Characterization of Total Phenolic Constituents from the Stems of Spatholobus suberectus Using LC-DAD-MSn and Their Inhibitory Effect on Human Neutrophil Elastase Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Identification of Phenolic Constituents
| No. | tR (min) | UV (nm) | Ion (+) | Ion (-) | MS2(-) | Compounds |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.68 | 214, 273 | gallic acid | |||
| 2 | 7.20 | 218,259,293 | 579 | unknown | ||
| 3 | 9.49 | 232, 279 | 579 | 577 | 425, 407, 289 | procyandin B1 |
| 4 | 10.29 | 232, 278 | 595 | 593 | 425, 407, 305, 289 | prodelphinidin dimer |
| 5 | 10.90 | 232, 278 | 579 | 577 | 425, 407, 289 | procyandin B-type dimer |
| 6 | 11.49 | 233, 279 | 867 | 865 | 739, 695, 577, 425, 287 | procyandin B-type trimer |
| 7 | 11.97 | 229, 279 | 289 | 245, 205 | catechin | |
| 8 | 12.47 | 228, 279 | 563, 867 | 561, 865 | 435, 289, 739, 695, 577, 425, 287 | propelargonidin dimer and procyandin trimer |
| 9 | 13.22 | 232, 278 | 579 | 577 | 425, 407, 289 | procyandin B-type dimer |
