Phenolic Antioxidants Identified by ESI-MS from Yerba Maté (Ilex paraguariensis) and Green Tea (Camelia sinensis) Extracts
Abstract
:Introduction
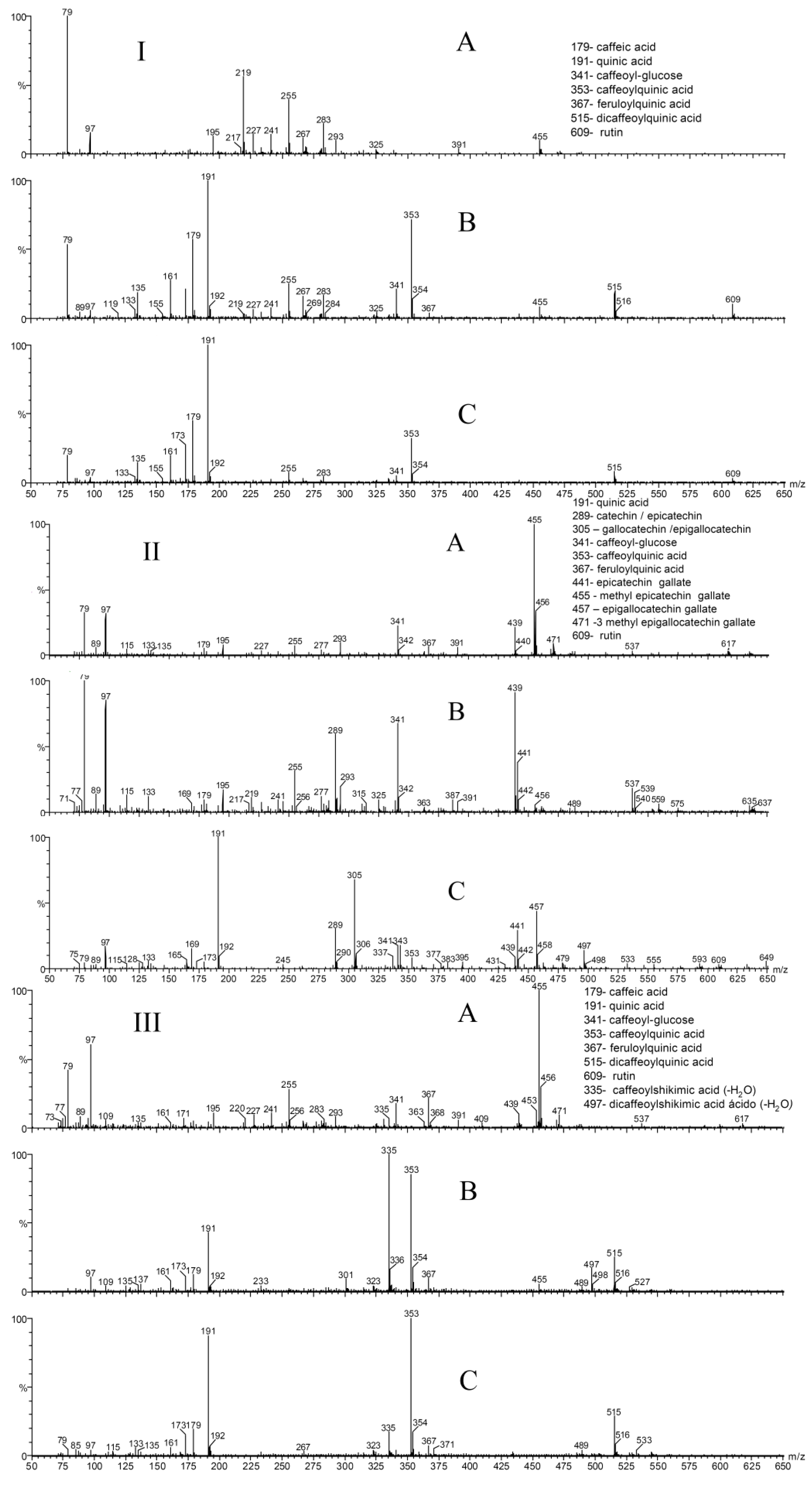
Results and Discussion
| Phenolic Content (mg/mL) | DPPH scavenging activity (I%)* | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| solvent | solvent | |||||
| water | ethanol | ether | water | ethanol | ether | |
| Green maté (G-YM) | 7.73±0.15 aA | 3.80±0.12 aB | 0.02±0.00aC | 90.45±0.22 aA | 88.93±0.22aA | 29.47±3.8aB |
| Roasted maté (R-YM) | 6.71±0.33bA | 2.83+0.07 bB | 0.03±0.0 aC | 87.78±0.76 bA | 92.05+0.60bA | 35.38±3.10aB |
| Green tea (GT) | 7.15±0.14 cA | 13.08±0.14 cB | 0.07±0.00 aC | 88.36 ±0.76 bA | 92.20±0.52bB | 91.74±0.47bB |
| ESI- MS ions (m/z) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Compound | Deprotonated Ions [M-H]- m/z | MS/MS íons m/z |
| caffeic acid | 179 | 135, 179 |
| quinic acid | 191 | 85, 93, 111, 127, 173 |
| catechin/epicatechin | 289 | 109, 125, 179, 203, 205, 245 |
| caffeoylshikimic acid | 335 | 135, 161, 179 |
| caffeoyl glucose | 341 | 119, 179 |
| caffeoylquinic acid | 353 | 135, 173, 179, 191 |
| feruloylquinic acid | 367 | 173, 191, 193 |
| epicatechin gallate | 441 | 135, 169, 289 |
| methyl epicatechin gallate | 455 | 375, 407 |
| epigallocatechin gallate | 457 | 169, 305, 331 |
| 3 methyl epigallocatechin gallate | 471 | 407, 441 |
| dicaffeoylshikimic acid | 497 | 161, 179, 335 |
| dicaffeoylquinic acid | 515 | 173, 179, 191, 353 |
| rutin | 609 | 301 |
Experimental
General
Extraction procedure
Determination of phenolic content
Radical DPPH Scavenging Activity
Statistical Analysis
Acknowledgments
References
- Nishino, H.; Murakoshi, M.; Mou, X. Y.; Wada, S.; Masuda, M.; Ohsaka, Y.; Satomi, Y.; Jinno, K. Cancer prevention by phytochemicals. Oncology 2005, 69 Suppl. 1, 38–40. [Google Scholar]
- Salka, E. R.; Hanne, F.; Kirstine, S. K.; Lea, P. Dietary proanthocyanidins: Occurrence, dietary intake, bioavailability, and protection against cardiovascular disease. Mol. Nutrit. Food Res. 2000, 49, 159–174. [Google Scholar]
- Alligiannis, N.; Mitaku, S.; Tsitsa-Tsardis, E.; Harvala, C.; Tsaknis, I.; Lalas, S.; Haroutounian, S. Methanolic extract of Verbascum macrurum as a source of natural preservatives against oxidative rancidity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 7308–7312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwivedi, S.; Vasavada, M. N.; Cornforth, D. Evaluation of antioxidant effects and sensory attributes of chinese 5-spice ingredients in cooked ground beef. J. Food Sci. 2006, 71, C12–C17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Matéos, M.; Lanier, T. C.; Boyd, L. C. Effects of rosemary and green tea extracts on frozen surimi gels fortified with omega-3 fatty acids. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2006, 86, 558–567. [Google Scholar]
