Novel Antihypertensive Peptides Derived from Adlay (Coix larchryma-jobi L. var. ma-yuen Stapf) Glutelin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Effect of the Ultrafiltration Pressure on the Glutelin Hydrolysate’s ACE Inhibitory Activity
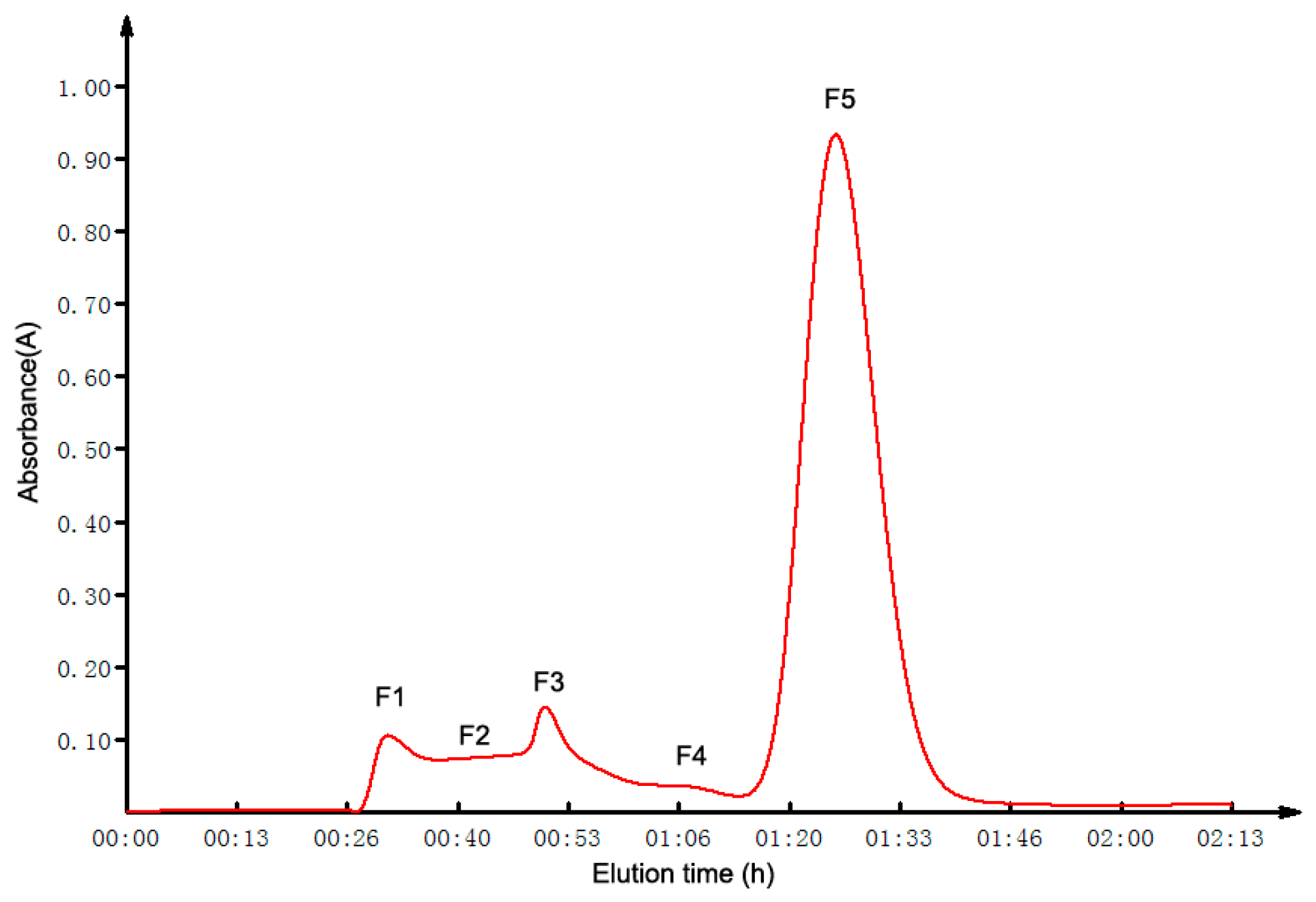
2.2. GFC Isolation of ACE Inhibitory Peptides
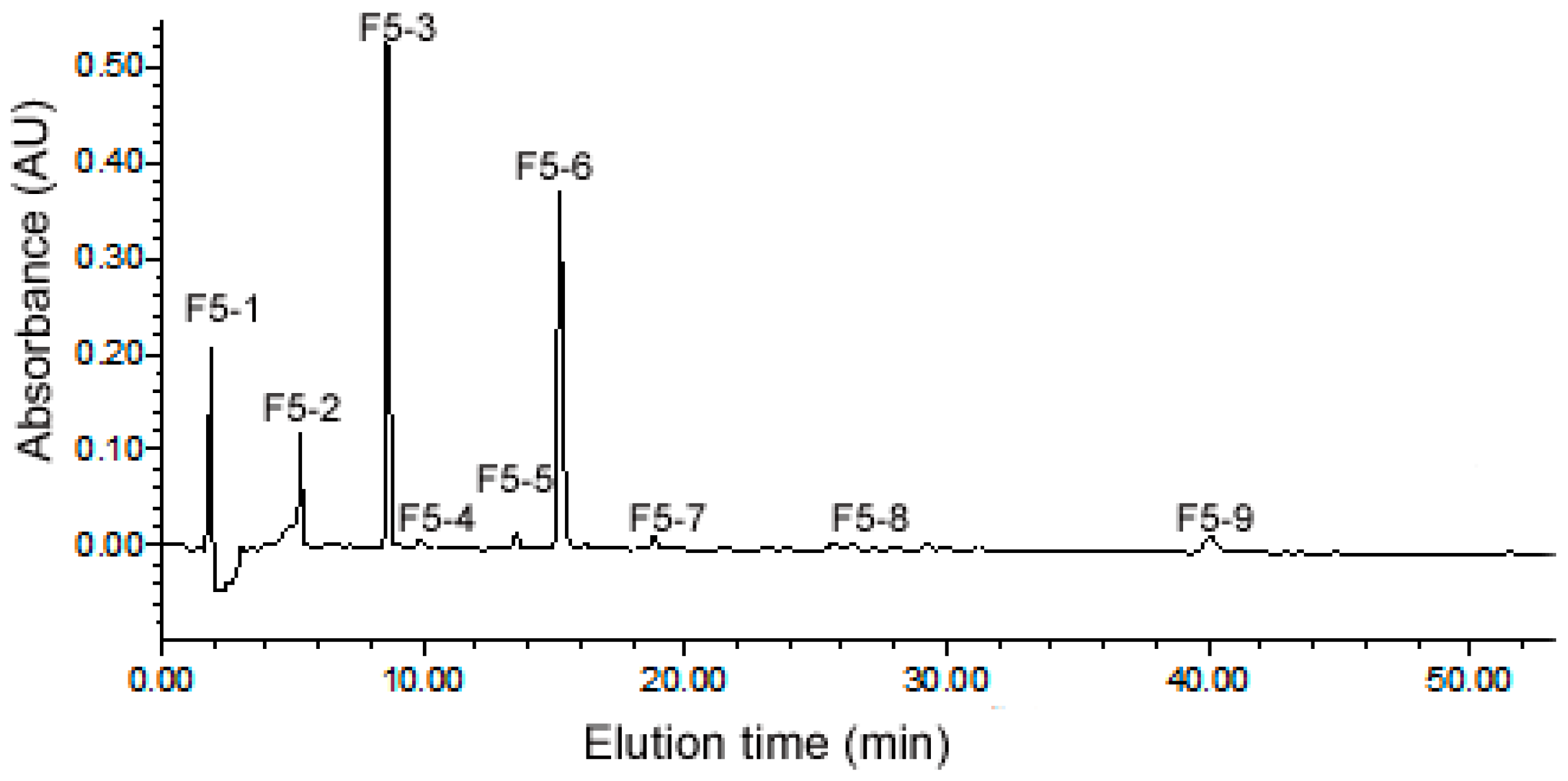
2.3. Purification of ACE Inhibitory Peptides by RP-HPLC
2.4. Identification of Peptides from Sub-Fraction F5-3
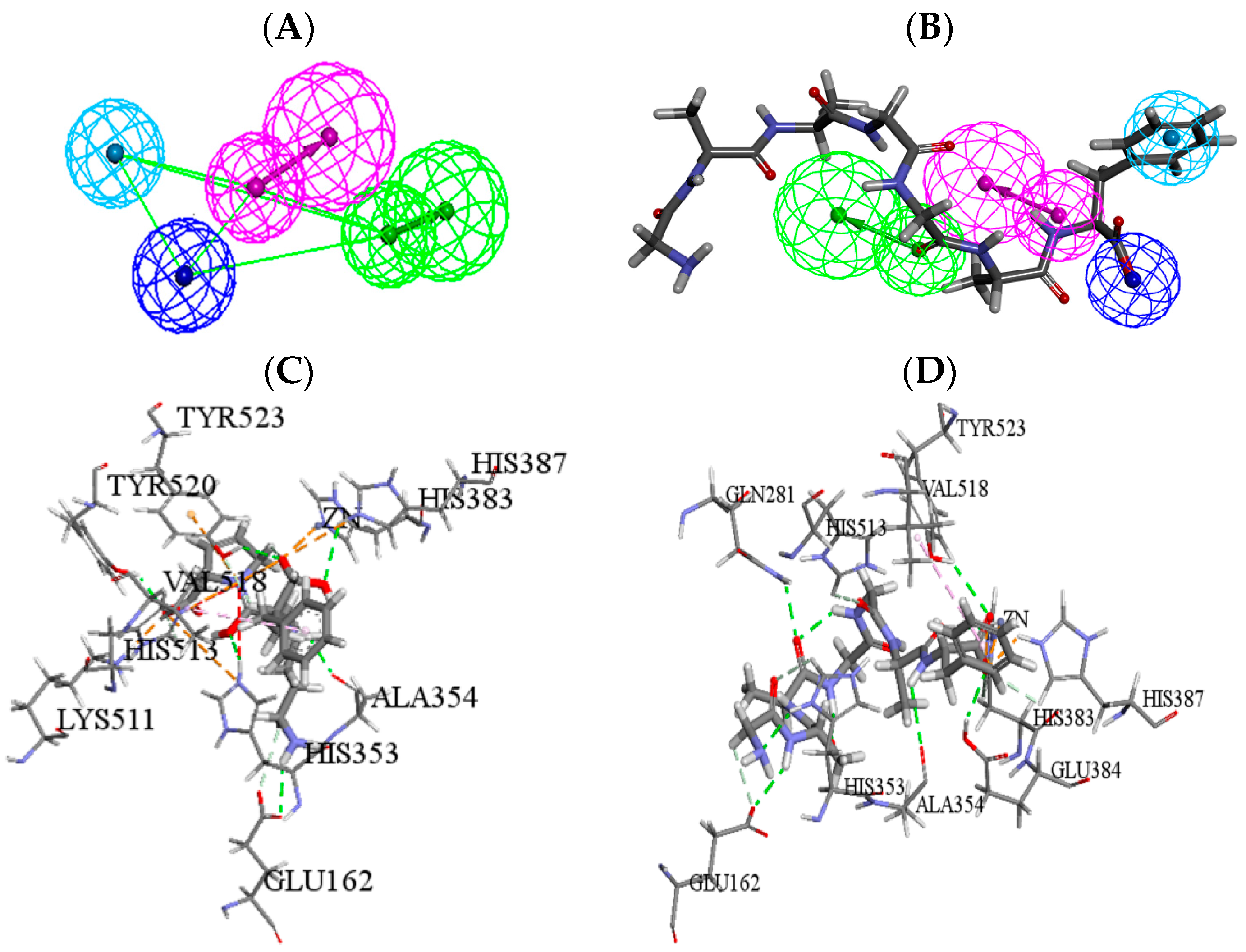
2.5. Molecular Simulation Screening and Further Optimization
2.6. The Antihypertensive Effect of GAAGGAF In Vivo
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material and Chemicals
4.2. Preparation of Enzymatic Hydrolysate of Coix Glutelin
4.3. Ultrafiltration (UF) of the CGH
4.4. Gel Filtration Chromatography (GFC) Separation
4.5. Reverse-Phase High Performance Liquid Chromatography (RP-HPLC) Purification
4.6. Estimation of Peptide Content
4.7. ACE Inhibitory Activity Assay
4.8. Mass Spectrometry Analysis of ACE-Inhibitory Peptides
4.9. Pharmacophore Mapping of Identified Peptides
4.10. Structural Optimization for Peptides by Molecular Docking
4.11. Synthesis of the Optimized Peptide
4.12. Antihypertensive Effect of Synthesized Peptide in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Manosroi, J.; Khositsuntiwong, N.; Manosroi, A. Biological activities of fructooligosaccharide (FOS)-containing Coix lachryma-jobi Linn. extract. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 51, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanimura, A. Studies on anti-tumor component in the seeds of Coix Lachryma-Jobi L. var. Ma-yuen Stapf. II. Thestructure of coixenolide. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1961, 9, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.J.; Liu, S. Antitumor effect of Kanglaite(R) injection in human pancreatic cancer xenografts. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.-J.; Shih, C.-K.; Hsu, H.-Y.; Chiang, W. Mast cell-dependent allergic responses are inhibited by ethanolic extract of adlay (Coix lachryma-jobi L. var. ma-yuen Stapf) testa. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 2596–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, C.-C.; Chiang, W.; Liu, G.-P.; Chien, Y.-L.; Chang, J.-Y.; Lee, C.-K.; Lo, J.-M.; Huang, S.