| 10 | 13.69 | 232, 278 | 579 | 577 | 425, 407, 289 | procyandin B2 |
| 11 | 14.44 | 230, 279 | 867, 889 | 865 | 739, 695, 577, 425, 287 | procyandin B-type trimer |
| 12 | 15.12 | 232, 278 | 291 | 289 | 245, 205 | epicatechin |
| 13 | 16.32 | 232, 279 | 889, 867 | 865 | 739, 695, 577, 425, 287 | procyanidin C1 |
| 14 | 16.68 | 232, 278 | 563, 585 | 561 | 543, 435, 289 | propelargonidin dimer |
| 15 | 18.14 | 232, 278 | 851, 873 | 849, 1137 | 697, 577, 559, 407, 289, 967, 847, 695, 577 | propelargonidin trimer and tetramer |
| 16 | 18.63 | 232, 278 | 851, 873, 1139 | 849, 1137 | 697, 577, 559, 407, 289, 967, 847, 695, 577 | propelargonidin trimer and tetramer |
| 17 | 20.02 | 233, 279 | 867, 1155 | 865, 1153 | 739, 695, 577, 425, 287 983, 865, 695, 577 | procyanidin trimer and tetramer |
| 18 | 20.44 | 232, 278 | 835, 1155 | 833, 1153 | 561, 543, 983, 865, 695, 577 | propelargonidin trimer and procyanidin tetramer |
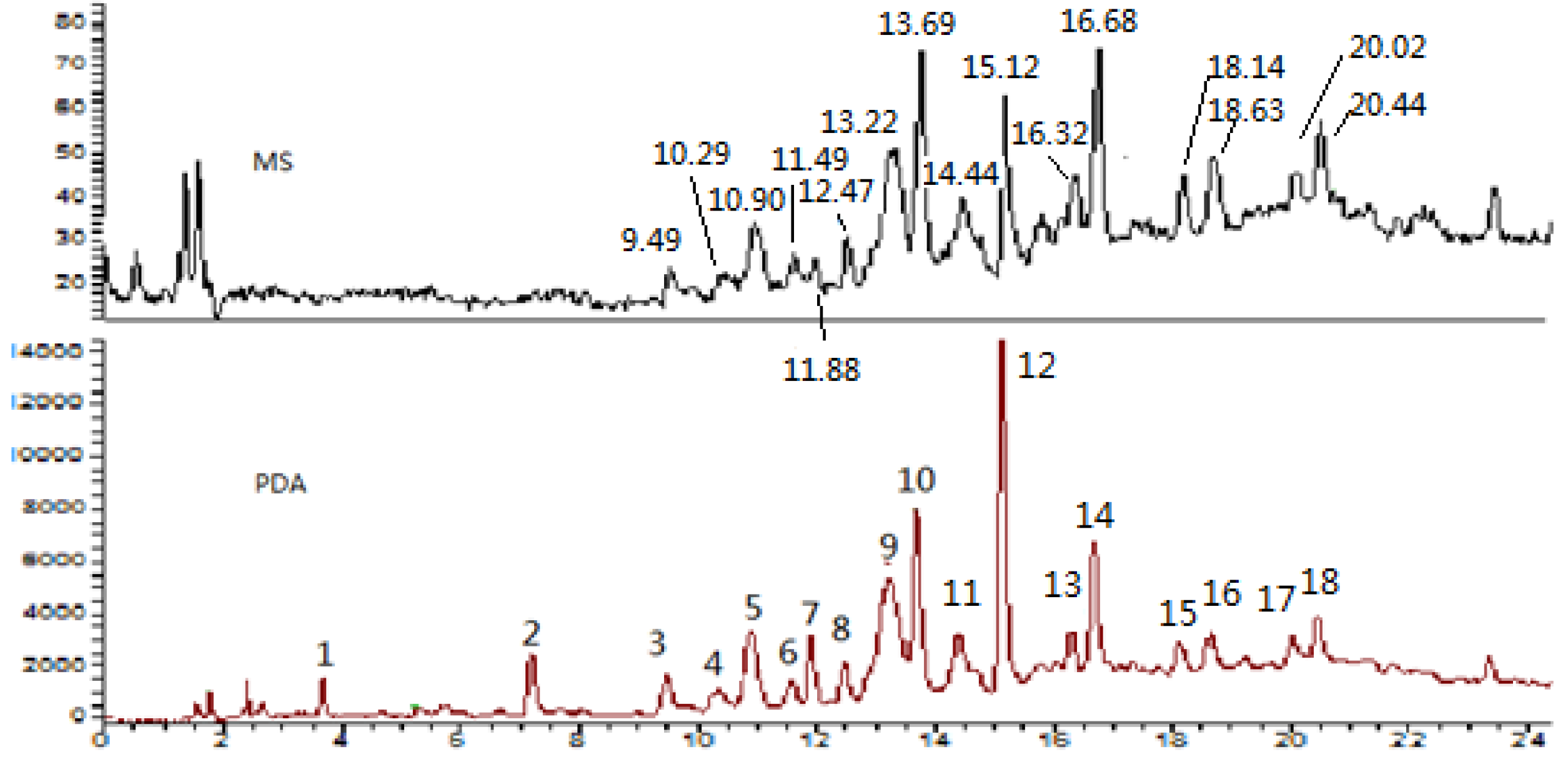
