Secondary Metabolites from Inula britannica L. and Their Biological Activities
Abstract
:1. Introduction

1.1. Perspective Secondary Metabolites
| Chemical compound(s) | Part/Fraction | Reference(s) |
|---|---|---|
| Bisdesacetylbritannin; dihydrodihydrobritannin; acetyldihydrobritannin; bisdesacetyldihydrobritannin; methyl ester of 2α,6α-diacetoxy-4β-hydroxy-7α(H),8,10β(H)-pseudoguai-8,12-olidylmethylenethioacetic acid and methyl ester of 2α,6α-diacetoxy-4β-hydroxy-7α(H),8,10β(H)-13-methylpseudoguai-8,12-olidylmethylenethioacetic acid | Derivatives/synthesis | [16, 17, 18, 19] |
| 2-O-Alkyloxime-3-phenyl)-propionyl-1-O-acetylbritannilactone esters | Derivatives/Synthesis | [20] |
| Britannilide, oxobritannilactone, eremobritanilin | Flowers /Ethyl acetate | [21, 22] |
| Pulchellin C | Flowers/Acetone | [23] |
| Inuchinenolides A, B, and C, tomentosin, ivalin, 4-epi-isoinuviscolide, gaillardin | Aerial / Ethyl acetate | [24] |
| 4α,5β-Epoxyeupatolide; 4α,5β-epoxydesacetylovatifolin; 5α-hydroxydehydroleucodin; 14-hydroxy-2-oxoguaia-1(10),3-dien-5α,11βH-12,6α-olide and 2-oxo-8α,10β,dihydroxyguai-3-en-1-α,6β,11βH-12,6-olide | Flowers | [26] |
| Salicylic, p-hydroxybenzoic, protacatechuic, vanillic, syringic, p-hydroxyphenylacetic, p-coumaric, caffeic, and ferulic acids | Aerial parts | [28] |
| 2,3,4,5-Tetrahydro-1-benzooxepin-3-ol, | Essential oils | [29] |
| Kaurane glycosides- Inulosides A and B | Flowers/Butanol | [30, 72] |
| Triterpene fatty acid esters, 3β,16β–dihydroxylupeol 3-palmitate 3β,16β-dihydroxylupeol 3-myristate, 6-hydroxykaempferol 3-sulfate; epi-friedelinol, β -amyrin palmitate, olean-13(18)-en 3-acetate, sitosteryl 3-glucoside; quercetin 3-sulfate | Aerial parts | [31] |
| Britanlins A, B, C, D | Dried flower/Ethanol extract | [75] |
| Compound | Plant part | Extract/Fraction | Yield | Activity | Standard | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
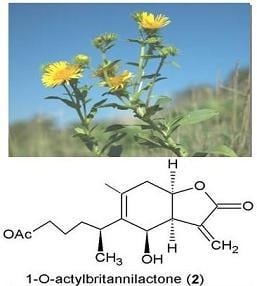
| 1-O-Acetylbritannilactone (2) | Flower | 95% EtOH | 1.1 g | Cytotoxic, apopotic, inflammation | Streptomycin | [3,25,57,58] |
| 1,6-O,O-diacetylbritannilactone (3) | 32 mg | |||||
| 6α-O-(2-methylbutyryl)-britannilactone (11) | 63 mg | |||||
| Neobritannilactone A (9) | 15 mg | |||||
| Neobritannilactone B (10) | 102 mg | |||||
| Inulanolides A (5) | Aerial part | EtOAc | 9 mg | Inflammation | Nm | [37] |
| Inulanolides B (6) | 31 mg | |||||
| Inulanolides C (7) | 89 mg | |||||
| Inulanolides D (8) | 37 mg | |||||
| Ergolide (4) | Flowers | 80% MeOH | 110 mg | Inflammation iNOS, NF-KB, IKB, COX-2 | Nm | [35] |
| Taraxasteryl acetate (13) | Aerial part | CHCl3 | 39 mg | Hepato--protective | Nm | [38] |
| Patuletin (14) | Flowers | 80% MeOH | 70 mg | Antioxidant, | Garlic acid/DPPH | [4,39] |
| Axillarin (18) | 60 mg | |||||
| Nepitrin (21) | 60 mg | |||||
| Quercetin (27) | Flowers | 95% EtOH | 1.2 g | Antioxidant, balloon injury, cytotoxic | DPPH | [43,73] |
| Spinacetin (28) | 75 mg | |||||
| Diosmetin (24) | 32 mg |
1.1.1. Sesquiterpenes

1.1.2. Triterpenoids


1.1.3. Flavonoids
2. Pharmacological Significance
2.1. Antioxidant Activity
2.2. Anti-Cancer Activities
2.3. Neuroprotective Activities
2.4. Anti-Inflammatory Activities
2.5. Hepatoprotective Affect
2.6. Enzyme Inhibition Activities
3. Conclusions
Acknowledgment
- Samples Availability: Samples not available
References and Notes
- Zhao, Y.M.; Zhang, M.L.; Shi, Q.W.; Kiyota, H. Chemical constituents of plants from the genus. Inula. J. Chem. Biod. 2006, 3, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.I.; Qaiser, M.; Abid, R. Flora of Pakistan – Astereaceae; University of Karachi, Karachi Printing Press: Karachi, Pakistan, 1992; Volume 210, p. 71. [Google Scholar]