-L.; Shih, M.-C.; Kuo, Y.-H. 2,2’-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl radical-scavenging active components from adlay (Coix lachryma-jobi L. var. ma-yuen Stapf) hulls. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 5850–5855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, M.; Kato, M.; Ayugase, J. Anti-diabetic effects of adlay protein in type 2 diabetic db/db mice. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2012, 18, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrane, M.M.; Essery, E.; Obbagy, J.; Lyon, J.; MacNeil, P.; Spahn, J.; van Horn, L. Dairy consumption, blood pressure, and risk of hypertension: An evidence-based review of recent literature. Curr. Cardiovasc. Risk Rep. 2011, 5, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonios, T.F.; MacGregor, G.A. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors in hypertension: Potential problems. J. Hypertens. 1995, 13, S11–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Hu, J.; Miyaguchi, Y.; Bai, X.; Du, Y.; Lin, B. Isolation and characterization of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides derived from porcine hemoglobin. Peptides 2006, 27, 2950–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Ling, Y.; Cui, S.; Zhang, X. Angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory and antioxidant activity ofadlay(coix lacryma-jobi L. var. ma-yuenstapf) glutelinhydrolysate. Ital. J. Food Sci. 2014, 26, 282–288. [Google Scholar]
- Ghassem, M.; Arihara, K.; Babji, A.S.; Said, M.; Ibrahim, S. Purification and identification of ACE inhibitory peptides from Haruan (Channa striatus) myofibrillar protein hydrolysate using HPLC–ESI-TOF MS/MS. Food Chem. 2011, 129, 1770–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, T.; Li, C.H.; Osajima, Y. Preparation and characterization of novel bioactive peptides responsible for angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibition from wheat germ. J. Pept. Sci. 1999, 5, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Malomo, S.A.; Alashi, A.; Girgih, A.T.; Ju, X.; Aluko, R.E. Purification and hypotensive activity of rapeseed protein-derived renin and angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory peptides. J. Funct. Foods 2013, 5, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Tao, G.; Liu, J. Peptide with angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory activity from hydrolyzed corn gluten meal. