Processes 2021, 9(12), 2108; https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9122108 - 24 Nov 2021
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 2840
Abstract
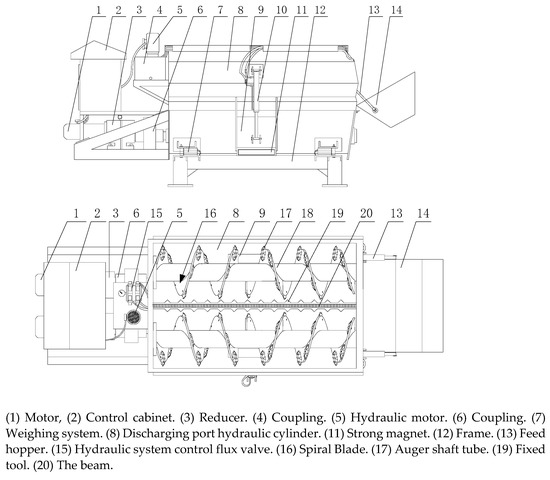
Aiming at the problems of high-power consumption and insufficient kneading and cutting of roughage in the total mixed ration mixer. In this paper, licorice stems were taken as experimental objects, the horizontal twin-shaft TMR mixer was used to carry out the experimental study.
[...] Read more.
Aiming at the problems of high-power consumption and insufficient kneading and cutting of roughage in the total mixed ration mixer. In this paper, licorice stems were taken as experimental objects, the horizontal twin-shaft TMR mixer was used to carry out the experimental study. It should be as brief as possible and concise. Through the kneading and cutting process power analysis, determine the influencing factors of kneading and cutting power consumption. The auger speed, processing time and blade type were taken as experimental factors, with standard straw length rate and power consumption as indicators, Box–Behnken test with three factors and three levels was carried out, analysis of variance was performed on the test results, the results show that the significant effect of each factor on the standard grass length is processing time, blade type and auger speed in descending order. The significance of the influence on power consumption from large to small is auger speed, processing time and blade type. The response surface analysis and parameter optimization were carried out, the results show that the auger speed is 20 r/min, the processing time is 29 min, and the blade type is quincunx blade. At this time, the standard straw length was 82.634%; Power consumption 4525.815 kJ, TMR mixer performance reached the best. The results can provide a theoretical basis for the subsequent research and development of TMR mixer.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Design and Optimization in Process Engineering)
►
Show Figures