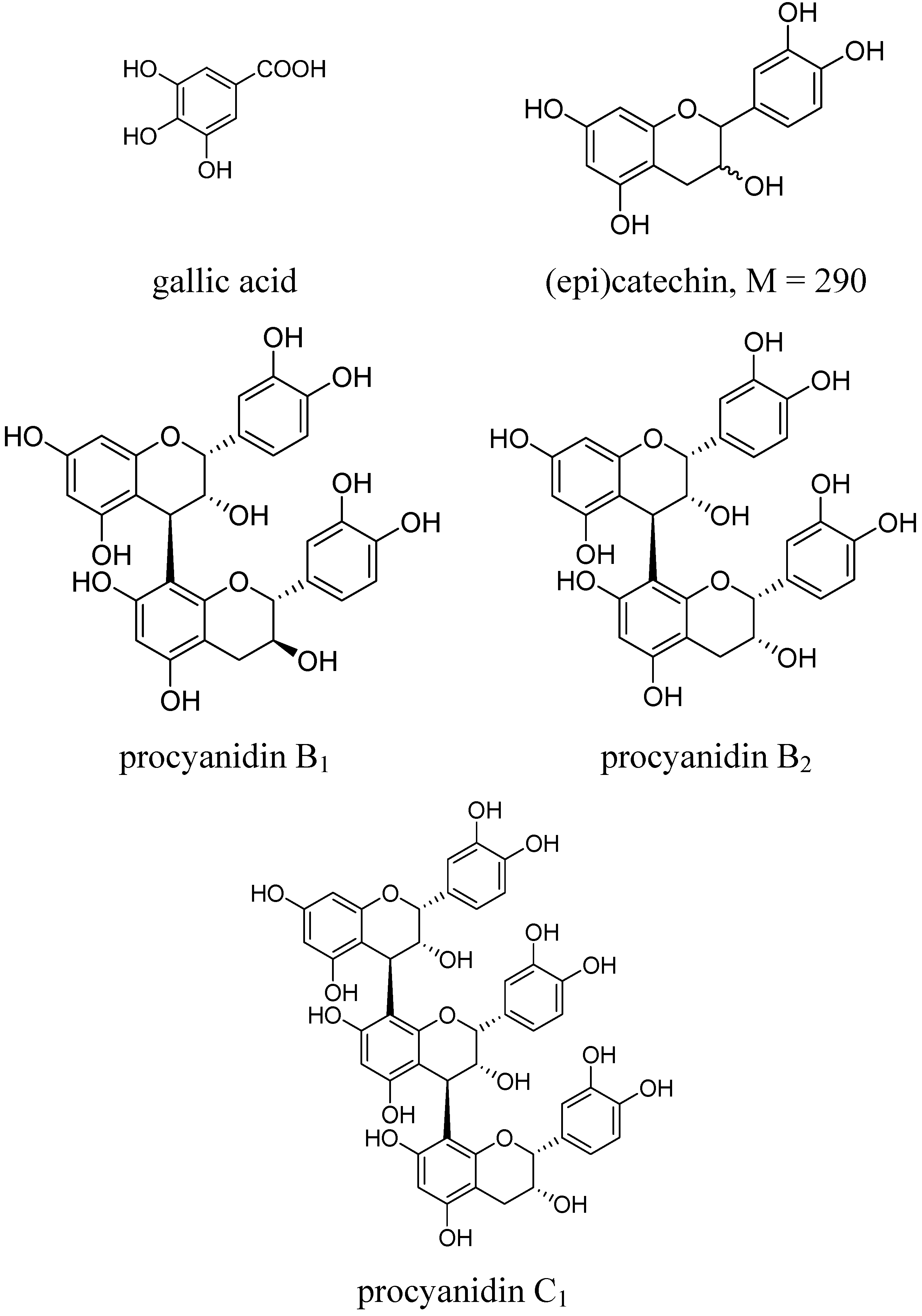
2.2. Total Phenolic Contents
2.3. Inhibition of HNE
| Sample | Blank | 0.5 µg/mL | 1.5 µg/mL | 5 µg/mL | 15 µg/mL | 50 µg/mL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phenolics | 0 ± 1.67% | 40.97 ± 1.06% | 53.26 ± 0.61% | 60.09 ± 1.37% | 63.73 ± 1.67% | 66.46 ± 0.76% |
3. Experimental
3.1. Plant Materials
3.2. Preparation of Total Phenolics
3.3. LC-MS Apparatus
3.4. Phenolic Content Assay
3.5. Inhibition of HNE
- Acontrol: the absorbance of the group with only HNE and the substrate.
- Asample: the absorbance of the group with test samples, substrate and HNE.
- Azero: the absorbance of the group with test samples, Tris-HCl buffer and HNE.
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, S.W.; Xuan, L.J. New Phenolic constituents from the stems of Spatholobus suberectus. Helv. Chim. Acta 2006, 89, 1241–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia; China medical science press: Beijing, China, 2010; Volume I, p. 180.
