Brain Sci. 2022, 12(1), 47; https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12010047 - 30 Dec 2021
Cited by 13 | Viewed by 4171
Abstract
Specific language impairment (SLI) is a common neurodevelopmental disorder (NDD) that displays high heritability estimates. Genetic studies have identified several loci, but the molecular basis of SLI remains unclear. With the aim to better understand the genetic architecture of SLI, we performed whole-exome
[...] Read more.
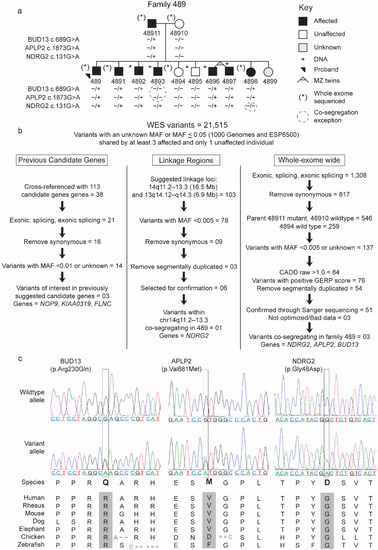
Specific language impairment (SLI) is a common neurodevelopmental disorder (NDD) that displays high heritability estimates. Genetic studies have identified several loci, but the molecular basis of SLI remains unclear. With the aim to better understand the genetic architecture of SLI, we performed whole-exome sequencing (WES) in a single family (ID: 489; n = 11). We identified co-segregating rare variants in three new genes: BUD13, APLP2, and NDRG2. To determine the significance of these genes in SLI, we Sanger sequenced all coding regions of each gene in unrelated individuals with SLI (n = 175). We observed 13 additional rare variants in 18 unrelated individuals. Variants in BUD13 reached genome-wide significance (p-value < 0.01) upon comparison with similar variants in the 1000 Genomes Project, providing gene level evidence that BUD13 is involved in SLI. Additionally, five BUD13 variants showed cohesive variant level evidence of likely pathogenicity. Bud13 is a component of the retention and splicing (RES) complex. Additional supportive evidence from studies of an animal model (loss-of-function mutations in BUD13 caused a profound neural phenotype) and individuals with an NDD phenotype (carrying a CNV spanning BUD13), indicates BUD13 could be a target for investigation of the neural basis of language.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Language and Brain: From Genes to Behavior)
►
Show Figures