- Pizzale, L.; Bortolomeazzi, R.; Vichi, S.; Uberegger, E.; Lanfrando, S.C. Antioxidant activity of sage (Salvia officinalis and S. fruticosa) and oregano (Origanum onitus and O. indercedens) extracts related to their phenolic compound content. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2002, 82, 1645–1651. [Google Scholar]
- Gugliucci, A.; Menini, T. Three different pathways for human LDL oxidation are inhibited in vitro by aqueous extracts of the medicinal herb Achyrocline satureoides. Life Sci. 2002, 71, 693–705. [Google Scholar]
- Gugliucci, A. Antioxidant effects of Ilex paraguariensis: Induction of decreased oxidability of human LDL in Vivo. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 1996, 224, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gugliucci, A.; Stahl, A. J. Low density lipoprotein oxidation is inhibited by extracts of Ilex paraguariensis. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Int. 1995, 35, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bracesco, N.; Dell, M.; Rocha, A.; Behtash, S.; Menini, T.; Gugliucci, A.; Nunes, E. Antioxidant Activity of a botanical Extract Preparation of Ilex paraguariensis: Prevention of DNA double-strand breaks in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and human low-density lipoprotein oxidation. J. Altern Complem. Med. 2003, 9, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, S.; Mejia, E. G. Polyphenolic compounds, antioxidant capacity and quinone reductase activity of aqueous extract of Ardisis compressa in comparison to maté (Ilex paraguariensis) and green (Camellia sinesnsis) teas. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 3583–3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez-Mares, M.; Chandra, S.; Mejia, E. G. In vitro chemopreventive activity of Camelia sinesnsis, Ilex paraguariensis and Ardisis compressa tea extracts and selected polyphenols. Mutat. Res. 2004, 554, 53–65. [Google Scholar]
- Bastos, D. H. M.; Ishimoto, E. Y.; Marques, M. O.; Ferri, A. F.; Torres, E. A. F. Essential oil and antioxidant activity of green maté and maté-tea (Ilex paraguariensis) infusions. J. Food Comp. Anal. 2006, 19(6-7), 538–543. [Google Scholar]
- Nanjo, F.; Goto, K.; Seto, R.; Suzuki, M.; Sakai, M.; Hara, Y. Scavenging effects of tea catechins and their derivatives on 1,1-Diphenyl-2-Picrylhydrazyl radical. Free Rad. Biol. Med. 1996, 6, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, L. K.; Su, Y.; Chen, R.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Z.Y. Theafalvins in black tea and catechins in green tea are equally effective antioxidants. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 2248–2251. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yokosawa, T.; Nakagawa, T.; Kitani, K. Antioxidative activity of green tea polyphenol in cholesterol-fed rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 3549–3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brand-Willians, W.; Cuvelier, M.E.; Berset, C. Use of a free radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. Food Sci. Technol. 