Electronics 2023, 12(6), 1347; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12061347 - 12 Mar 2023
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 2719
Abstract
Semantic segmentation is a key technology for remote sensing image analysis widely used in land cover classification, natural disaster monitoring, and other fields. Unlike traditional image segmentation, there are various targets in remote sensing images, with a large feature difference between the targets.
[...] Read more.
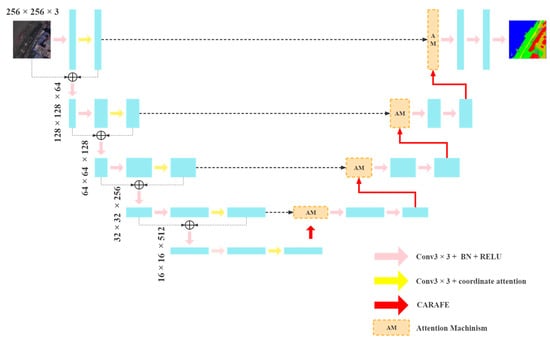
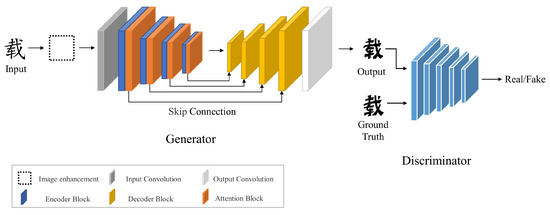
Semantic segmentation is a key technology for remote sensing image analysis widely used in land cover classification, natural disaster monitoring, and other fields. Unlike traditional image segmentation, there are various targets in remote sensing images, with a large feature difference between the targets. As a result, segmentation is more difficult, and the existing models retain low accuracy and inaccurate edge segmentation when used in remote sensing images. This paper proposes a multi-attention-based semantic segmentation network for remote sensing images in order to address these problems. Specifically, we choose UNet as the baseline model, using a coordinate attention-based residual network in the encoder to improve the extraction capability of the backbone network for fine-grained features. We use a content-aware reorganization module in the decoder to replace the traditional upsampling operator to improve the network information extraction capability, and, in addition, we propose a fused attention module for feature map fusion after upsampling, aiming to solve the multi-scale problem. We evaluate our proposed model on the WHDLD dataset and our self-labeled Lu County dataset. The model achieved an mIOU of 63.27% and 72.83%, and an mPA of 74.86% and 84.72%, respectively. Through comparison and confusion matrix analysis, our model outperformed commonly used benchmark models on both datasets.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advanced Techniques in Computing and Security)
►
Show Figures