- Mullar, S. Diversity of Management practices required to ensure conservation of rare and locally threatened plant species in grasslands: A case study at regional scale Lorraine, France. Biod. Cons. 2002, 11, 1173–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawar, R. Biosystematics of Genus Inula from Pakistan and Kashmir; Department of Botany, University of Karachi: Karachi, Pakistan, 1998; pp. 99–100. [Google Scholar]
- Chevallier, A. The Encyclopaedia of Medicinal Plants; Dorling Kindersley: London, UK, 1996; p. 301. [Google Scholar]
- Latif, A.; Shinwari, Z.K.; Hussain, J.; Murtaza, S. NTFPs: An alternative to forest logging in Miandam and Sulatanr Valley, Swat. Lyonia 2006, 11, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Clapham, A.R.; Tutin, T.G.; Warburg, E.F. Flora of the British Isles; Cambridge University Press: London, UK, 1962; pp. 174–175. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Q.H.; Kobayashi, T.; Hong, T.; Cyong, J.C. Effects of Inula britannica on the production of antibodies and cytokines and on T cell differentiation in C57BL/6 mice immunized by ovalbumin. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2002, 30, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, N.; Lai, C.S.; He, K.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, L.; Quan, Z.; Zhu, N.; Zheng, Q.; Pan, M.H.; Ho, C.T. Sesquiterpene lactones from Inula britannica and their cytotoxic and apoptotic effects on human cancer cell lines. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 531–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.R.; Park, M.J.; Lee, M.K.; Sung, S.H.; Park, E.J.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.Y.; Oh, T.H.; Markelonis, G.J.; Kim, Y.C. Flavonoids of Inula britannica protect cultured cortical cells from necrotic cell death induced by glutamate. Free Rad. Biol. Med. 2002, 32, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Song, Q.H.; Hong, T.; Kitamura, H.; Cyong, J.C. Preventative effects of the flowers of Inula britannica on autoimmune diabetes in C57BL/KsJ mice induced by multiple low doses of streptozotocin. Phytoth. Res. 2002, 16, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, J.A.; Ayensu, E.S. Medicinal Plants of China; Reference Publications. Inc: Algonac, MI, USA, 1985; p. 311. [Google Scholar]
- Zemlinskii, S.E. Medicinal Plants of the USSR (in Russian); Meditsina Publishers: Moscow, Russia, 1958; p. 109. [Google Scholar]
- Bown, D. Encyclopedia of Herbs and Their Uses; Dorling Kindersley Limited: London, UK, 1995; p. 293. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.L.; Gilani, S.A.; Fujii, Y. Watanabe K.N. Monograph on Inula britannica L.; Mimatsu Corporation: Tokyo, Japan, 2008; p. 21. [Google Scholar]
- Chugnov, P.V.; Sheichenko, V.I.; Ban'kovskii, A.I.; Rybalko, K.S. Structure of britannin, a sesquiterpene lactone from Inula britannica. Khim. Prirod. Soed. 1971, 7, 276–280. [Google Scholar]
- Artemova, N.P.; Nikitina, L.E.; Yushkov, D.A.; Shigabutdinova, O.G.; Plemenkov, V.V.; Klochkov, V.V.; Khairutdinov, B.I. Synthesis of S-containing derivatives of the sesquiterpene lactone britanin. Chem. Nat. Comp. 2005, 41, 45–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustinov, A.K.; Klochkov, S.G.; Tkachenko, S.E. Oxidation of Britannin. Chem. Heterocyc.Comp. 2000, 36, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Rybalko, K.S.; Sheichenko, V.I.; Maslova, G.A.; Kiseleva, E.Y.; Gubanov, I.A. Britannin, a lactone from Inula britannica. Khim. Prirod. Soed. 1968, 4, 251–252. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Liu, H.; Yan, W.; Zhang, L.; Bai, N.; Ho, C.T. Design, synthesis, and anti-tumor activity of (2-O-alkyloxime-3-phenyl)-propionyl-1-O-acetylbritannilactone esters. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2005, 13, 2783–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, N.; Zhou, B.N.; Zhang, L.; Sang, S.; He, K.; Zheng, Q.Y. Three new sesquiterpene lactones from Inula britannica. In Oriental Foods and Herbs: Chemistry and Health Effects; Ho, C.T., Lin, J.K., Zheng, Q.Y, Eds.; American Chemical Society Symposium Series: Washington, DC, USA, 2003; pp. 271–278. [Google Scholar]
- Chun, J.K.; Seo, D.W.; Ahn, S.H.; Park, J.H.; You, J.S.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, J.C.; Kim, Y.K.; Han, J.W. Suppression of the NF-kappaB signaling pathway by ergolide, sesquiterpene lactone, in HeLa cells. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2007, 59, 561–566. [Google Scholar]
- Serkerov, S.V.; Mir-Babaev, N.F. Pulchellin C from Inula britannica. Khim. Prirod. Soed. 1988, 6, 879–880. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, K.; Iida, T. Seven sesquiterpene lactones from Inula britannica var. chinensis. Phytochemistry 1981, 20, 271–273. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.; Bai, N.; Lin, L.; Cordell, G.A. Sesquiterpene lactones from Inula britannica. Phytochemistry 1993, 34, 249–52. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, J.; Fu, Y.; Shi, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Shi, Q. Sesquiterpene lactones and their anti-tumor activity from the flowers of Inula britannica. Lett. Drug Des. Discov. 2008, 5, 433–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yunzhi, W.; Zha, J.; Yang, S.; Shi, X.; Zhang, D. Separation and structure identification of triterpenes and steroids in Inula britannica L. Zhong Cao Yao 2006, 37, 666–668. [Google Scholar]
- Krolikowska, M.; Wolbis, M. Polyphenolic compounds in Inula britannica. Acta Polon. Pharm. 1981, 38, 107–114. [Google Scholar]
- Zha, J.; Fu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Guo, C.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Y. Study of chemical constituents of the essential oil from Inula britannica L. by GC-MS. Zhong Yao Cai 2005, 28, 466–468. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Y.; Bai, N.; Zhou, B. Kaurane glycosides from Inula britannica. Phytochemistry 1996, 42, 783–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksuz, S.; Topcu, G. Triterpene fatty acid esters and flavonoids from Inula britannica. Phytochemistry 1987, 26, 3082–3084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.N.; Wang, Y.Z.; Zhang, D. Study on RP-HPLC determination of 1-O-acetylbritannilactone in Inula britannica L. Chin. J. Pharm. Anal. 2005, 25, 205–207. [Google Scholar]
- Rafi, M.; Bai, N.; Ho, C.T.; Rosen, R.T.; White, E.; Perez, D.; Dipaola, R.S. A sesquiterpenelactone from Inula britannica induces anti-tumor effects dependent on Bcl-2 phosphorylation. Antican. Res. 2005, 25, 313–318. [Google Scholar]
- Han, M.; Wen, J.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, D. Acetylbritannilatone suppresses NO and PGE2 synthesis in RAW 264.7 macrophages through the inhibition of iNOS and COX-2 gene expression. Life Sci. 2004, 75, 675–684. [Google Scholar]