1995, 28, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Parejo, I.; Viladomat, F.; Bastida, J.; Rosas-Romero, A.; Saavedra, G.; Murcia, M. A.; Jiménez, M.; Codina, C. Investigation of Bolivian plant extracts for their radical scavenging activity and antioxidant activity. Life Sci. 2003, 73, 1667–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Takamura, H.; Matoba, T.; Terão, J. HPLC method for evaluation of the free radical scavenging activity of foods by using 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrazylhydrazyl. Biosic. Biotech. Biochem. 1998, 62, 1201–1204. [Google Scholar]
- Molyneux, P. The use of stable free radical diphenylpicrylhydrazil(DPPH) for estimating antioxidant activity. J. Sci. Technol. 2004, 26, 211–219. [Google Scholar]
- Balentine, D. A.; Wiseman, S. A.; Bouwens, L. C. M. The chemistry of tea flavonoids. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1997, 37, 693–704. [Google Scholar]
- Sousa, W. R.; da Rocha, C.; Cardoso, C. L.; Silva, D. H. S.; Zanoni, M. V. B. Determination of the relative contribution of phenolic antioxidants in orange juice by voltammetric methods. J. Food Comp. Anal. 2004, 17(5), 619–633. [Google Scholar]
- Singleton, V. L.; Rossi., J. A. Colorimetric of total phenolics with phosphomolybidic-phosphotungstic acid reagents. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1965, 16, 144–158. [Google Scholar]
- Carini, M.; Facino, R. M.; Aldini, G.; Calloni, M.; Colombo, L. Characterization of phenolic antioxidants from Maté (Ilex paraguariensis) by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry and liquid chromatography/Tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 1998, 12, 1813–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, N.; Yu, S.; Prior, R. Characterization of phenolic constituents in dried plums. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 3579–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawaya, A. C. H. F.; Tomazela, D. M.; Cunha, I. B. S.; Vassya, S.; Bankova, V. S.; Maria, C.; Marcucci, M. C.; Angela, R.; Custodio, A. R.; Eberlin, M. N. Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry fingerprinting of própolis. Analyst 2004, 129, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atoui, A. K.; Mansouri, A.; Boskou, G.; Kefalas, P. Tea and herbal infusions: their antioxidant activity and phenolic profile. Food Chem. 2005, 89, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miketova, P.; Schram, K. H.; Whitney, J.; Li, M.; Huang, R.; Kerns, E.; Valcic, S.; Timmermann, B. N.; Rourick, R.; Klohr, S. Tandem mass spectrometry studies of green tea catechins: Identification of three minor components in the polyphenolic extract of green tea. J. Mass Spectr. 