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 7891–7895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Qiu, N.; Yi, J. Production and characterization of angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.) kernel protein hydrolysate. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2010, 231, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escudero, E.; Mora, L.; Fraser, P.D.; Aristoy, M.C.; Arihara, K.; Toldrá, F. Purification and identification of antihypertensive peptides in Spanish dry-cured ham. J. Proteom. 2013, 78, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.; Fang, M.; Wu, H.; Xie, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, P.; Zhang, D.; Huang, Z.; Xia, Y.; Zhou, L. A novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptide from Phascolosoma esculenta water-soluble protein hydrolysate. J. Funct. Foods 2013, 5, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaniak, A.; Minkiewicz, P.; Darewicz, M. Food-originatingACE inhibitors, including antihypertensive peptides, as preventive food components in blood pressure reduction. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2014, 13, 114–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Lv, S.; Zhang, X.; Lu, J.; Ye, Y.; Jiang, S. ACE inhibitory peptides derived from aquatic protein. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2013, 14, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasamai, M.; Jalil, J.; Jantan, I. Molecular docking study on platelet-activating factor antagonistic activity of bioactive compounds isolated from Guttiferae and Ardisia species. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 29, 1055–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Bao, X.; Yu, K.; Luo, X.; Zhu, W.; Jiang, H. Pharmacophore-based virtual screening versus docking-based virtual screening: A benchmark comparison against eight targets. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2009, 30, 1694–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Jin, H.; Wang, W.; Huo, J. Angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides: Chemical feature based pharmacophore generation. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 3428–3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hai-Bang, T.; Shimizu, K. Potent angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory tripeptidesidentified by a computer-based approach. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2014, 53, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marczak, E.D.; Usui, H.; Fujita, H.; Yang, Y.; Yokoo, M.; Lipkowski, A.W.; Yoshikawa, M. New antihypertensive peptides isolated from rapeseed. Peptides 2003, 24, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, N.; Kawaguchi, K.; Yamamoto, N. Study of the mechanism of antihypertensive peptides VPP and IPP in spontaneously hypertensive rats by DNA microarray analysis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 620, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehlers, P.I.; Nurmi, L.; Turpeinen, A.M.; Korpela, R.; Vapaatalo, H. Casein-derived tripeptide Ile-Pro-Pro improves angiotensin-(1–7)-and bradykinin-induced rat mesenteric artery relaxation. Life Sci. 2011, 88, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, D.; Kassan, M.; del Mar Contreras, M.; Carrón, R.; Recio, I.; Montero, M.-J.; Sevilla, M.-Á. Long-term intake of a milk casein hydrolysate attenuates the development of hypertension and involves cardiovascular benefits. Pharmacol. Res. 2011, 63, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, T.; Ueno, T.; Tanaka, M.; Oka, H.; Miyamoto, T.; Osajima, K.; Matsumoto, K. Antiproliferative action of an angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptide, Val-Tyr, via an l-type Ca2+ channel inhibition in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. Hypertens. Res. 2005, 28, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciccocioppo, R.; di Sabatino, A.; Corazza, G. The immune recognition of gluten in coeliac disease. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2005, 140, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y. Study on the Methodology of Chinese Medicine Virtual Screening Based on Pharmacophores; Beijing University of Chinese Medicine: Beijing, China, 2006. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Natesh, R.; Schwager, S.L.; Sturrock, E.D.; Acharya, K.R. Crystal structure of the human angiotensin-converting enzyme-lisinopril complex. Nature 2003, 421, 551–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafarga, T.; O’Connor, P.; Hayes, M. Identification of novel dipeptidyl peptidase-IV and angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from meat proteins using in silico analysis. Peptides 2014, 59, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors.