- Park, E.J.; Kim, J. Cytotoxic sesquiterpene lactones from Inula britannica. Planta Med. 1998, 64, 752–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.W.; Lee, B.G.; Kim, Y.K.; Yoon, J.W.; Jin, H.K.; Hong, S.; Lee, H.Y.; Lee, K.R.; Lee, H.W. Ergolide, sesquiterpene lactone from Inula britannica, inhibits inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclo-oxygenase-2 expression in RAW 264.7 macrophages through the inactivation of NF-kB. Brit. J. Pharm. 2001, 133, 503–512. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, H.Z.; Lee, D.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, K.; Hong, Y.S.; Choung, D.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Lee, J.J. New sesquiterpene dimers from Inula britannica inhibit NF-kappaB activation and NO and TNF-alpha production in LPS-stimulated RAW264. 7 cells. Planta Med. 2005, 72, 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Iijima, K.; Kiyohara, H.; Tanaka, M.; Matsumoto, T.; Cyong, J.C.; Yamada, H. Preventive effect of taraxasteryl acetate from Inula britannica subsp. japonica on experimental hepatitis in vivo. Planta Med. 1995, 61, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.J.; Kim, Y.; Kim, J. Acylated flavonol glycosides from the flower of Inula britannica. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 34–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orhan, I.; Kupeli, E.; Terzioglu, S.; Yesilada, E. Bioassay-guided isolation of kaempferol-3-O-B-d-galactoside with anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive activity from the aerial part of Calluna vulgaris L. J. Ethnopharm. 2007, 114, 32–37. [Google Scholar]
- Nazari, A.S.; Dias, S.A.; Da-Costa, W.F.; Bersani-Amado, C.A.; Vidotti, G.J.; De-Souza, M.C.; Sarragiotto, M.H. Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities of Randia hebecarpa and major constituents. Pharm. Bio. 2006, 44, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, E. Flavonoids in the Living System; Plenum Press: New York, USA, 1998; p. 181. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, N.; Zhou, Z.; Zhu, N.; Zhang, L.; Quan, Z.; He, K.; Zheng, Q.Y.; Ho, C. Antioxidant flavonoids from the flower of Inula britannica. J. Food Lip. 2005, 12, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maffei, M.E.; Mitho, A.; Boland, W. Insects feeding on plants: Rapid signals and responses preceding the induction of phytochemical release. Phytochemistry 2007, 68, 2946–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foyer, C. H.; Noctor, G. Oxidant and antioxidant signalling in plants: A re-evaluation of the concept of oxidative stress in a physiological context. Plant Cell Environ. 2005, 28, 1056–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valko, M.; Leibfritz, D.; Moncol, J.; Cronin, M.T.D.; Mazur, M.; Telser, J. Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 39, 44–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandhair, V.; Sekhon, B.S. Reactive oxygen species and antioxidants in plants: An overview. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 2006, 15, 71–78. [Google Scholar]
- Duthie, G.; Crosier, A. Plant-derived phenolic antioxidants. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2000, 3, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.L.; Khan, H.; Hussain, J.; Adnan, M.; Hussain, I.; Khan, T.; Rehman, A. Sesquiterpenes: A potent antioxidants-A review. Pak. J. Sci. Ind. Res. 2008, 51, 343–350. [Google Scholar]
- Lotito, S.B.; Frei, B. Consumption of flavonoid-rich foods and increased plasma antioxidant capacity in humans: Cause, consequence, or epiphenomenon? Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2006, 41, 1727–1746. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, N.; Ho, C.T.; Zhou, Z. Phytochemicals from Inula britannica and their scavenging effects on 2,2-diphenyl-1-picryhydrazyl radicals. In Proceedings of the Abstracts of 219th ACS National Meeting, San Francisco, USA, 26−30 March 2000; p. 89.
