, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 1–3 are not available from the authors.
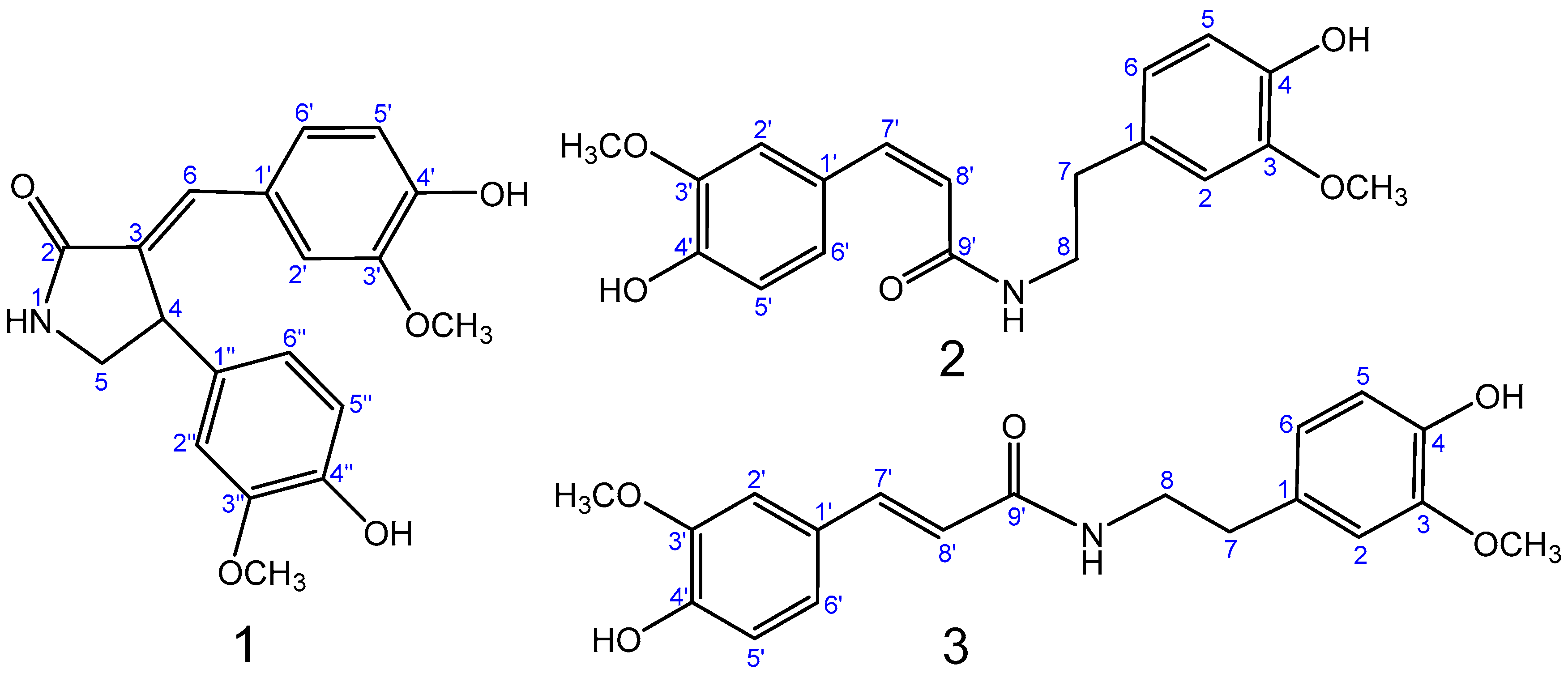
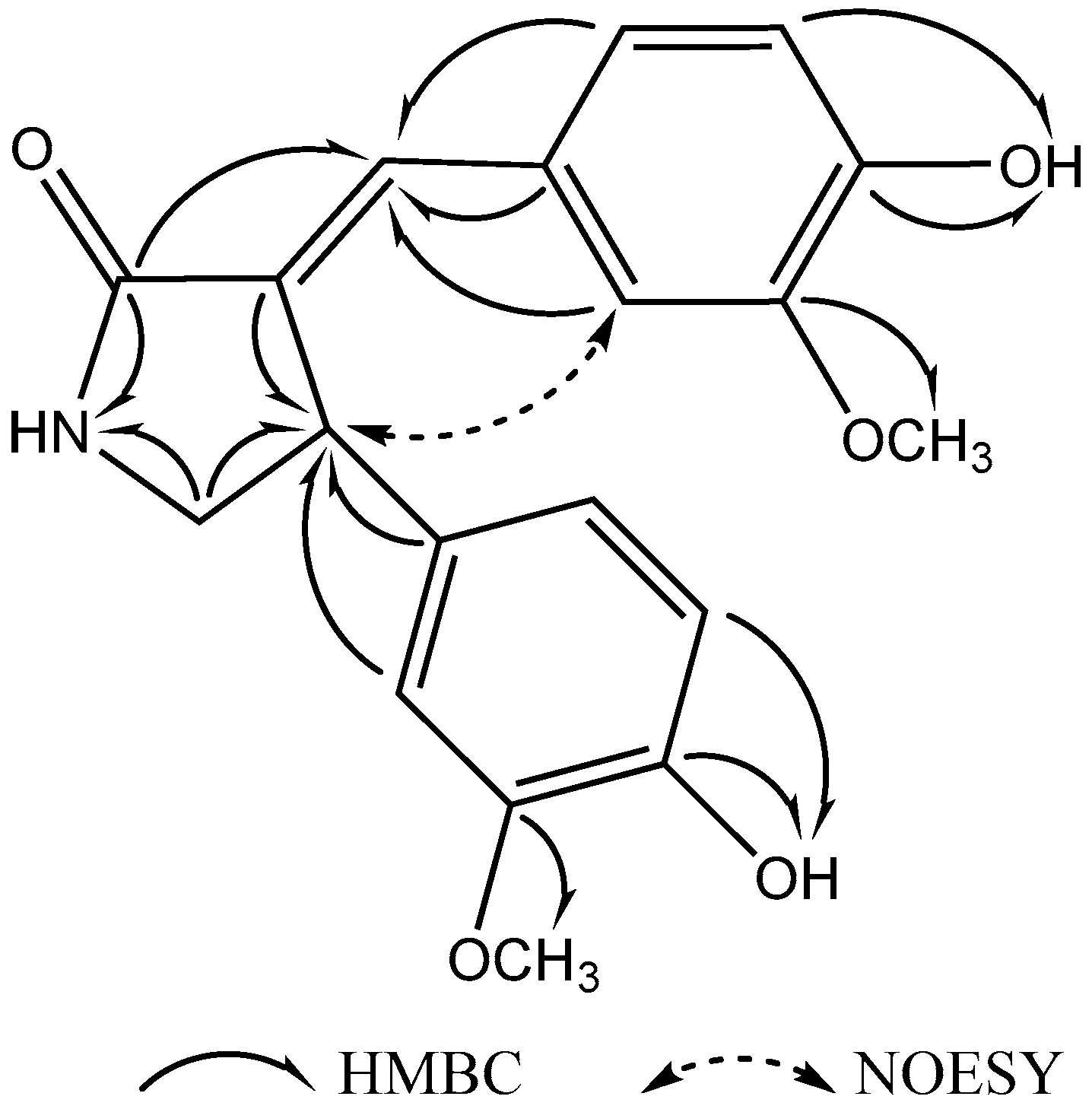
| No. | δH (Mult., J (Hz)) | δC (Mult.) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 7.95 s | - |
| 2 | - | 171.2 C |
| 3 | - | 131.1 C |
| 4 | 4.53 d (8.0) | 41.9 CH |
| 5 | 3.78 dd (10.0, 8.0) | 49.1 CH2 |
| 3.03 d (10.0) | ||
| 6 | 7.23 s | 130.9 CH |
| 1′ | - | 126.1 C |
| 2′ | 6.86 d (2.0) | 112.9 CH |
| 3′ | - | 147.4 C |
| 4′ | - | 147.3 C |
| 5′ | 6.68 d (8.4) | 115.3 CH |
| 6′ | 6.88 dd (8.4, 2.0) | 124.5 CH |
| 1′′ | - | 134.3 C |
| 2′′ | 6.83 d (2.0) | 111.3 CH |
| 3′′ | - | 147.8 C |
| 4′′ | - | 145.2 C |
| 5′′ | 6.66 d (8.4) | 115.6 CH |
| 6′′ | 6.57 dd (8.4, 2.0) | 118.7 CH |
| 3′-OCH3 | 3.51 s | 55.2 CH3 |
| 3′′-OCH3 | 3.67 s | 55.5 CH3 |
| 4′-OH | 9.34 s | - |
| 4′′-OH | 8.84 s | - |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, Y.; Jiang, C.-S.; Sun, N.; Li, W.-Q.; Niu, Y.; Han, H.-Q.; Miao, Z.-H.; Zhao, X.-X.; Zhao, J.; Li, J. Tamaractam, a New Bioactive Lactam from Tamarix ramosissima, Induces Apoptosis in Rheumatoid Arthritis Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes. Molecules 2017, 22, 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010096
Yao Y, Jiang C-S, Sun N, Li W-Q, Niu Y, Han H-Q, Miao Z-H, Zhao X-X, Zhao J, Li J. Tamaractam, a New Bioactive Lactam from Tamarix ramosissima, Induces Apoptosis in Rheumatoid Arthritis Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes. Molecules. 2017; 22(1):96. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010096
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Yao, Cheng-Shuai Jiang, Na Sun, Wei-Qi Li, Yang Niu, Huai-Qin Han, Zhen-Hua Miao, Xun-Xia Zhao, Jing Zhao, and Juan Li. 2017. "Tamaractam, a New Bioactive Lactam from Tamarix ramosissima, Induces Apoptosis in Rheumatoid Arthritis Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes" Molecules 22, no. 1: 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010096
APA StyleYao, Y., Jiang, C.-S., Sun, N., Li, W.-Q., Niu, Y., Han, H.-Q., Miao, Z.-H., Zhao, X.-X., Zhao, J., & Li, J. (2017). Tamaractam, a New Bioactive Lactam from Tamarix ramosissima, Induces Apoptosis in Rheumatoid Arthritis Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes. Molecules, 22(1), 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010096





