Electronics 2022, 11(24), 4194; https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11244194 - 15 Dec 2022
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 3387
Abstract
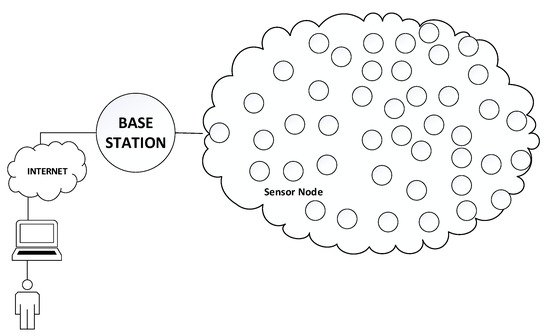
In a typical Wireless Sensor Network (WSN), thousands of sensor nodes can be distributed in the environment. Then, each sensor node transmits its detected data to the base station with the help of cooperation. In this type of network, data aggregation protocols are
[...] Read more.
In a typical Wireless Sensor Network (WSN), thousands of sensor nodes can be distributed in the environment. Then, each sensor node transmits its detected data to the base station with the help of cooperation. In this type of network, data aggregation protocols are used to increase the network’s lifetime and reduce each sensor node’s communication load and energy consumption. With Data Clustering, the density of data circulating in the network is reduced, thus increasing the network’s life. Energy, delay, and efficiency are essential criteria in Data Clustering; however, security is another crucial aspect to be considered. A comprehensive solution for secure data clustering has yet to be seen when the literature is examined. In the solutions developed, data availability, which means that the WSN is resistant to Denial of Service (DOS) attacks, has been neglected too much, even though confidentiality, integrity, and authentication are met with different algorithms. This study developed a comprehensive, secure clustering protocol by considering all security requirements, especially data availability. The developed protocol uses the blowfish encryption algorithm, EAX mode, and RSA algorithm. The proposed protocol was theoretically analyzed, empirically evaluated, and simulated from many perspectives. Comparisons were made with LSDAR, SUCID, and OOP-MDCRP protocols. As a result of the study, a comprehensive security solution is provided and more successful results were obtained according to Energy Efficiency, Network Lifetime, Average Delay, and Packet delivery ratio criteria.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Wireless Sensor Networks)
►
Show Figures