- Kim, J.; Park, E.J. Cytotoxic candidates from natural resources. Med. Chem. Antican. Ag. 2002, 2, 485–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilani, S.A.; Kikuchi, A.; Shinwari, Z.K.; Khattak, Z.I.; Watanabe, K.N. Phytochemical, pharmalogical and ethnobotanical uses of Rhazya stricta (D.). Phytoth. Res. 2007, 21, 301–307. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, J.G.; Quinn, M.L.; Fabricant, D.S.; Farnsworth, N.R. Plants used against cancer-an extension of the work of Jonathan Hartwell. J. Ethnopham. 2004, 73, 347–377. [Google Scholar]
- Rafi, M.; Bai, N.; Rosen, R.T.; Dipaola, R.S.; Ho, C.T. Cytotoxic and Bcl-2 phosphorylating molecules from a Chinese medicinal flower Inula britannica. In 224th ACS National Meeting, Boston, MA, United States, 18–22 August 2002.
- Rafi, M.; Bai, N.; Ho, C.T.; Rosen, R.T.; Ghai, G.; Perez, D.; White, E.; Dipaola, R.S. Britannilactone, a novel derivative isolated from Inula britannica is cytotoxic through the phosphorylation of Bcl-2 at a Paclitaxel phosphorylation site. In 221st ACS National Meeting, San Diego, CA, US, April 1–5, 2001.
- Ho, C.T.; Rafi, M.; Bai, N.; Dipaola, R.S.; Ghai, G.; Rosen, R.T. Inducing cell apoptosis and treating cancer using 1-O-acetylbritannilactone or 1,6-O,O-diacetylbritannilactone. US Pat. No. 6,627,623, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, M.H.; Chiou, Y.; Cheng, A.C.; Bai, N.; Lo, C.Y.; Tan, D.; Ho, C.T. Involvement of MAPK, Bcl-2 family, cytochrome-c, and caspases in induction of apoptosis by 1,6-O,O-diacetylbritannilactone in human leukemia cells. Mol. Nut. Food Res. 2007, 51, 229–238. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Wang, D.S.; Wang, R. Neuroprotective activities of enzymatically hydrolyzed peptides from porcine hide gelatin. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2008, 1, 283–293. [Google Scholar]
- Kajta, M. Apoptosis in the central nervous system: Mechanisms and protective strategies. Pol. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 56, 689–700. [Google Scholar]
- Hinz, B.; Brune, K. Cyclooxygenase – 2 - 10 years later. J. Pharm. Experim. Therap. 2002, 300, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiart, C. Ethnophamacology of Medicinal Plants Asia and the Pacific; Hunama Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 31–33. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Han, M.; Wen, J.K. Acetylbritannilactone inhibits neointimal hyperplasia after balloon injury of rat artery by suppressing NF-kB Activation. J. Pharm. Experim. Therap. 2008, 324, 292–298. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.J.; Lee, D.Y.; Kim, S.N.; Lee, K.R.; Lee, H.W.; Han, J.W.; Kang, D.W.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, Y.K. Apoptotic potential of sesquiterpene lactone ergolide through the inhibition of NF-kappaB signaling pathway. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2005, 57, 1591–1597. [Google Scholar]
- Dahanukar, S.A.; Kulkarni, R.A.; Rege, N.N. Pharmacology of medicinal plants and natural products. Ind. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 32, 81–118. [Google Scholar]
- Je, K.H.; Han, A.; Lee, H.T.; Mar, W.; Seo, E.K. The inhibitory principle of lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide production from Inula britannica var. chinensis. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2004, 27, 83–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.H.; Kobayashi, T.; Iijima, K.; Hong, T.; Cyong, J.C. Hepatoprotective effects of Inula britannica on hepatic injury in mice. Phytoth. Res. 2006, 14, 180–186. [Google Scholar]
- Serkerov, S.V.; Mir-Babaev, N.F. Pulchellin C from Inula britannica. Khim. Prirod. Soed. 1998, 6, 879–880. [Google Scholar]
- Fatope, O.; Nair, R.S.; Marwah, R.G.; Al-Nadhiri, H.S.H. New sesquiterpenes from Pluchea arabica. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1925–1928. [Google Scholar]