- Lee, M.H.; Lin, Y.P.; Hsu, F.L.; Zhan, G.R.; Yen, K.Y. Bioactive constituents of Spatholobus suberectus in regulating tyrosinase-related proteins and mRNA in HEMn cells. Phytochemistry 2006, 67, 1262–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, J.P.; Wang, D.M. Advances in studies on chemical constituents in Spatholobi Caulis and their pharmacological activities. Chin. Trad. Herb. Drugs 2011, 42, 1229–1234. [Google Scholar]
- Shim, S.H. 20S Proteasome inhibitory activity of flavonoids isolated from Spatholobus suberectus. Phytother. Res. 2011, 25, 615–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.S.; Sung, S.H.; Park, J.H.; Kim, Y.C. Flavonoids from Spatholobus suberectus. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2004, 27, 589–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, A.R.; Park, H.J.; Chen, D.F.; Jang, D.S.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, S.K.; Seo, E.K. Topoisomerase-II-Inhibitory principles from the stems of Spatholobus suberectus. Chem. Biodivers. 2007, 7, 1487–1491. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.C.; Lin, Z.K.; Ding, P.; Xu, H.H. Studies on systematical quality evaluation of Spatholobus suberectus. Chin. Pharm. J. 2009, 44, 1765–1768. [Google Scholar]
- Ryoo, I.J.; Yun, B.S.; Lee, I.K.; Kim, Y.H.; Lee, I.S.; Ahn, J.S.; Bae, K.H.; Yoo, I.D. Hydroxyhibiscone A, a novel human neutrophil elastase inhibitor from Hibiscus syriacus. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 20, 1189–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, S.D. Neutrophil Elastase: Path clearer, pathogen killer, or just pathologic? Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2002, 26, 266–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alasbahi, R.; Melzig, M. The in vitro inhibition of human neutrophil elastase activity by some Yemeni medicinal plants. Sci. Pharm. 2008, 76, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwata, K.; Doi, A.; Ohji, G.; Oka, H.; Oba, Y.; Takimoto, K.; Igarashi, W.; Gremilloin, D.H.; Shimada, T. Effect of Neutrophil Elastase Inhibitor (Sivelestat Sodium) in the treatment of acute lung injury (ALI) and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS): A systematic review and meta-analysis. Intern. Med. 2010, 49, 2423–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.K.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, J.J.; Choi, J.D. Inhibitory effects of 150 plant extracts on elastase activity and their anti-inflammatory effects. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 1999, 21, 71–82. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, T.L.; Leu, Y.L.; Kao, S.H.; Tang, M.C.; Chang, H.L. Viscolin, a new chalcone from Viscum coloratum, inhibits human neutrophil superoxide anion and elastase release via a cAMP/dependent pathway. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2006, 41, 1433–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.L.; Chang, F.R.; Chen, J.S.; Wang, H.P.; Wu, C.C.; Hwang, T.L. Inhibitory effects of 16-hydroxycleroda-3,13(14)E-dien-15-oic acid on superoxide anion and elastase release in human neutrophils through multiple mechanisms. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 586, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melzig, M.F.; Loser, B.; Ciesielski, S. Inhibiton of neutrophil elastase activity by phenolic compounds from plants. Pharmazie 2001, 56, 967–970. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, L.W.; Kelm, M.A.; Hammerstone, J.F.; Beecher, G.; Holden, J.; Haytowitz, D.; Prior, R.L. Screening of foods containing proanthocyanidins and their characterization using LC-MS/MS and thiolytic degradation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 25, 7513–7521. [Google Scholar]
- Kajdzanoska, M.; Gjamovski, V.; Stefova, M. HPLC-DAD-ESI-MSn identification of phenolic compounds in cultivated strawberries from Macedonia. Maced. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. 2010, 29, 181–194. [Google Scholar]
- Hellstrom, J.; Sinkkonen, M.; Karonen, M.; Mattila, P. Isolation and structure elucidation of procyanidin oligomers from Saskatoon Berries (Amelanchier alnifolia). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia; China medical science press: Beijing, China; Volume I, p. Appendix XB.
- Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds including gallic acid, catechin, epicatechin, procyanidin B1, B2 and C1 are available from the authors.
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Y.; Chen, L.; Feng, L.; Guo, F.; Li, Y. Characterization of Total Phenolic Constituents from the Stems of Spatholobus suberectus Using LC-DAD-MSn and Their Inhibitory Effect on Human Neutrophil Elastase Activity. Molecules 2013, 18, 7549-7556. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18077549
Huang Y, Chen L, Feng L, Guo F, Li Y. Characterization of Total Phenolic Constituents from the Stems of Spatholobus suberectus Using LC-DAD-MSn and Their Inhibitory Effect on Human Neutrophil Elastase Activity. Molecules. 2013; 18(7):7549-7556. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18077549
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Youwu, Liang Chen, Li Feng, Fujiang Guo, and Yiming Li. 2013. "Characterization of Total Phenolic Constituents from the Stems of Spatholobus suberectus Using LC-DAD-MSn and Their Inhibitory Effect on Human Neutrophil Elastase Activity" Molecules 18, no. 7: 7549-7556. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18077549
APA StyleHuang, Y., Chen, L., Feng, L., Guo, F., & Li, Y. (2013). Characterization of Total Phenolic Constituents from the Stems of Spatholobus suberectus Using LC-DAD-MSn and Their Inhibitory Effect on Human Neutrophil Elastase Activity. Molecules, 18(7), 7549-7556. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18077549




