Antibiotics 2023, 12(2), 243; https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics12020243 - 25 Jan 2023
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 3675
Abstract
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a global health issue disproportionately affecting low- and middle-income countries. In Tanzania, multi-drug-resistant bacteria (MDR) are highly prevalent in clinical and community settings, inhibiting effective treatment and recovery from infection. The burden of AMR can be alleviated if antimicrobial
[...] Read more.
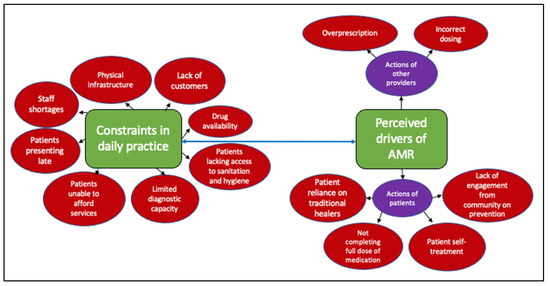
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a global health issue disproportionately affecting low- and middle-income countries. In Tanzania, multi-drug-resistant bacteria (MDR) are highly prevalent in clinical and community settings, inhibiting effective treatment and recovery from infection. The burden of AMR can be alleviated if antimicrobial stewardship (AMS) programs are coordinated and incorporate local knowledge and systemic factors. AMS includes the education of health providers to optimise antimicrobial use to improve patient outcomes while minimising AMR risks. For programmes to succeed, it is essential to understand not just the awareness of and receptiveness to AMR education, but also the opportunities and challenges facing health professionals. We conducted in-depth interviews (n = 44) with animal and human health providers in rural northern Tanzania in order to understand their experiences around AMR. In doing so, we aimed to assess the contextual factors surrounding their practices that might enable or impede the translation of knowledge into action. Specifically, we explored their motivations, training, understanding of infections and AMR, and constraints in daily practice. While providers were motivated in supporting their communities, clear issues emerged regarding training and understanding of AMR. Community health workers and retail drug dispensers exhibited the most variation in training. Inconsistencies in understandings of AMR and its drivers were apparent. Providers cited the actions of patients and other providers as contributing to AMR, perpetuating narratives of blame. Challenges related to AMR included infrastructural constraints, such as a lack of diagnostic testing. While health and AMR-specific training would be beneficial to address awareness, equally important, if not more critical, is tackling the challenges providers face in turning knowledge into action.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue One Health: Opportunities and Challenges of Antibiotic Resistance and Stewardship)
►
Show Figures