Modular Synthesis of Heparin-Related Tetra-, Hexa- and Octasaccharides with Differential O-6 Protections: Programming for Regiodefined 6-O-Modifications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
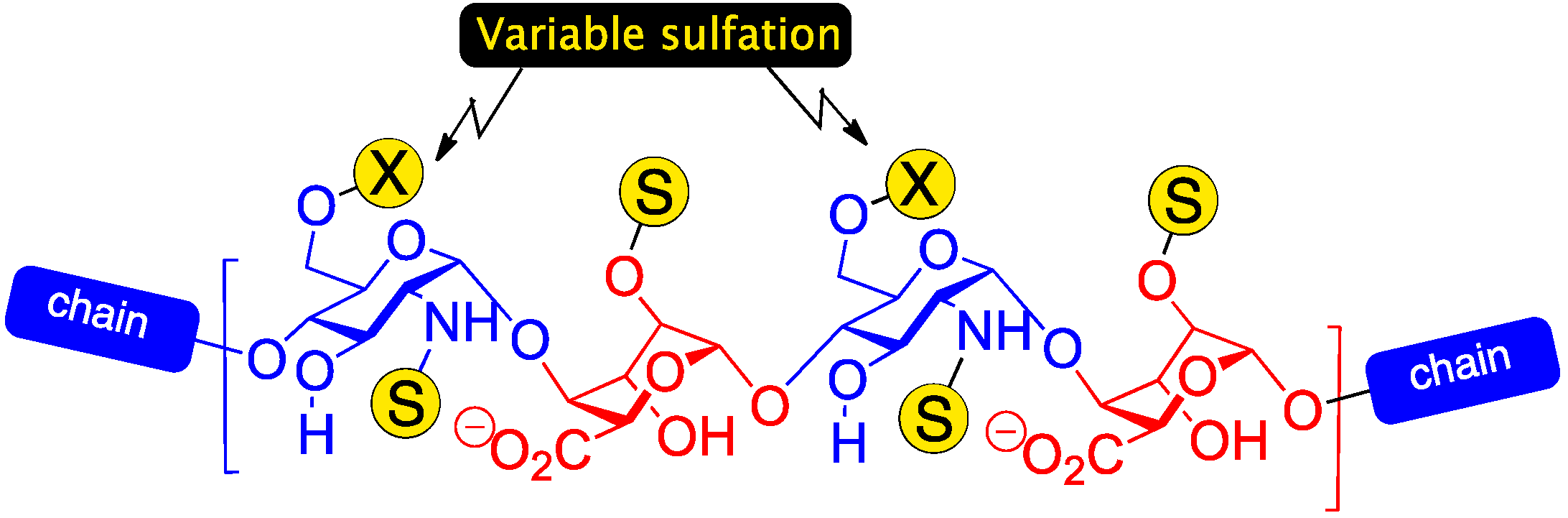
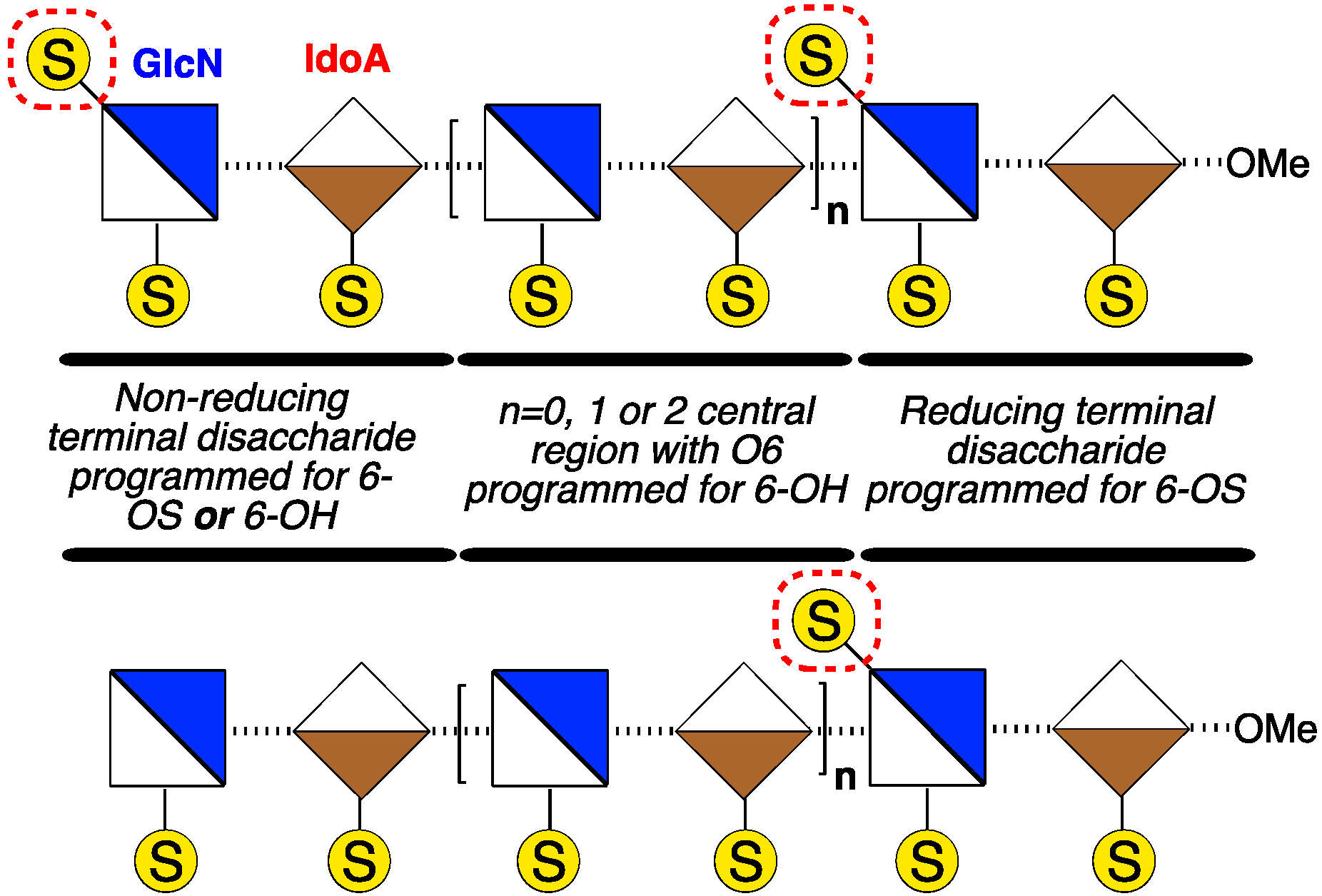
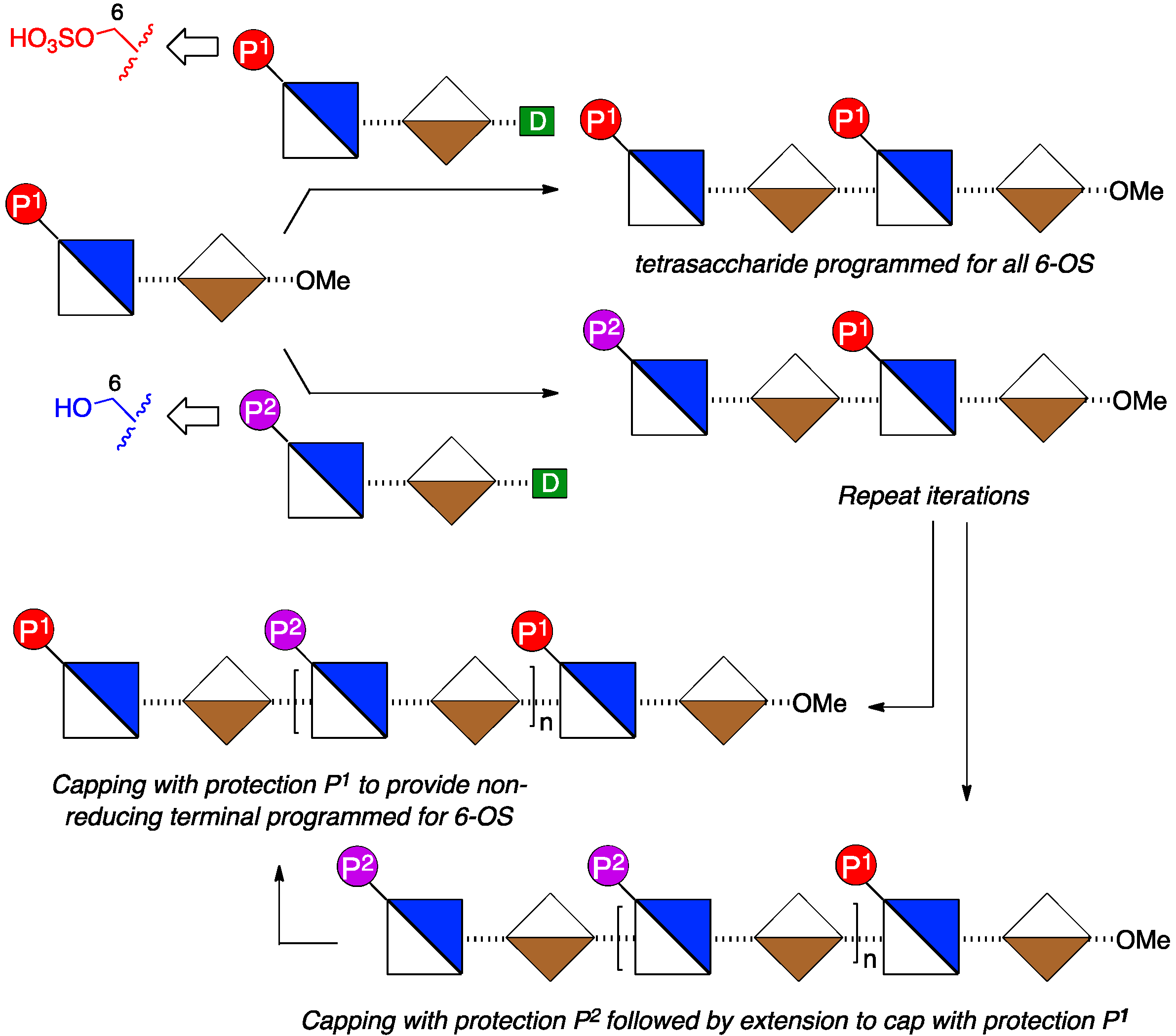
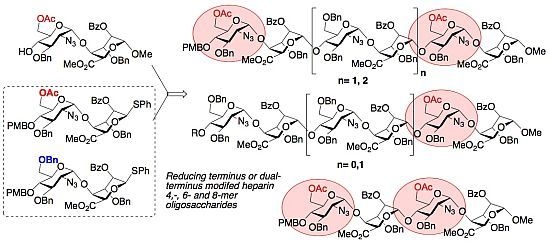
2. Results and Discussion
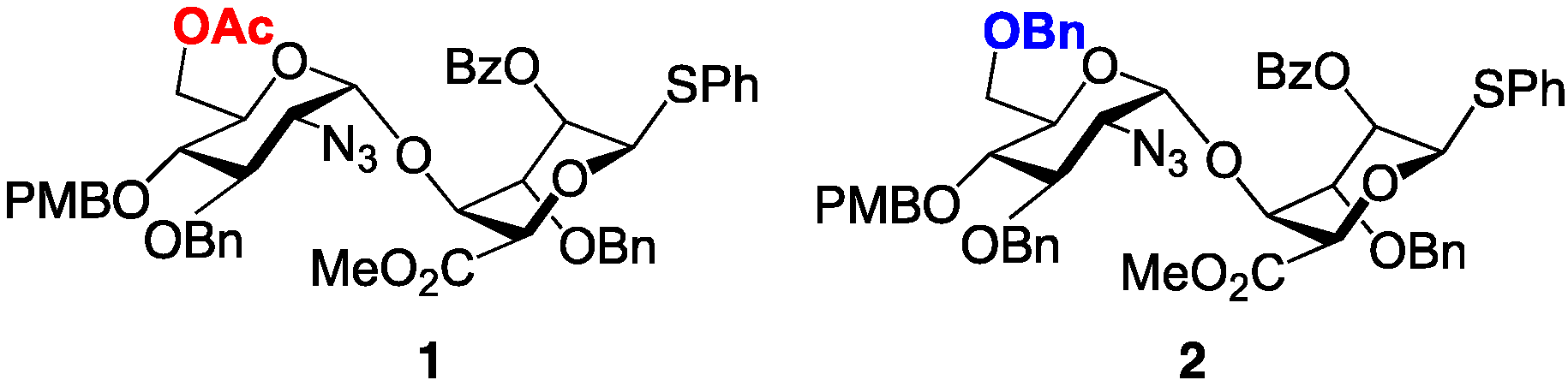
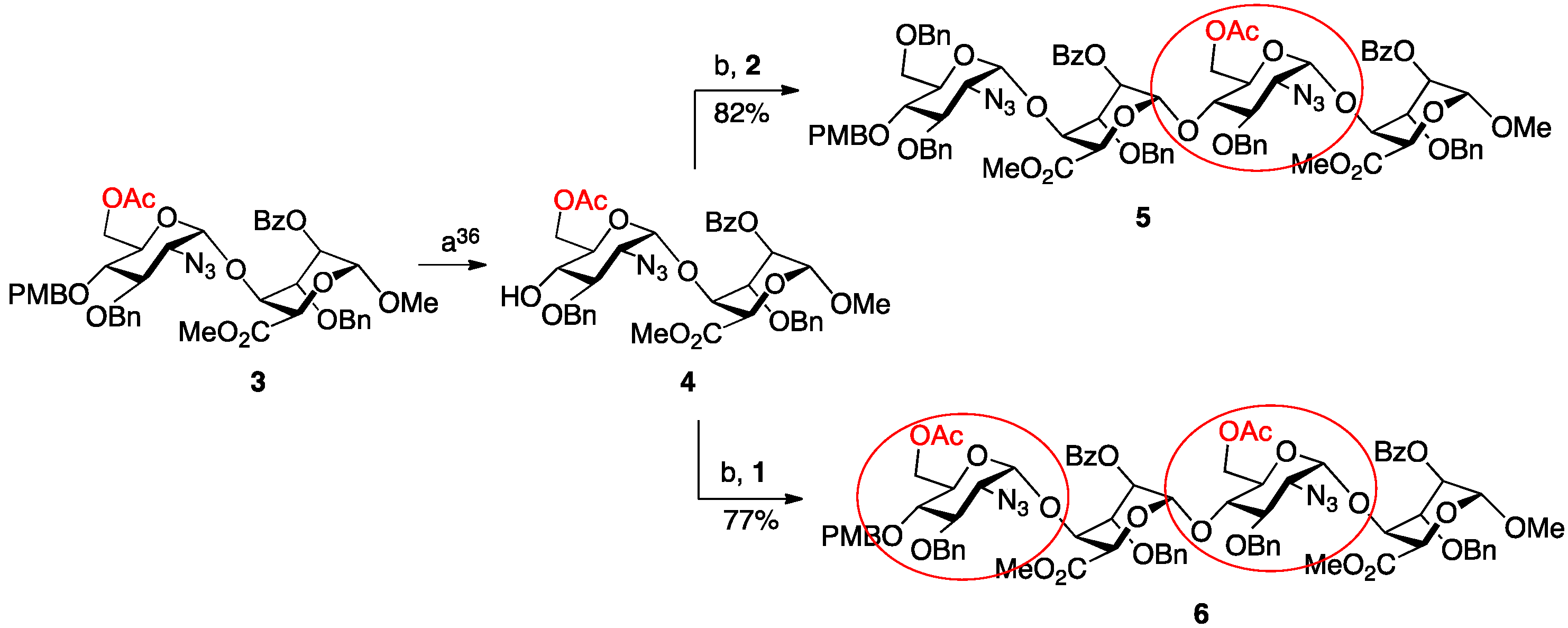


3. Experimental Section
General Information
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Casu, B.; Naggi, A.; Torri, G. Heparin-derived heparan sulfate mimics to modulate heparan sulfate-protein interaction in inflammation and cancer. Matrix Biol. 2010, 29, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, J.; Schuksz, M.; Esko, J.D. Heparan sulphate proteoglycans fine-tune mammalian physiology. Nature 2007, 446, 1030–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeberger, P.H.; Werz, B. Synthesis and medical applications of oligosaccharides. Nature 2007, 446, 1046–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zulueta, M.M.L.; Lin, S.-Y.; Hu, Y.-P.; Hung, S.-C. Synthetic heparin and heparan sulfate oligosaccharides and their protein interactions. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2013, 17, 1023–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindahl, U.; Kjellén, L. Pathophysiology of heparan sulphate: Many diseases, few drugs. J. Int. Med. 2013, 273, 555–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paz, J.