1
College of Computer Science and Engineering, Sichuan University of Science and Engineering, Zigong 643033, China
2
Sichuan Key Provincial Research Base of Intelligent Tourism, Zigong 643033, China
†
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Electronics 2023, 12(4), 887; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12040887 - 9 Feb 2023
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 2483
Abstract
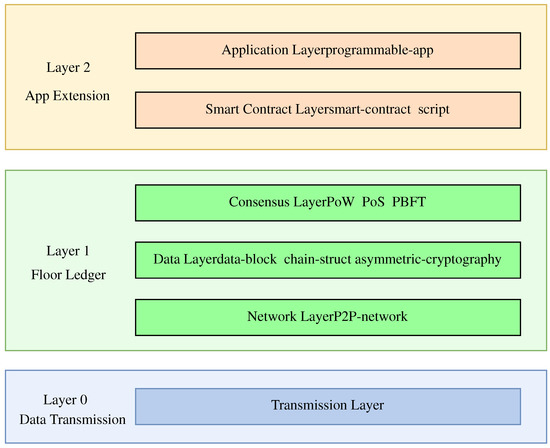
NFT is a kind of virtual token derived from the blockchain. In 2019, the NFT transaction market became a new force in the field of the digital economy, while NFT fraud was also widespread. There is no efficient technology or methods to ensure
[...] Read more.
NFT is a kind of virtual token derived from the blockchain. In 2019, the NFT transaction market became a new force in the field of the digital economy, while NFT fraud was also widespread. There is no efficient technology or methods to ensure the authenticity of the source data (which have not been stored on the blockchain yet) on a blockchain traceability system. To solve this problem and to safeguard the rights and interests of members of the blockchain application, we propose a method to measure the user’s credit degree by obtaining the data before it stores on the blockchain. We first analyze some NFT trading markets’ business processes and dealing models. Then, based on the analytic hierarchy process (AHP) in the operational research theory, some indexes of credit rating have been made. A credit rating system has been established by calculating the evaluation matrix and efficacy coefficient of each index. The experimental results show that the credit evaluation system can be used as a method to judge the user’s credit rating on a blockchain traceability system. This method provides a reference for the decision of whether to restrict the transaction of some users with abnormal behavior.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Recent Advances in Blockchain Technology and Its Applications)
▼
Show Figures