| No. | Peptide Sequence | Mr(exp) | Mr(calc) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | QEKQKL | 756.41 | 756.40 |
| 2 | EKHNRL | 796.44 | 796.42 |
| 3 | QSGDQQEF | 938.32 | 938.36 |
| 4 | VGQLGGAAGGAF | 1004.47 | 1004.49 |
| 5 | QQQQQQQQQQQQSL | 1740.73 | 1740.76 |
| 6 | PATAHKQQQQADANMAKL | 1966.94 | 1966.95 |
| NO. a | Peptide Sequence | Fitvalue b | -CDOCKER ENERGY c | NO. a | Peptide Sequence | Fitvalue b | -CDOCKER ENERGY c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-1 | QEKQKL | none | none | 2-4 | GGAAGGAF | 0.95 | 165.39 |
| 1-2 | EKHNRL | none | none | 3-1 | GAAGGAF | 0.96 | 163.62 |
| 1-3 | QSGDQQEF | 0.97 | none | 3-2 | AAGGAF | 0.95 | 143.18 |
| 1-4 | VGQLGGAAGGAF | 0.96 | 180.40 | 3-3 | AGGAF | 0.96 | 132.88 |
| 1-5 | QQQQQQQQQQQQSL | none | none | 3-4 | GGAF | 0.96 | 119.30 |
| 1-6 | PATAHKQQQQADANMAKL | none | none | 3-5 | GAF | 0.95 | 112.38 |
| 2-1 | VGQL | none | 108.65 | 3-6 | AF | 0.23 | 99.54 |
| 2-2 | GGAAGGA | none | 137.75 | 4 | lisinopril | 0.95 | 71.22 |
| 2-3 | VGQ | none | 112.56 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, B.; Qiao, L.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Wang, L.; Qiao, Y. Novel Antihypertensive Peptides Derived from Adlay (Coix larchryma-jobi L. var. ma-yuen Stapf) Glutelin. Molecules 2017, 22, 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010123
Li B, Qiao L, Li L, Zhang Y, Li K, Wang L, Qiao Y. Novel Antihypertensive Peptides Derived from Adlay (Coix larchryma-jobi L. var. ma-yuen Stapf) Glutelin. Molecules. 2017; 22(1):123. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010123
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Bin, Liansheng Qiao, Lingling Li, Yanling Zhang, Kai Li, Lingzhi Wang, and Yanjiang Qiao. 2017. "Novel Antihypertensive Peptides Derived from Adlay (Coix larchryma-jobi L. var. ma-yuen Stapf) Glutelin" Molecules 22, no. 1: 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010123
APA StyleLi, B., Qiao, L., Li, L., Zhang, Y., Li, K., Wang, L., & Qiao, Y. (2017). Novel Antihypertensive Peptides Derived from Adlay (Coix larchryma-jobi L. var. ma-yuen Stapf) Glutelin. Molecules, 22(1), 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22010123