-L.; Moseman, A.; Noti, C.; Polito, L.; von Andrian, U.H.; Seeberger, P.H. Profiling Heparin-Chemokine Interactions Using Synthetic Tools. ACS Chem. Biol. 2007, 2, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noti, C.; Seeberger, P.H. Chemical Approaches to Define the Structure-Activity Relationship of Heparin-like Glycosaminoglycans. Chem. Biol. 2005, 12, 731–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dulaney, S.B.; Huang, X. Strategies in Synthesis of Heparin/Heparan Sulfate Oligosaccharides. Adv. Carbohydr. Chem. Biochem. 2012, 67, 95–136. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zong, C.; Venot, A.; Dhamale, O.; Boons, G.-J. Fluorous Supported Modular Synthesis of Heparan Sulfate Oligosaccharides. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 342–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guedes, N.; Czechura, P.; Echeverria, B.; Ruiz, A.; Michelena, O.; Martin-Lomas, M.; Reichardt, N.-C. Toward the Solid-Phase Synthesis of Heparan Sulfate Oligosaccharides: Evaluation of Iduronic Acid and Idose Building Blocks. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 78, 6911–6934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Masuko, S.; Takieddin, M.; Xu, H.; Liu, R.; Jing, J.; Mousa, S.A.; Linhardt, R.J.; Liu, J. Chemoenzymatic Synthesis of Homogeneous Ultralow Molecular Weight Heparins. Science 2011, 334, 498–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Codée, J.D.C.; Stubba, B.; Schiattarella, M.; Overkleeft, H.S.; van Boeckel, C.A.A.; van Boom, J.H.; van der Marel, G.A.A. Modular Strategy Toward the Synthesis of Heparin-like Oligosaccharides Using Monomeric Building Blocks in a Sequential Glycosylation Strategy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 3767–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poletti, L.; Lay, L. Chemical Contributions to Understanding Heparin Activity: Synthesis of Related Sulfated Oligosaccharides. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 16, 2999–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paz, J.