- Rosa, A.; Deiana, M.; Atzeri, A.; Corona, G.; Incani, A.; Melis, M.P.; Appendino, G.; Dess, M.A. Evaluation of the antioxidant and cytotoxic activity of arzanol, a prenylated α-pyrone-phloroglucinol etherodimer from Helichrysum italicum subsp. Microphyllum. Chem-Biol. Inter. 2007, 165, 117–126. [Google Scholar]
- Klika, K.D.; Demirci, B.; Salminen, J.P.; Ovcharenko, V.V.; Vuorela, S.; Baser, H.C.; Pihlaja, K. New, sesquiterpenoid-type bicyclic compounds from the buds of Betula pubescens-ring-contracted products of β-caryophyllene? Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2004, 2627–2635. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, Y.; Bai, N.; Zhou, B. Inuloside A and B, two new diterpene glycosides from Inula britannica L. var chinensis. Chin. Chem. Lett. 1994, 5, 757–760. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Wen, J.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, B.; Han, M. Flavonoids from Inula britannica L. inhibits injury-induced neointimal hyperplasia through suppressing oxidative stress generation. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 229. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wen, J.; Wo, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, D.; Han, M. 1,6-O,O-diacetylbritannilactones inhibits IκB kinase β-dependent NF-κB activation. Phytomedicine 2009, 16, 156–160. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Liu, L.; Shi, Y. Britanlins A–D, four novel sesquiterpenoids from Inula britannica. Tetrahed. Lett. 2009, 50, 6315–6317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loguercio, C.; Di Pierro, M. The role of glutathione in the gastrointestinal tract: A review. Ital. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 1999, 31, 401–407. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L. Oral Chinese medicinal composition for treating asthma, and its preparation method (in Chinese). Faming Zhuanli Shenqing Gongkai Shuomingshu 2007, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Rankin, J.A.; Kaliner, M.; Reynolds, H.Y. Histamine levels in bronchoalveolar lavage from patients with astma, sarcoidosis, and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J. Allergy. Clin. Immunol. 1987, 79, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, M.; Ram, A.; Ghosh, B. Luteolin alleviates bronchoconstriction and airway hyperreactivity in ovalbumin sensitized mice. Inflamm. Res. 2003, 52, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Lee, C.; Jung, I.; Lee, J.; Jeong, Y.; Chang, J.; Chun, S.; Kim, M.; Choi, I.; Ahn, S.; Shin, Y.; Yeom, S.; Park, Y. Quercetin regulates Th1/Th2 balance in a murine model of asthma. Inter. Immunopharm. 2009, 3, 261–267. [Google Scholar]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, A.L.; Hussain, J.; Hamayun, M.; Gilani, S.A.; Ahmad, S.; Rehman, G.; Kim, Y.-H.; Kang, S.-M.; Lee, I.-J. Secondary Metabolites from Inula britannica L. and Their Biological Activities. Molecules 2010, 15, 1562-1577. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules15031562
Khan AL, Hussain J, Hamayun M, Gilani SA, Ahmad S, Rehman G, Kim Y-H, Kang S-M, Lee I-J. Secondary Metabolites from Inula britannica L. and Their Biological Activities. Molecules. 2010; 15(3):1562-1577. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules15031562
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Abdul Latif, Javid Hussain, Muhammad Hamayun, Syed Abdullah Gilani, Shabir Ahmad, Gauhar Rehman, Yoon-Ha Kim, Sang-Mo Kang, and In-Jung Lee. 2010. "Secondary Metabolites from Inula britannica L. and Their Biological Activities" Molecules 15, no. 3: 1562-1577. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules15031562
APA StyleKhan, A. L., Hussain, J., Hamayun, M., Gilani, S. A., Ahmad, S., Rehman, G., Kim, Y.-H., Kang, S.-M., & Lee, I.-J. (2010). Secondary Metabolites from Inula britannica L. and Their Biological Activities. Molecules, 15(3), 1562-1577. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules15031562