2000, 35, 860–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepe, B.; Sokmen, M.; Akpulat, H. A.; Sokmen, A. Screening of the antioxidant potentials of six Salvia species from Turkey. Food Chem. 2006, 95, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papetti, A.; Daglia, M.; Aceti, C.; Quaglia, M.; Gregotti, C.; Gazzani, G. Isolation of an in vitro and ex vivo antiradical melanoidin from roased barley. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 1209–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daglia, M.; Papetti, A.; Gregotti, C.; Berte, F.; Gazzani, G. In vitro antioxidant and ex vivo protective activities of green and roasted coffee. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 1449–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuster, M. D.; Mitchell, A. E.; Ochi, H.; Shibamoto, T. Antioxidative activities of heterocyclic Compounds Formed in Brewed Coffee. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 5600–5603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagimoto, K.; Lee, K.; Ochi, H.; Shibamoto, T. Antioxidative activity of Heterocyclic compounds found in coffee volatiles produced by Maillard Reaction. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 5480–5484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, F. J.; Babbel, M. B. J. Melanoidins exert a weak antiradical activity in watery fluids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 4657–4661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado-Andrade, C.; Rufian-Henares, J. A.; Morales, F. J. Assessing the antioxidant activity of melanoidins from coffee brews by different antioxidant methods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 3, 7832–7836. [Google Scholar]
- Sample availability: Contact the authors
© 2007 by MDPI (http://www.mdpi.org). Reproduction is permitted for noncommercial purposes.
Share and Cite
Bastos, D.H.; Saldanha, L.A.; Catharino, R.R.; Sawaya, A.; Cunha, I.B.; Carvalho, P.O.; Eberlin, M.N. Phenolic Antioxidants Identified by ESI-MS from Yerba Maté (Ilex paraguariensis) and Green Tea (Camelia sinensis) Extracts. Molecules 2007, 12, 423-432. https://doi.org/10.3390/12030423
Bastos DH, Saldanha LA, Catharino RR, Sawaya A, Cunha IB, Carvalho PO, Eberlin MN. Phenolic Antioxidants Identified by ESI-MS from Yerba Maté (Ilex paraguariensis) and Green Tea (Camelia sinensis) Extracts. Molecules. 2007; 12(3):423-432. https://doi.org/10.3390/12030423
Chicago/Turabian StyleBastos, Deborah H, Luciane A Saldanha, Rodrigo R Catharino, Alexandra Sawaya, Ildenize B Cunha, Patricia O Carvalho, and Marcos N Eberlin. 2007. "Phenolic Antioxidants Identified by ESI-MS from Yerba Maté (Ilex paraguariensis) and Green Tea (Camelia sinensis) Extracts" Molecules 12, no. 3: 423-432. https://doi.org/10.3390/12030423
APA StyleBastos, D. H., Saldanha, L. A., Catharino, R. R., Sawaya, A., Cunha, I. B., Carvalho, P. O., & Eberlin, M. N. (2007). Phenolic Antioxidants Identified by ESI-MS from Yerba Maté (Ilex paraguariensis) and Green Tea (Camelia sinensis) Extracts. Molecules, 12(3), 423-432. https://doi.org/10.3390/12030423