-L.; Angulo, J.; Lassaletta, J.M.; Nieto, P.M.; Horcajo, M.-R.; Lozano, R.M.; Gallego, G.G.; Martín-Lomas, M. The activation of fibroblast growth factors by heparin: Synthesis, structure, and biological activity of heparin like oligosaccharides. ChemBioChem 2001, 2, 673–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Yang, B.; Tiruchinapally, G.; Sun, B.; Liu, R.; Liu, S.D.J.; Huang, X. Preactivation-Based, One-Pot Combinatorial Synthesis of Heparin-like Hexasaccharides for the Analysis of Heparin-Protein Interactions. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 8365–8375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Paz, J.L.; Martín-Lomas, M. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of a Heparin-Like Hexasaccharide with the Structural Motifs for Binding to FGF and FGFR. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 2005, 1849–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwörer, R.; Zubkova, O.V.; Turnbull, J.E.; Tyler, P.C. Synthesis of a Targeted Library of Heparan Sulfate Hexa- to Dodecasaccharides as Inhibitors of β-Secretase: Potential Therapeutics for Alzheimer’s Disease. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 6817–6823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arungundram, S.; Al-Mafraji, K.; Asong, J.; Leach, F.E.; Amster, I.J.; Venot, A.; Turnbull, J.E.; Boons, G.-J. Modular Synthesis of Heparan Sulfate Oligosaccharides for Structure-Activity Relationship Studies. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 17394–17405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poletti, L.; Fleischer, M.; Vogel, C.; Guerrini, M.; Torri, G.; Lay, L. A Rational Approach to Heparin-Related Fragments—Synthesis of Differently Sulfated Tetrasaccharides as Potential Ligands for Fibroblast Growth Factors. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2001, 14, 2727–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paz, J.-L.; Ojeda, R.; Reichardt, N.; Lomas, M.-M. Some Key Experimental Features of a Modular Synthesis of Heparin-Like Oligosaccharides. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 17, 3308–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiruchinapally, G.; Yin, Z.; el Dakdouki, M.; Wang, Z.; Huang, X. Divergent Heparin Oligosaccharide Synthesis with Preinstalled Sulfate Esters. Chem.-Eur. J. 2011, 17, 10106–10112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gama, C.I.; Tully, S.E.; Sotogaku, N.; Clark, P.M.; Rawat, M.; Vaidehi, N.; Goddard, W.A.; Nishi, A.; Hsieh-Wilson, L.C. Sulfation patterns of glycosaminoglycans encode molecular recognition and activity. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2006, 2, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.-P.; Lin, S.-Y.; Huang, C.-Y.; Zulueta, M.M.L.; Liu, J.-Y.; Chang, W.; Hung, S.-C. Synthesis of 3-O-sulfonated heparan sulfate octasaccharides that inhibit the herpes simplex virus type 1 host-cell interaction. Nat. Chem. 2011, 3, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.-P.; Zhong, Y.-Q.; Chen, Z.-G.; Chen, C.-Y.; Shi, Z.; Zulueta, M.M.L.; Ku, C.-C.; Lee, P.-Y.; Wang, C.-C.; Hung, S.-C. Divergent synthesis of 48 heparan sulfate-based disaccharides and probing the specific sugar−fibroblast growth factor-1 interaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 20722–20727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-C.; Ho, I.-H.; Ku, C.-C.; Zhong, Y.-Q.; Hu, Y.-P.; Chen, Z.-G.; Chen, C.-Y.; Lin, W.-C.; Zulueta, M.M.L.; Hung, S.-C.; et al. Interactions That Influence the Binding of Synthetic Heparan Sulfate Based Disaccharides to Fibroblast Growth Factor-2. ACS Chem. Biol. 2014, 9, 1712–1717. [Google Scholar]
