Coatings 2023, 13(1), 20; https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13010020 - 22 Dec 2022
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 3155
Abstract
Dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs) were developed by exploiting the photovoltaic effect to convert solar energy into electrical energy. The photoanode layer thickness significantly affects the semiconductor film’s ability to carry electronic charges, adsorb sensitizing dye molecules, and lower the recombination of photo-excited electrons
[...] Read more.
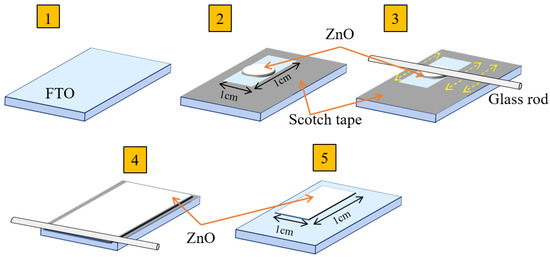
Dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs) were developed by exploiting the photovoltaic effect to convert solar energy into electrical energy. The photoanode layer thickness significantly affects the semiconductor film’s ability to carry electronic charges, adsorb sensitizing dye molecules, and lower the recombination of photo-excited electrons injected into the semiconductor. This study investigated the dependence of the zinc oxide (ZnO) photoanode thin-film thickness and the film soaking time in N719 dye on the photocurrent–voltage characteristics. The ZnO photoanode was applied to glass using the doctor blade method. The thickness was varied by changing the scotch tape layers. The ZnO-based DSSC attained an efficiency of 2.77% with three-layered photoanodes soaked in the dye for three hours, compared to a maximum efficiency of 0.68% that was achieved with three cycles using the dip-coating method in other research. The layer thickness of the ZnO photoanode and its optimal adsorption time for the dye are important parameters that determine the efficiency of the DSSC. Therefore, this work provides important insights to further improve the performance of DSSCs.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Oxidation, Wear, Corrosion Behaviors and Activated Bonding Properties of Coatings Deposited on Metals)
►
Show Figures