- Handel, T.M.; Johnson, Z.; Crown, S.E.; Lau, E.K.; Proudfoot, A.E. Regulation of protein function by glycosylaminoglycans–as exemplified by chemokines. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2005, 74, 385–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spillmann, D.; Witt, D.; Lindahl, U. Defining the interleukin-8-binding domain of heparan sulfate. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 15487–15493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchimura, K.; Morimoto-Tomita1, M.; Bistrup, A.; Li, J.; Lyon, M.; Gallagher, J., 3rd; Werb, Z.; Rosen, S.D. HSulf-2, an extracellular endoglucosamine-6-sulfatase, selectively mobilizes heparin-bound growth factors and chemokines: effects on VEGF, FGF-1, and SDF-1. BMC Biochem. 2006. [CrossRef]
- Jastrebova, N.; Vanwildemeersch, M.; Rapraeger, A.C.; Giménez-Gallego, G.; Lindahl, U.; Spillmann, D. Heparan Sulfate-related Oligosaccharides in Ternary Complex Formation with Fibroblast Growth Factors 1 and 2 and Their Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 26884–26892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, C.L.; Hansen, S.U.; Baráth, M.; Rushton, G.; Gardiner, J.M.; Avizienyte, E.; Jayson, G.C. Synthetic heparan sulfate oligosaccharides inhibit endothelial cell function essential for angiogenesis. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreras, C.; Rushton, G.; Cole, C.; Babur, M.; Telfer, B.A.; van Kuppevelt, T.H.; Gardiner, J.M.; Williams, K.J.; Jayson, G.C.; Avizienyte, E. Endothelial heparan sulfate 6-O-sulfation levels regulate angiogenic responses of endothelial cells to fibroblast growth factor 2 and vascular endothelial growth factor. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 36132–36146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Cai, C.; Chandarajoti, K.; Hsieh, P.-H.; Li, L.; Pham, T.-Q.; Sparkenbaugh, E.M.; Sheng, J.; Key, N.S.; Pawlinski, R.; et al. Design of homogeneous and reversible low molecular weight heparins. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2014, 10, 248–252. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, G.J.; Hansen, S.U.; Avizienyte, E.; Rushton, G.; Cole, C.; Jayson, G.C.; Gardiner, J.M. Efficient chemical synthesis of heparin-like octa-, deca- and dodecasaccharides and inhibition of FGF2- and VEGF165-mediated endothelial cell functions. Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 3218–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, S.U.; Miller, G.J.; Cole, C.; Rushton, G.; Avizienyte, E.; Jayson, G.C.; Gardiner, J.M. Tetrasaccharide iteration synthesis of a heparin-like dodecasaccharide and radiolabelling for in vivo tissue distribution studies. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, S.U.; Miller, G.J.; Jayson, G.C.; Gardiner, J.M. First Gram-Scale Synthesis of a Heparin-Related Dodecasaccharide. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, G.J.; Hansen, S.U.; Baráth, M.; Johannessen, C.; Blanch, E.W.; Jayson, G.C.; Gardiner, J.M. Synthesis of a heparin-related GlcN-IdoA sulfation-site variable disaccharide library and analysis by Raman and ROA spectroscopy. Carbohydr. Res. 2014, 400, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferro, D.R.; Provasoli, A.; Ragazzi, M.; Torri, G.; Casu, B.; Gatti, G.; Jacquinet, J.C.; Sinay, P.; Petitou, M.; Choay, J. Evidence for conformational equilibrium of the sulfated l-iduronate residue in heparin and in synthetic heparin mono- and oligo-saccharides: NMR and force-field studies. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1986, 108, 6773–6778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: For availability of samples of compounds contact the corresponding author.
© 2015 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baráth, M.; Hansen, S.U.; Dalton, C.E.; Jayson, G.C.; Miller, G.J.; Gardiner, J.M. Modular Synthesis of Heparin-Related Tetra-, Hexa- and Octasaccharides with Differential O-6 Protections: Programming for Regiodefined 6-O-Modifications. Molecules 2015, 20, 6167-6180. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20046167
Baráth M, Hansen SU, Dalton CE, Jayson GC, Miller GJ, Gardiner JM. Modular Synthesis of Heparin-Related Tetra-, Hexa- and Octasaccharides with Differential O-6 Protections: Programming for Regiodefined 6-O-Modifications. Molecules. 2015; 20(4):6167-6180. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20046167
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaráth, Marek, Steen U. Hansen, Charlotte E. Dalton, Gordon C. Jayson, Gavin J. Miller, and John M. Gardiner. 2015. "Modular Synthesis of Heparin-Related Tetra-, Hexa- and Octasaccharides with Differential O-6 Protections: Programming for Regiodefined 6-O-Modifications" Molecules 20, no. 4: 6167-6180. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20046167
APA StyleBaráth, M., Hansen, S. U., Dalton, C. E., Jayson, G. C., Miller, G. J., & Gardiner, J. M. (2015). Modular Synthesis of Heparin-Related Tetra-, Hexa- and Octasaccharides with Differential O-6 Protections: Programming for Regiodefined 6-O-Modifications. Molecules, 20(4), 6167-6180. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules20046167